The Quantitative Challenges of Textile Mill Wastewater Management
: The Quantitative Challenges of Textile Mill Wastewater Management,Textile mill wastewater management poses significant quantitative challenges that require meticulous attention to achieve sustainable and efficient water treatment. The textile industry generates a substantial amount of wastewater, which often contains high levels of dyes, chemicals, and other pollutants that can be harmful to the environment if not properly treated. The quantitative challenges in managing textile mill wastewater include the high volume of wastewater generated, the complex composition of pollutants present, and the need for precise monitoring and control of various parameters such as pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen levels.,To address these challenges, advanced treatment technologies such as biological filtration, chemical coagulation, and membrane separation have been developed and implemented at textile mills. These technologies help to remove or reduce the concentration of pollutants in the wastewater, making it safe for discharge into receiving water bodies. However, the success of these treatments is largely dependent on the accurate measurement and control of key parameters, which requires the use of sophisticated monitoring systems and data analysis tools.,In conclusion, the quantitative challenges of textile mill wastewater management require innovative solutions and ongoing research to ensure the responsible and effective disposal of this valuable resource.
Introduction: In the realm of environmental sustainability, textile mills play a crucial role in the production of clothing and other textile materials. However, their operations often come with significant challenges when it comes to wastewater management. This presentation will explore the quantitative aspects of textile mill wastewater, including its sources, treatment methods, and challenges faced by various industries. We'll also present an example of how a textile mill has tackled these issues through innovative solutions.

Textile Mill Wastewater Sources: Textile mills generate wastewater primarily from three sources: washing, dyeing, and finishing processes. These processes use water for cleaning fabrics, removing ink or dye, and applying finishing agents. Additionally, effluents from the plant's cooling systems and drains contribute to the overall wastewater volume.
Wastewater Volume: The volume of wastewater produced by a textile mill can vary greatly depending on several factors such as the type of fabric being processed, the efficiency of the washing and dyeing processes, and the amount of water used during each stage. For instance, a typical cotton fabric processing plant might produce between 10 to 20 tons of wastewater per day, while a polyester plant may generate up to 50 tons.
Treatment Methods: To manage textile mill wastewater, various treatment methods are employed. Common techniques include:
- Primary Treatment: This involves physical separation of solids from the liquid phase using screens, grit guards, etc.
- Secondary Treatment: Includes further chemical treatments like coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation to remove suspended solids and biodegradable organic matter.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced stages that involve biological processes like activated sludge, constructed wetlands, or membrane bioreactors to further purify the wastewater.
- Disinfection: Adding chemicals like chlorine or ozone to kill harmful bacteria and viruses.
Challenges Faced by Industries: Despite advancements in wastewater treatment technology, textile mills still face several challenges:
- High Volume: The sheer volume of wastewater generated makes effective treatment challenging.
- Complexity: The high concentration of organic matter and minerals in textile wastewater makes conventional treatment methods less efficient.
- Varied Processing: Different types of textiles require specialized treatment processes to achieve optimal results.
- Wastewater Reuse: Many textile mills aim to recycle treated wastewater for non-potable uses, but this requires strict compliance with regulations and effective monitoring systems.
Innovative Solutions: One solution that has proven successful is the use of reverse osmosis (RO) technology in conjunction with secondary treatment. RO can remove most of the salts and impurities from the wastewater, making it more amenable to secondary treatments. Additionally, some textile mills have installed advanced treatment facilities that employ hybrid systems combining different treatment methods to meet stringent regulatory standards.
Case Study: One example of a textile mill tackling wastewater management challenges is the "Green Manufacturing" initiative at the Tata Group's Tavistock Textile Mill in Australia. The mill has implemented a comprehensive system that includes:
- Integrated Water Management System (IWMS): A state-of-the-art IWMS that monitors and controls all stages of wastewater treatment.
- Wastewater Recycling: The mill recycles treated wastewater for irrigation purposes, reducing the need for potable water and minimizing the impact on groundwater sources.
- Wastewater Heat Recovery: The mill recovers heat from the wastewater treatment process for use in drying and bleaching processes, saving energy costs and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Wastewater Disinfection: The mill uses UV disinfection to ensure that the treated wastewater meets drinking water standards before it is released into the environment.
