The Art of Textiles:A Comprehensive Guide to Fabric Design and Production
"The Art of Textiles: A Comprehensive Guide to Fabric Design and Production" is a comprehensive guide that covers the entire process of designing and producing textiles. It provides an in-depth understanding of the various techniques used in fabric design, such as pattern drafting, cutting, and sewing. The book also covers the production process, including the selection of materials, cutting, stitching, finishing, and packaging.,The author, who has over 20 years of experience in the textile industry, provides practical tips and techniques for both beginners and professionals. The book includes case studies and examples of successful textile designs, which can serve as inspiration for designers and producers alike.,In addition to providing technical information, "The Art of Textiles" also offers insights into the cultural and historical context of textile design. It discusses the influence of different cultures on textile design, and explores the evolution of textile technology over time.,Overall, "The Art of Textiles" is a valuable resource for anyone interested in learning more about textile design and production. Whether you are a designer, producer, or just curious about the world of textiles, this book provides a comprehensive overview of the subject matter.
Introduction Textiles, the fabrics we wear and touch every day, are an integral part of our lives. From the softness of a cotton sweater to the durability of a polyester jacket, textiles play a significant role in shaping our daily routines and creating a sense of comfort and style. In this guide, we will explore the various types of textiles, their design principles, production methods, and how they have evolved over time. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the textile industry and its impact on modern life.
Types of Textiles Textiles can be broadly categorized into two main groups: natural and synthetic fibers.
-
Natural Fibers Natural fibers include plant-based materials such as wool, silk, cotton, hemp, and linen. These fibers are derived from plants and animals and offer unique properties that make them ideal for specific applications. For example, wool is warm and soft but prone to shrinkage, while silk is smooth and luxurious but expensive. Cotton, on the other hand, is breathable, absorbent, and durable but may not be as soft or smooth as synthetic fibers. Hemp, another natural fiber, is biodegradable and resistant to pests but may have a higher cost due to its lower yield per acre. Linen, known for its strong and lightweight texture, is popular for its breathability and moisture-wicking properties.
-
Synthetic Fibers Synthetic fibers are man-made materials made from petroleum byproducts or other chemicals. They offer a wide range of properties that can mimic those of natural fibers or surpass them. Some examples include polyester (poplin), nylon (such as nylon stockings), acrylic (such as rayon), and spandex (used in athletic apparel). Polyester, for example, is highly durable, easy to clean, and resistant to stains but may feel rough against the skin. Nylon is strong, lightweight, and resistant to water but may not be as breathable as natural fibers. Acrylic offers a smooth and silky texture but may be more prone to pilling and fading. Spandex is stretchy and elastic, making it ideal for sportswear but may cause allergic reactions in some people.

Design Principles The design of textiles involves several key principles, including functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability.
-
Functionality Functionality refers to the ability of textiles to meet specific needs and requirements. This includes factors such as warmth, breathability, durability, comfort, and fit. For example, a winter coat should be designed to keep the wearer warm and dry, while a summer dress should be lightweight and breathable. Additionally, textiles must be able to withstand regular wear and tear without losing their shape or performance.
-
Aesthetics Aesthetics involve the visual appeal of textiles, including patterns, colors, textures, and shapes. Textile designers use these elements to create visually appealing designs that appeal to the eye and elevate the overall look of clothing or home decor. For instance, a patterned scarf may add a pop of color to a neutral outfit or a bold geometric print may create a modern and sophisticated look.
-
Sustainability Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the textile industry as consumers demand more eco-friendly products. This includes using renewable resources, reducing waste, minimizing carbon emissions, and promoting fair trade practices. For example, organic cotton is grown without harmful chemicals and uses fewer pesticides than conventional cotton, making it a more sustainable option for clothing. Additionally, many textile companies are implementing recycling programs and using recycled materials in their production processes to reduce waste and promote sustainability.
Production Methods The production methods used to create textiles vary depending on the type of fiber and desired outcome.
-
Weaving Weaving is the oldest method of producing textiles and involves interlacing warp threads and filling threads to create a woven fabric. This technique is commonly used in the production of rugs, carpets, and traditional clothing like saris and shawls.
-
Knitting Knitting is a form of weaving where loops of yarn are pulled through a series of needles to create a fabric. This technique is used in the production of sweaters, hats, and socks.
-
Patterning Patterning involves creating specific designs on a fabric using techniques such as embroidery, applique, and screen printing. This method is commonly used in the production of decorative items such as wall hangings and tablecloths.

-
Printing Printing involves applying dyes or pigments onto a fabric surface to create patterns or designs. This technique is used in the production of t-shirts, jeans, and other casual wear items.
-
Embroidery Embroidery involves stitching tiny details onto a fabric using thread or beads. This technique is commonly used in the production of clothing accessories such as belts, purses, and scarves.
