The Cost Structure of Textiles:An In-depth Analysis
This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the cost structure of textiles. It begins by outlining the various components that make up the cost of producing textiles, such as raw materials, labor, and transportation. The author then goes on to discuss the impact of these costs on the overall price of textiles, and how they vary depending on the type of textile being produced.,The paper also explores the role that technology plays in shaping the cost structure of textiles. For example, it discusses the use of automation and other technological advancements that can reduce production costs and improve efficiency. Additionally, the paper examines the potential for new materials and processes to drive down costs and create more competitive markets for textile products.,Overall, this paper provides a thorough understanding of the complexities involved in analyzing the cost structure of textiles, and offers insights into the ways in which industry players can optimize their operations to maximize profits.
In the world of textiles, the cost structure is a crucial aspect that affects not only the profit margins but also the overall market dynamics. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various components that contribute to the production and retail price of textile products, including raw materials, labor, transportation, and overhead costs. By understanding these factors, businesses can make informed decisions about sourcing, pricing, and inventory management.
Raw Materials: The Foundation of Textile Production
The raw materials used in textile manufacturing are the backbone of the industry. These include cotton, polyester, wool, silk, and other natural and synthetic fibers. Each type of material has its own unique characteristics, such as durability, softness, and colorfastness, which affect the final product's quality and appeal.
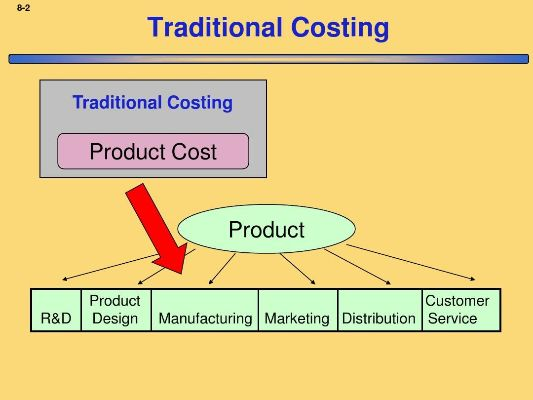
Labor: The Human Touch
While raw materials are the physical building blocks of textiles, labor is the human touch that brings them to life. From weaving to knitting, each step requires skilled workers who apply their knowledge and expertise to produce high-quality products. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the skill level of the workforce and the complexity of the task at hand.
Transportation: Moving from the Fiber to the Finished Product
Once the raw materials and labor have been assembled into textiles, they need to be transported to the factories where they undergo further processing before being packaged and shipped to retailers or end consumers. The cost of transportation can be significant, especially for bulky or fragile items like fabrics or carpets.
Overhead Costs: The Unseen Expenses
Beyond raw materials, labor, and transportation, there are several other overhead costs that can add up quickly. These include rent or lease payments for factory space, utility bills (such as electricity and water), insurance, and maintenance expenses. These costs may seem small individually, but when added up over time, they can significantly impact a company's bottom line.
Case Study: The Cost Structure of Levi Strauss & Co.
To illustrate how different components contribute to the cost structure of textiles, let's take a closer look at the case study of Levi Strauss & Co., one of the world's leading denim manufacturers.
Levi Strauss & Co. sources its denim fabric from a variety of suppliers, including domestic mills and internationally sourced fibers. The company's raw materials cost accounts for a significant portion of its total cost structure, with the most expensive component being the fibers themselves. However, the company also invests heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and sustainability of its production processes.
Labor costs are another critical component of Levi Strauss & Co.'s cost structure. The company employs a highly skilled workforce that specializes in denim manufacturing techniques, ensuring that every stitch is made with precision and quality. Additionally, Levi Strauss & Co. has implemented advanced automation systems to reduce labor costs while maintaining high standards of production quality.
Transportation plays an important role in the cost structure of Levi Strauss & Co.'s denim products. The company's factories are located in various parts of the United States, allowing it to leverage economies of scale by sourcing raw materials and producing denim locally. However, due to the size and weight of some of its products, transportation remains a significant expense that must be carefully managed to avoid additional costs.
Overhead costs are also a critical part of Levi Strauss & Co.'s cost structure. The company operates several manufacturing facilities across the globe, necessitating significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance. Additionally, Levi Strauss & Co. maintains strict environmental standards for its factories, requiring regular inspections and upgrades to ensure compliance with regulations.
In conclusion, the cost structure of textiles is a complex and multifaceted topic that encompasses various components such as raw materials, labor, transportation, and overhead costs. By understanding these factors, businesses can optimize their operations, minimize waste, and ultimately increase their profitability.
大家好,今天我们来聊聊纺织品的成本构成,纺织品的成本涉及到多个方面,包括原材料、生产成本、设计成本、营销成本等,下面我们将详细说明纺织品的成本构成包括哪些内容。
原材料
纺织品的成本构成中,原材料是基础,原材料主要包括纤维、纱线、面料等,纤维是纺织品的骨架,决定了纺织品的强度和耐用性,纱线则是纺织品的细丝部分,决定了纺织品的轻薄度和弹性,面料则是经过织造、染整等工艺制成的最终产品。
生产成本
生产成本是纺织品的生产过程中产生的费用,主要包括以下几个方面:
- 人工成本:包括生产工人工资、福利等费用。
- 设备折旧和维护费用:用于购买和维护生产设备。
- 原材料采购成本:包括从供应商处采购原材料的费用。
- 生产过程中的能源消耗和环保成本:用于生产过程中的能源消耗和环保处理。
设计成本
设计成本是指为了满足市场需求和提升产品竞争力而产生的费用,设计师需要投入时间和精力来设计出符合消费者需求的产品,这包括设计研发、样品制作等费用。
营销成本
营销成本是指为了扩大产品市场份额和提高品牌知名度而产生的费用,这可能包括广告宣传费用、市场营销活动费用等。
下面我们通过一个具体的英文案例来说明纺织品的成本构成,假设一家纺织品公司生产一款新型面料,其成本构成如下:
面料成本表:
| 原材料 | 数量(千克) | 单价(元/千克) | 总成本(元) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维 | 500千克 | ¥50/千克 | ¥25,000 |
| 纱线 | 300米 | ¥8/米 | ¥2400 |
| 设计研发 | X元 | 未提供 | 未确定 |
| 总计 | ¥32,500元 |
案例说明:该公司的新型面料在设计上注重环保和舒适性,同时在生产过程中采用了先进的工艺和技术,从而降低了生产成本,为了扩大市场份额和提高品牌知名度,公司还投入了一定的广告宣传费用和市场营销活动费用,该案例表明了纺织品的成本构成不仅包括原材料和生产成本,还包括设计成本和营销成本等多个方面。
纺织品的成本构成包括原材料、生产成本、设计成本和营销成本等多个方面,在生产过程中,企业需要根据市场需求和产品特点,合理规划生产成本和营销成本,从而降低产品成本,提高市场竞争力。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Leather-Soaked Luxury:A Deep Dive into the World of Yecheng Textiles
The Art of Textile Stitching with Pattern Pressing
The Magic of Red Iron Textiles
The Fabric of Our Future:A Comprehensive Guide to Textile Innovations