The Expanding Horizons of Textile CAD Applications
The Textile CAD (Computer-Aided Design) applications have been expanding significantly in recent years, with a growing number of users and projects utilizing these tools. These applications are used for creating complex designs, optimizing patterns, and generating technical specifications for textile products. The increasing demand for high-quality, customized, and efficient textile products has driven the development of advanced CAD software that can handle a wide range of textile materials and processes. This expansion is driven by factors such as increased competition in the textile industry, changing consumer preferences, and advancements in technology that make it easier to create and manage complex designs. As a result, textile CAD applications are becoming more sophisticated and versatile, offering new possibilities for designers and manufacturers alike.
Introduction: In the realm of textile manufacturing, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way we approach design, production, and optimization. From creating intricate patterns to managing inventory, CAD applications have become an integral part of the textile industry's workflow. In this article, we will explore the various facets of textile CAD applications and showcase some practical examples to illustrate their impact.
Textile CAD Applications:
- Pattern Design: CAD tools enable designers to create digital patterns for fabrics, ensuring consistency across different batches or even different factories. This not only saves time but also reduces errors and inconsistencies.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Pattern editing | Allows for easy modification of existing designs |
| Batch generation | Creates multiple identical patterns for mass production |
| Variation management | Ensures consistent quality across different products |
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software can simulate the effects of different fabric properties on the final product, helping manufacturers make informed decisions about material selection and production processes.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Material simulation | Analyzes the performance of different fabric materials under various conditions |
| Stress analysis | Determines the strength and durability of the fabric under load |
| Durability prediction | Predicts how a fabric will perform over time based on its construction |
- Quality Control: CAD systems are instrumental in maintaining high standards of quality control within the textile industry. They provide real-time data on fabric dimensions, color accuracy, and pattern fidelity.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Color inspection | Automatically checks for color variations within a batch |
| Dimensional control | Ensures that fabrics meet strict dimensional requirements |
| Pattern verification | Complies with customer specifications by checking against predefined patterns |
- Supply Chain Management: CAD tools help textile manufacturers manage their supply chain more efficiently, from sourcing raw materials to tracking shipments.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Supplier integration | Links with suppliers to monitor raw material availability and quality |
| Warehouse management | Optimizes storage space and improves inventory turnover |
| Shipping optimization | Plans efficient delivery routes based on geographical and logistical factors |
- Customization and Innovation: CAD tools empower designers to create bespoke textiles and facilitate innovation in new materials or designs.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Bespoke design | Allows for customization of patterns and colors to suit specific clients’ needs |
| New material research | Facilitates testing and development of innovative textiles like eco-friendly or biodegradable materials |
| Digital printing | Uses CAD software to optimize print settings for high-resolution digital prints |
- Efficiency and Productivity: CAD tools automate many routine tasks, freeing up time for designers to focus on creative endeavors.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Automated drafting | Reduces manual labor and error rates in pattern creation |
| Time-to-market reduction | Streamlines the entire design and production process, resulting in faster deliveries |
| Collaboration tools | Encourages teamwork and sharing of ideas through digital collaboration platforms |
- Training and Education: CAD systems are often integrated with online training modules, providing ongoing education for both employees and designers.
| Feature | Example |
|---|---|
| Onboarding training | Guides new users through the basic functions of the CAD software |
| Continuous learning | Offers access to advanced features and tutorials as needed |
| Certification programs | Elevate employees' skills and knowledge in CAD application areas |
Case Study: Consider a textile manufacturer who specializes in producing high-quality sportswear using innovative materials. The company uses CAD software to streamline its design process, allowing designers to quickly iterate on patterns and colors based on customer feedback. By implementing a system that allows for seamless collaboration between designers, pattern makers, and production staff, the company was able to reduce lead times significantly, while maintaining high levels of product quality. This case study highlights the power of CAD applications in streamlining the textile industry's workflow and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: The textile CAD application landscape is constantly evolving, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated CAD tools tailored to the unique challenges faced by the textile industry. Whether it's designing complex patterns, analyzing material properties, or managing supply chains, textile CAD applications are transforming the way we work with textiles, paving the way for a brighter future in the global textile industry.
