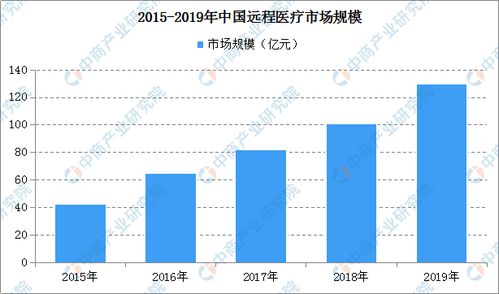
Understanding the Science Behind Yarn Dyeing Techniques
Yarn dyeing techniques have been a cornerstone of textile industry for centuries, employing a wide range of chemical and physical processes to impart color onto fibers. The science behind these methods is complex, involving the interaction between dye molecules and the natural or synthetic fibers, as well as the application of heat and pressure to facilitate penetration and fixation of color.,The choice of dye depends on the desired shade and intensity of the color, as well as the type of fiber being used. Dyes are typically categorized based on their molecular structure, with acidic and basic dyes being the most common types. Acid dyes are more effective at dissolving in cellulosic materials, while basic dyes are better suited for wool and silk.,The dyeing process itself involves several steps, including dispersion, fixation, and washing to remove any excess dye. The dispersion step involves mixing the dye with water and other additives to create a homogeneous solution. The dye then penetrates the fiber through various mechanisms, such as diffusion or electrostatic attraction.,The fixation step involves applying heat and pressure to the dyed fabric, which causes the dye to bond to the fiber and become permanently embedded. This process can be done using various techniques, including pad-batch, pad-steam, and machine-dyeing.,In conclusion, yarn dyeing techniques involve a complex interplay of chemistry and engineering principles, from the selection of dyes to the application of heat and pressure to achieve optimal color coverage and stability. By understanding these processes, designers and manufacturers can optimize dyeing results and improve the overall quality and performance of their products.
Introduction to Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing is a textile finishing process that involves applying colorants to yarn, creating vibrant fabrics with unique patterns and shades. This technique is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic appeal of clothing, upholstery, and other textile products. In this article, we will explore the principles behind yarn dyeing, including the basic concepts of dyeing and the various techniques used in practice. We will also discuss some common challenges faced during dyeing and how to overcome them, as well as provide an example of a successful yarn dyeing project.
Basic Concepts of Yarn Dyeing
Before delving into the details of yarn dyeing, it's essential to understand the basic principles involved. Yarn dyeing typically involves two main steps: pre-treatment and dyeing. Pre-treatment refers to any chemical or mechanical processes applied to the yarn before dyeing to achieve optimal results. These processes can include washing, scouring, softening, and even bleaching if necessary. The dyeing step involves applying dyes to the yarn, which are then either fixed or washed off to create the desired color.
There are several types of dyes used in yarn dyeing, each with its own characteristics and limitations. Some common dyes include direct, reactive, and acid dyes. Direct dyes are non-reactive and do not require a separate fixation step, making them faster and more cost-effective. Reactive dyes, on the other hand, react with the fiber to form a stable color, but they may require additional treatment steps to ensure uniformity. Acid dyes are also non-reactive and produce vibrant colors, but they can be difficult to remove from the yarn without damaging it.
Common Challenges in Yarn Dyeing
Despite the many benefits of yarn dyeing, there are several challenges that can arise during the process. One major issue is color bleeding, where the dye transfers from the yarn to adjacent areas such as the backing or seam. This can result in uneven color coverage and poor appearance. Another challenge is the risk of shrinkage or warping during the dyeing process, which can cause the yarn to become shorter or more prone to twisting. Finally, maintaining consistent dye levels and avoiding over-dyeing can be challenging, especially when working with complex designs or patterns.
To overcome these challenges, manufacturers often use specialized equipment and techniques such as controlled heating, vacuuming, and precise dye application. They also implement quality control measures, including testing samples before full production runs and monitoring dyeing conditions closely throughout the process. By addressing these challenges head-on, manufacturers can achieve high-quality yarn dyeings that meet consumer demands and exceed industry standards.
Example of Successful Yarn Dyeing Project
One example of a successful yarn dyeing project is the creation of a luxurious cashmere sweater by a leading fashion brand. The brand approached the yarn dyeing process with meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that every aspect of the process was optimized for optimal results. They used a combination of direct and reactive dyes to achieve a rich, deep shade that perfectly complemented the cashmere fiber.
