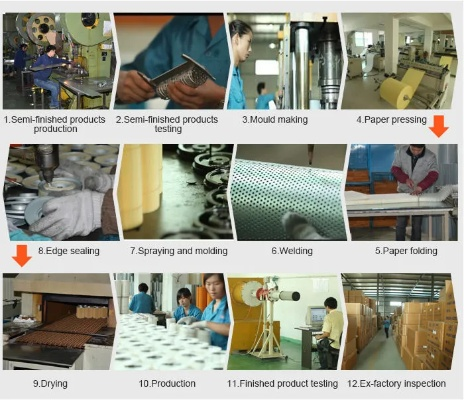
The Art of Dyeing:A Comprehensive Guide to Textile Factory Dyers
"The Art of Dyeing: A Comprehensive Guide to Textile Factory Dyers" is an in-depth guide on the art and techniques used by textile factory dyers. The book covers a wide range of topics, including the history and philosophy behind dyeing, the different types of dyes and their applications, dyeing processes such as batch and continuous dyeing, and the importance of quality control during the dyeing process.,The author provides practical tips and tricks for both beginners and experienced dyers, covering everything from choosing the right dyes for specific fabrics to troubleshooting common problems. The book also includes case studies and examples of successful dyeing projects, making it a valuable resource for anyone involved in the textile industry.,Overall, "The Art of Dyeing" is an essential resource for anyone looking to learn more about the complex world of textile dyeing. Whether you are a professional dyer or just starting out, this book will provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed in this rewarding craft."
Introduction: In the world of textile production, dyeing is a crucial step that transforms raw materials into colorful fabrics. At a textile factory, this process involves mixing dyes with water and other chemicals to create vibrant colors for garments, carpets, and more. In this guide, we will explore the intricacies of dyeing techniques, including the different types of dyes used, the steps involved in dyeing, and some common challenges faced by dyers. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of how dyeing works and what it takes to produce high-quality textiles.
Types of Dyes Used in Textile Dying: There are several types of dyes used in textile dyeing, each with its unique properties and applications. Here's a breakdown of some of the most common dyes:

-
Direct Dyes: These dyes are added directly to the fiber during the spinning process. They can be either acid or basic dyes, depending on their pH level. Direct dyes offer fast color development and low environmental impact.
-
Alkali Dyes: These dyes are added to the fiber after spinning and before finishing. They work by reacting with the fiber's amino groups to create a stable color. Alkali dyes are commonly used for polyester and nylon fabrics.
-
Acid Dyes: These dyes are added to the fiber during the spinning process. They can be either direct or alkaline dyes, depending on their pH level. Acid dyes offer a wide range of colors and are commonly used for cotton and linen fabrics.
-
Emulsion Dyes: These dyes are added to the fiber during the spinning process as a suspension in water. They can be either acid or basic dyes, depending on their pH level. Emulsion dyes offer excellent coverage and fast color development.
-
Solvent Dyes: These dyes are added to the fiber during the spinning process as a solution in a solvent (such as alcohol or acetone). They can be either acid or basic dyes, depending on their pH level. Solvent dyes offer good coverage and fast color development but may require additional processing steps.
Common Challenges Faced by Dyers: While textile dyeing is a highly efficient process, there are several challenges that dyers face on a daily basis. Here are a few examples:
-
Color Stability: One of the biggest challenges facing textile dyers is ensuring that the colors produced are stable over time. This requires careful monitoring of the dye bath and proper finishing processes to prevent color fade and fading.
-
Environmental Concerns: Textile dyeing often involves the use of harmful chemicals, which can have negative impacts on the environment. Dyers must strive to minimize these impacts by using eco-friendly dyes and reducing waste through recycling and proper disposal practices.
-
Quality Control: Dyers must ensure that the final product meets quality standards before it leaves the factory. This requires rigorous testing protocols and close monitoring of the dye bath and finishing processes to ensure consistent results.