在探讨纺织品CAD应用时,我们首先可以简要概述其涵盖的主要领域,纺织品CAD是一种先进的计算机辅助设计技术,广泛应用于多个行业,包括但不限于服装、家居装饰、纺织品生产等,以下是关于纺织品CAD应用的一些主要方面及其具体案例说明。
纺织品CAD应用的主要领域
设计与开发阶段
纺织品CAD在设计和开发阶段主要涉及以下几个方面:
(1)面料设计:利用CAD软件进行面料图案、颜色、纹理的设计和优化。
(2)纱线编织:通过CAD软件模拟纱线的编织过程,优化纱线的结构,提高织物的性能。
(3)纺织品生产流程模拟:模拟纺织品从原料到成品的生产流程,优化生产过程,提高生产效率。
生产和质量控制阶段
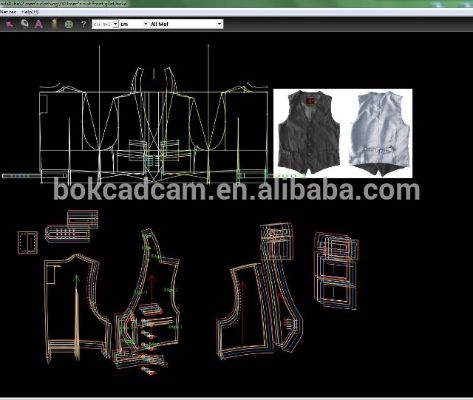
纺织品CAD在生产和质量控制阶段主要涉及以下几个方面:
(1)质量控制:利用CAD软件进行纺织品的质量检测和质量控制,确保产品质量符合标准。
(2)生产过程监控:通过实时监测生产过程中的参数和工艺,确保生产过程的稳定性和一致性。
(3)供应链管理:利用CAD软件进行供应链管理,优化供应链流程,提高供应链效率。
具体案例说明
面料设计领域的应用案例
在面料设计领域,纺织品CAD的应用主要体现在以下几个方面:
(1)服装品牌:某知名服装品牌利用CAD软件进行面料图案设计,优化面料纹理和颜色,提高产品的时尚感和舒适度。
(2)家居装饰公司:家居装饰公司利用CAD软件模拟纱线编织过程,制作出各种风格的家纺产品,满足不同客户的需求。
生产流程模拟领域的应用案例
在生产流程模拟领域,纺织品CAD的应用主要体现在以下几个方面:
(1)纺织企业:纺织企业利用CAD软件模拟纺织品从原料到成品的生产流程,优化生产过程,提高生产效率,某大型纺织企业通过使用CAD软件进行生产流程模拟,实现了生产过程的自动化和智能化,大大提高了生产效率。
(2)高校科研机构:高校科研机构利用CAD软件进行纺织品的质量检测和质量控制,确保产品质量符合标准,通过模拟生产过程,为科研人员提供实验数据和参考方案。
英文案例说明 The Application of Textile CAD in Various Fields 补充说明:
纺织品CAD应用领域概览
| 应用领域 | 具体应用 | 案例说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 设计与开发阶段 | 面料设计、纱线编织、生产流程模拟 | 服装品牌利用CAD软件进行面料图案设计,优化面料纹理和颜色;家居装饰公司利用CAD软件模拟纱线编织过程制作家纺产品 |
| 生产与质量控制阶段 | 生产过程监控、质量控制、供应链管理 | 纺织企业利用CAD软件进行生产流程模拟优化生产过程;高校科研机构利用CAD软件进行纺织品的质量检测和质量控制确保产品质量符合标准 |
纺织品CAD的应用范围广泛,涵盖了设计与开发、生产和质量控制等多个领域,随着科技的不断发展,纺织品CAD的应用将会越来越广泛,为各个行业带来更多的便利和效益。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Address of the Tri-City Textile Wholesale Market
Strategic Approaches to Sustaining Success in the Textile Industry