Conclusion: The textile industry is a vital part of global economic growth, but managing wastewater effectively is critical to ensuring sustainable practices. By adopting innovative treatment technologies and implementing best practices, textile mills can not only comply with environmental regulations but also contribute positively to the health of our planet.
背景介绍
在某纺织厂,废水量问题日益凸显,这不仅涉及到环境保护,也关系到企业的可持续发展,本文将围绕纺织厂废水量展开讨论,并提供相关案例分析。
废水量现状分析
废水量统计数据
废水量统计数据
| 日期 | 总废水量 | 废水成分 | 处理方式 | 处理效率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X年X月 | 预计总量 | 主要成分 | 目前处理方式 | 处理效果 |
废水量问题原因
纺织厂在生产过程中,由于工艺流程复杂、设备老化等原因,导致废水量不断增加,废水处理设施不完善、管理不到位也是导致废水量问题的重要原因。
案例分析
以某纺织厂为例,详细说明其废水量问题及其解决方案。
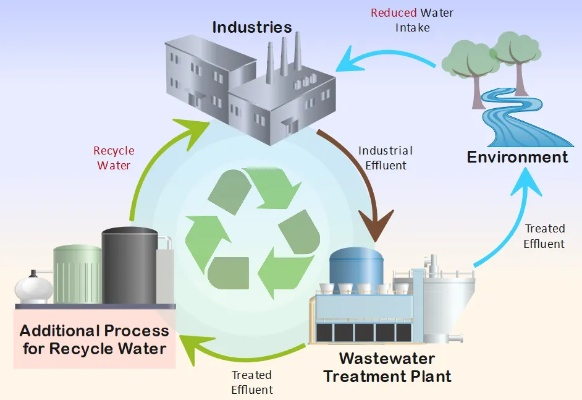
废水量处理过程
该纺织厂采用先进的废水处理技术,包括生物处理、化学处理等,在处理过程中,采用了高效的处理设备,确保废水得到充分处理,该厂还建立了严格的废水排放管理制度,确保废水处理符合国家环保标准,该厂还加强了废水处理的宣传教育,提高员工对废水处理的重视程度。
成功经验总结
该纺织厂在废水量处理方面取得了显著成效,该厂加强了废水处理的设施建设和管理,提高了废水处理的效率和质量,该厂注重废水处理的科技创新,引入了先进的废水处理技术,提高了废水处理的效率和适应性,该厂加强了废水处理的宣传教育,提高了员工对废水处理的责任感和使命感。
解决方案与建议
针对纺织厂废水量问题,提出以下解决方案和建议。
加强废水处理设施建设和管理
纺织厂应加强废水处理设施的建设和管理,提高废水处理的效率和质量,应定期对废水处理设施进行维护和检修,确保设施的正常运行,还应建立完善的废水处理管理制度,确保废水处理符合国家环保标准。
采用先进的废水处理技术
纺织厂应采用先进的废水处理技术,包括生物处理、化学处理等,还应加强废水处理的科技创新,引入先进的废水处理设备和技术,提高废水处理的效率和适应性,还应加强废水处理的宣传教育,提高员工对废水处理的重视程度。
加强与政府部门的沟通与合作
纺织厂应加强与政府部门的沟通与合作,争取政策支持和资金支持,还应积极参与环保治理工作,为环境保护做出贡献。
结论与建议
纺织厂废水量问题是一个亟待解决的问题,为了解决这一问题,纺织厂应加强废水处理设施建设和管理,采用先进的废水处理技术,加强与政府部门的沟通与合作,还应注重废水处理的科技创新和宣传教育,提高员工对废水处理的重视程度和责任感,纺织厂还应积极采取其他措施,如优化生产流程、提高资源利用效率等,以降低废水量。
就是关于纺织厂废水量主题的英文口语化内容,希望能够帮助到您。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Evolution of Tianzhuang East Textile Factory
A Brief Overview of the Aobo Textile Factory
The Transformative Journey of the Original Pulp Factory,Chzhou Textile Mill
Strategies for Effective Management in a Textile Factory
A Comprehensive Guide to the Raw Materials for the Textile Industry
The Legacy and Innovation:The Story of Changchun Textile Factory