-
Dyeing Dyeing involves treating fabric with dyes to change its color or create a unique pattern. This technique is used in the production of fashion garments, home decor items, and even food packaging.
Case Study: Nike's Air Max Foam Flyknit Technology Nike's Air Max Foam Flyknit technology is a revolutionary textile production method that combines knitting and foam technology to create a lightweight, breathable, and flexible shoe. The process involves knitting the upper part of the shoe using high-quality yarn and then adding a layer of foam material on top of the knitted structure. This creates a cushioned and comfortable footbed that provides excellent support and shock absorption for the feet during running or jumping activities. Additionally, the foam layer helps to regulate temperature and prevent blisters on hot surfaces. This innovative technology has revolutionized the sneaker industry and earned Nike numerous awards and accolades for its advanced design and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion Textiles are an essential part of our daily lives and have evolved significantly over time. From the simple homespun fabrics of ancient civilizations to the cutting-edge technology used in today's fashion and sportswear industries, textiles have captured the imagination and creativity of human beings for centuries. As we continue to push the boundaries of innovation and sustainability, the textile industry will undoubtedly continue to thrive and provide us with new opportunities for expression and enjoyment.
纺织品布料图解概览
今天我们来探讨一下纺织品布料图解的相关知识,纺织品布料是日常生活中常见的材料,广泛应用于服装、家居装饰等领域,本文将通过图表和案例说明,详细介绍纺织品布料的特点、种类以及图解方法。
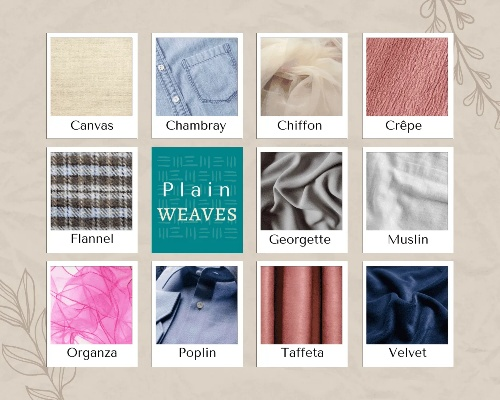
纺织品布料的特点
- 材质多样性:纺织品布料种类繁多,包括棉、麻、丝绸、涤纶等,每种材质都有其独特的质地、手感和特性。
- 功能性需求:根据不同的用途,纺织品布料需要具备不同的功能特性,如透气性、吸湿性、防潮防霉等。
- 美观与舒适性:纺织品布料在美观和舒适性方面也有很高的要求,不同材质的纺织品布料具有不同的视觉效果和触感体验。
纺织品布料的种类
- 棉布:棉布是一种天然纤维布料,具有吸湿性好、透气性强、柔软舒适等特点,棉布广泛应用于夏季服装、家居用品等领域。
- 麻布:麻布是一种天然纤维布料,具有吸湿性好、透气性强、耐用等特点,麻布常用于夏季凉席、床单等家居用品。
- 丝绸:丝绸是一种高级纺织材料,具有光滑细腻的质地、优雅高贵的特点,丝绸广泛应用于服装、家居装饰等领域。
- 涤纶布:涤纶布是一种合成纤维布料,具有强度高、耐磨性好、易洗易干等特点,涤纶布广泛应用于工业制品、服装等领域。
纺织品布料图解方法
- 选择合适的图解工具:选择一款适合展示纺织品布料的图解工具,如CAD软件、手工绘图等。
- 确定图解要素:根据纺织品布料的种类和特点,确定图解要素,如材质、图案、颜色等。
- 绘制基本图形:根据图解要素,绘制基本图形,如线条、矩形、圆形等。
- 添加细节和装饰:根据需要,在基本图形上添加细节和装饰,如绣花、印花、绣线等。
- 调整色彩和比例:根据纺织品布料的实际尺寸和比例,进行色彩和比例的调整。
案例说明
以涤纶布料为例,介绍纺织品布料图解的应用。
- 选择合适的图解工具:使用CAD软件进行涤纶布料的图解。
- 确定图解要素:根据涤纶布料的材质和特点,确定图解要素,如涤纶纤维的分布、图案等。
- 绘制基本图形:使用CAD软件绘制涤纶布料的轮廓线、纹理线等基本图形。
- 添加细节和装饰:在基本图形上添加涤纶纤维的细节和装饰,如涤纶纤维的绣花图案等。
- 调整色彩和比例:根据涤纶布料的实际尺寸和颜色要求,进行色彩和比例的调整。 通过以上案例说明,我们可以看到纺织品布料图解的应用广泛性和实用性,在日常生活和工作中,纺织品布料的应用越来越广泛,其图解方法和应用技巧也越来越成熟和多样化。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Art of Textiles:A Journey Through the World of Fabrics with Aiyu Textiles
The Star Standard for Textiles
The Magic of Adhesive Tapes in Fashion and Industrial Design