To address potential color bleeding issues, the brand employed a specialized dye bath that contained additives designed to minimize contact between the dye and the yarn's natural oils. Additionally, they implemented a thorough rinse cycle to ensure that any excess dye was removed before the yarn was ready for garment construction. To prevent shrinkage or warping, the brand used a low-temperature dye bath and monitored temperature and pressure carefully throughout the dyeing process.
Finally, to maintain consistency in dye levels and avoid over-dyeing, the brand employed a dedicated dye mixer that allowed for precise adjustments in dye concentration. They also conducted regular quality checks on the finished yarn and worked closely with their dye supplier to ensure that all dyes met their specifications.
The result of this meticulous approach was a stunning cashmere sweater that showcased the brand's commitment to high-quality finishes. The garment was praised for its luxurious feel and vibrant color, further solidifying the brand's reputation for excellence in the textile industry.
Conclusion
Yarn dyeing is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution to achieve high-quality results. By understanding the basic concepts of dyeing and addressing common challenges, manufacturers can successfully apply dyes to yarn to create beautiful fabrics that meet consumer demands. The success of a yarn dyeing project like the cashmere sweater showcased by the leading fashion brand serves as a testament to the importance of meticulous attention to detail and innovative solutions in this field.
纺织品经轴染色是一种常见的纺织工艺,其原理涉及多个步骤和操作要点,本文将通过图表和案例说明,详细解释纺织品经轴染色过程中的原理,帮助读者更好地理解。
纺织品经轴染色原理图解
原料准备
在纺织品经轴染色过程中,首先需要准备一系列原料,包括纤维原料、染料、染色剂等,这些原料需要符合染色工艺的要求,以确保染色效果和质量。
染色过程
(1)预处理:对纤维原料进行预处理,包括清洗、软化等操作,以提高染色效果。
(2)染色轴设置:根据织物的类型和染色要求,设置合适的染色轴,染色轴需要具有一定的旋转能力和张力控制。
(3)染色操作:在染色轴上进行染料加入和染色剂的搅拌混合,染料与纤维原料充分接触,染料在纤维原料中扩散和渗透,染色剂在纤维原料中产生化学反应,使纤维原料着色。
关键步骤解析
(1)纤维与染料的接触:这是染色过程中的关键步骤之一,纤维与染料需要充分接触,以确保染料能够均匀地分布在纤维中。
(2)温度控制:染色过程中需要控制好温度,以避免染料过度蒸发或温度过高导致染料分解或变色。
(3)张力控制:染色过程中需要保持一定的张力,以防止染色过程中出现气泡或杂质,张力也是控制染料扩散和渗透的重要因素。
案例说明
(1)案例一:丝绸织物的染色过程
在丝绸织物的染色过程中,首先需要对丝绸织物进行预处理,清洗干净,设置合适的染色轴,将适量的染料加入染色轴中,进行搅拌混合,在染色过程中,需要控制好温度和张力,确保染料能够均匀地分布在纤维中,经过染色处理后,丝绸织物呈现出鲜艳的色彩。
(2)案例二:棉布织物的染色过程
棉布织物的染色过程与丝绸织物类似,但具体操作步骤可能会有所不同,在棉布织物的染色过程中,同样需要准备一系列原料,包括棉布原料、染料、染色剂等,还需要注意染料的加入量、温度控制以及张力控制等因素,通过合理的操作步骤和注意事项,可以保证染色效果和质量。
补充说明
在纺织品经轴染色过程中,还需要注意一些细节问题,染料的种类和浓度需要根据织物的类型和要求进行选择;染料的加入量需要适量控制,避免过多或过少;还需要注意染料的保存和使用方法,以确保染色效果和质量,还需要注意染色的环境条件,如温度、湿度、通风等条件也需要符合染色的要求。
纺织品经轴染色是一种常见的纺织工艺,其原理涉及多个步骤和操作要点,通过本文的介绍和分析,读者可以更好地了解纺织品经轴染色过程中的原理和注意事项,在实际操作中,还需要注意细节问题和技术要点,以确保染色效果和质量。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Understanding the Tax Burden on Textiles Exported from Australia
Global Trade in Fashion Textiles:An Overview of Key Markets and Industries
The Magic of Small Stone Textiles in Fashion Advertising Video