-
Technology Adoption: With advances in technology, dyers must stay up-to-date with new methods and equipment to improve efficiency and reduce costs. This includes investing in automation and digital tools to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Case Study: Let's take a closer look at a real-world example of a textile factory that specializes in the dyeing of synthetic fabrics. This company has been operating in the industry for over a decade and has developed a reputation for producing high-quality products with exceptional color accuracy.
The company's primary focus is on producing bright, vibrant shades for apparel and accessories. To achieve this, they use a combination of direct and alkaline dyes, which allows them to achieve excellent coverage and fast color development. They also employ a dedicated team of experienced dyers who follow strict quality control protocols throughout the entire dyeing process.
One of the key challenges faced by this company is maintaining color stability over time. To address this issue, they invest in advanced monitoring systems that track dye bath performance and adjust the chemical composition accordingly. Additionally, they regularly review their finishing processes to ensure that any potential issues are identified and addressed promptly.
Another challenge they face is ensuring that their products meet stringent environmental regulations. To address this, they implement sustainable practices such as using eco-friendly dyes and minimizing waste through recycling and proper disposal. They also collaborate with third-party organizations to promote responsible sourcing and ethical production practices.
Conclusion: Dyeing is a complex process that requires meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the science behind color formation. From selecting the right type of dye to implementing effective quality control measures, textile dyers must constantly evolve their skills to meet the ever-changing demands of the industry. By embracing innovation and adopting sustainable practices, textile dyers can not only produce high-quality products but also make a positive impact on the environment and society at large.
纺织厂染缸操作简介
在纺织厂中,染缸操作是一项关键工艺,涉及到染料的制备、染色过程以及后续处理等多个环节,本文将围绕纺织厂染缸操作的主题,为您详细介绍相关知识。
染缸操作流程

原料准备
在染缸操作开始前,首先需要准备好染料原料,这些原料包括染料分子、助剂等,需要符合相关质量标准和安全要求。
染色过程
染色过程包括浸染、加热、搅拌、染色等步骤,在染缸中,工作人员需要根据染料的性质和织物的要求,控制染缸内的温度、湿度、搅拌速度等参数,以确保染料的均匀分布和染色效果。
后续处理
染色完成后,需要进行后续处理,包括清洗、烘干、整理等步骤,这些步骤的目的是去除染料残留、提高织物质量等。
案例说明
以一家纺织厂为例,详细介绍染缸操作的相关知识。
原料准备
该纺织厂在染缸操作中,需要准备高质量的染料原料,包括符合相关质量标准和安全要求的染料分子和助剂,还需要根据织物的要求,选择合适的染缸温度和搅拌速度等参数。
染色过程
在该纺织厂中,染色过程采用了先进的染色技术,工作人员在染缸中控制温度和搅拌速度等参数,确保染料的均匀分布和染色效果,还需要注意染料的用量和染色时间等参数,避免过度染色或染色不均匀等问题。
案例分析
在该纺织厂中,通过精细的操作和控制,成功完成了多批次高质量的织物染色任务,该纺织厂还注重环保和节能,采用了环保染缸和节能设备,降低了染缸操作的能耗和排放。
英文表格补充说明
以下是关于纺织厂染缸操作的一些英文表格补充说明:
表格1:纺织厂染缸操作流程表格
| 步骤 | 描述 | 相关说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 原料准备 | 准备染料原料、助剂等 | 符合相关质量标准和安全要求 |
| 染色过程 | 控制染缸温度、湿度、搅拌速度等参数 | 根据织物的要求进行染色操作 |
| 后续处理 | 清洗、烘干、整理等 | 提高织物质量等 |
纺织厂染缸操作是一项关键工艺,需要严格控制染缸操作参数和工艺流程,通过精细的操作和控制,可以确保染料的均匀分布和染色效果,同时还可以降低能耗和排放,提高织物质量,纺织厂还需要注重环保和节能,采用环保设备和工艺,实现可持续发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article: