The circular economy in textiles:a path towards sustainability and efficiency
The circular economy is a paradigm shift in the textile industry, aiming to achieve sustainability and efficiency through closed-loop production systems. This paper discusses the importance of circular economy principles in textiles, focusing on waste reduction, resource recovery, and product reuse. The adoption of circular economy practices can lead to reduced environmental impact, lower costs, and improved economic performance. However, challenges such as lack of awareness, technical barriers, and regulatory frameworks must be addressed for the circular economy to become a reality in textiles. Overall, the circular economy represents a promising path towards sustainable and efficient textile production, with significant potential to transform the industry towards a more circular and responsible future.
Introduction: The textile industry is one of the largest contributors to global commerce, with billions of dollars invested annually in production, distribution, and recycling. However, this sector has long been criticized for its high environmental footprint and resource consumption. As awareness of the need for sustainable practices grows, the concept of 'circular economy'—an economic model that seeks to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency—has gained traction in the textile industry. This essay explores the principles of circularity in textiles, the challenges faced by the industry, and how it can be implemented to create a more sustainable future for the sector.
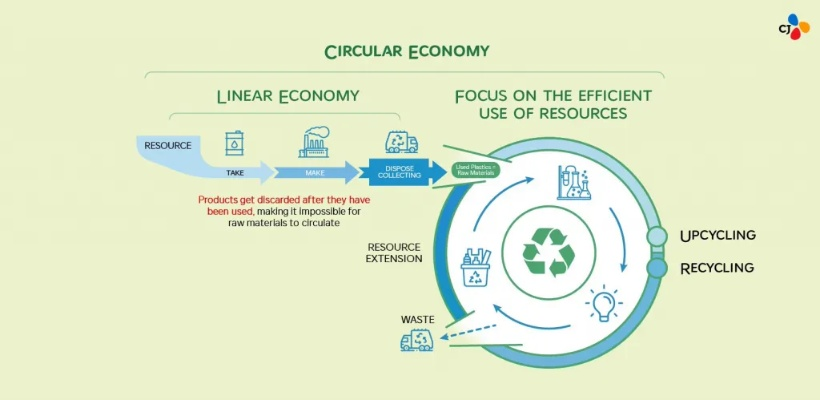
Circular Economy in Textiles: What It Means A circular economy in textiles involves designing products that are durable, recyclable, and reusable, thus minimizing the need for new raw materials. This approach aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and promote a circular flow of materials. By adopting circularity, the textile industry can achieve greater efficiency, lower costs, and improved environmental performance.
Benefits of Circular Economy in Textiles:
- Reduced Waste: A circular economy in textiles reduces the amount of waste produced by designing products that have a longer lifespan or can be easily recycled.
- Resource Efficiency: By focusing on reusing and recycling textiles, the industry can use fewer raw materials and reduce its carbon footprint.
- Cost Reduction: Reducing waste and using recycled materials can lead to lower production costs and higher profit margins.
- Environmental Impact: A circular economy in textiles can help mitigate pollution and protect natural resources by reducing the need for virgin fibers.
Challenges Faced by the Textile Industry: Despite the benefits of a circular economy, the textile industry faces several challenges that hinder its adoption. These include:
- Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardization across different textile products and processes makes it difficult to implement circularity effectively.
- Inefficient Production Processes: Many textile factories operate with outdated technology and inefficient production processes, making it challenging to produce products that are both sustainable and cost-effective.
- Limited Resource Availability: The availability of raw materials such as cotton, wool, and silk is limited, which can make it difficult to produce sustainable textiles.
- High Transportation Costs: The transportation of raw materials from distant sources adds significant costs to the production process, making it challenging to pass on these costs to consumers.
Implementing Circular Economy in Textiles: To implement a circular economy in textiles, several steps must be taken. These include:
- Encouraging Innovation: Companies should invest in research and development to develop new materials and technologies that are more sustainable and efficient.
- Improving Production Processes: Companies should upgrade their production facilities to adopt more efficient and eco-friendly methods of manufacturing.
- Promoting Sustainable Materials: Companies should focus on using sustainable materials such as recycled polyester or bamboo fibers instead of virgin fibers.
- Enhancing Resource Management: Companies should optimize their resource management strategies to ensure that they use resources efficiently and sustainably.
- Building Collaborative Partnerships: Companies should work together with other stakeholders such as suppliers, customers, and government agencies to promote a circular economy.
Case Study: One example of a circular economy initiative in the textile industry is the "Renew" program launched by the American Apparel Company (A&F) in 2017. Under this program, A&F aims to reduce its environmental impact by using sustainable materials in its clothing lines and promoting a circular economy through recycling and reuse programs. The company has also committed to reducing its carbon footprint by sourcing its raw materials from renewable sources and investing in energy-efficient technologies.
Conclusion: The textile industry has a crucial role to play in achieving a circular economy. By embracing sustainable practices and adopting innovative solutions, the industry can not only reduce its environmental impact but also improve its competitiveness and profitability. As more companies recognize the value of circularity, we can expect to see a shift towards a more sustainable and efficient future for the textile industry.
纺织品循环加工概述
随着全球纺织品的不断更新换代,纺织品循环加工已成为一个重要的环保和可持续发展的议题,纺织品循环加工不仅有助于减少资源浪费,还能降低环境污染,实现经济效益和社会责任的统一,本文将围绕纺织品循环加工及其利用展开讨论。
纺织品循环加工流程
- 原料收集与分类:从各种来源收集废旧纺织品,根据其材质、用途等进行分类。
- 初步处理:对废旧纺织品进行清洗、整理、修补等初步处理,去除杂质和瑕疵。
- 纺织材料再生利用:将处理后的废旧纺织品转化为新的纺织品材料,如再生纤维、再生布料等。
- 深度加工:对再生纺织品进行精细加工,如织造、印花、染整等,提高其附加值。
- 废弃物处理与资源化利用:将加工后的废弃物进行无害化处理,转化为资源或能源。
纺织品循环加工案例分析
某地区纺织品循环利用项目

某地区近年来大力推广纺织品循环利用项目,通过回收旧衣物、废旧纺织品等废弃物,将其转化为新的纺织品材料,该项目不仅减少了资源浪费,还降低了环境污染,通过先进的纺织材料再生利用技术,将废旧纺织品转化为再生纤维,用于制作新的床上用品、地毯等家居用品,该项目还注重废弃物的无害化处理和资源化利用,实现了经济效益和社会责任的统一。
纺织品再制造技术的创新应用
近年来,纺织品再制造技术得到了广泛的应用和创新,该技术通过精细加工,将废旧纺织品转化为新的纺织品材料,提高了其附加值,某公司采用先进的织造技术,将废旧针织衫转化为高品质的毛巾、围巾等家居用品,该技术还注重环保和可持续性,通过减少废弃物的产生和降低环境污染,实现了经济效益和生态效益的双重目标。
纺织品循环加工的利用途径
- 服装制造:将废旧纺织品转化为新的服装材料,满足市场需求的同时,实现了资源的循环利用。
- 家居用品:将废旧纺织品用于制作家居用品,如床上用品、地毯、窗帘等,提高家居品质和生活环境。
- 纺织材料替代品:利用再生纤维、再生布料等新型纺织材料替代传统材料,满足不同领域的需求。
- 能源和化工领域:将废弃物转化为能源和化工原料,实现废弃物的有效利用和资源的循环利用。
纺织品循环加工及其利用是环保和可持续发展的必然趋势,通过循环加工,可以减少资源浪费和环境污染,实现经济效益和社会责任的统一,纺织品循环加工还可以促进科技创新和产业升级,推动经济发展和环境保护的双赢局面,我们应该继续推广纺织品循环加工的理念和技术,为可持续发展做出更大的贡献。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Fabric of Emotions A Deep Dive into 思念纺织品有限公司]



