Textile Fiber Particle Size Testing:A Comprehensive Guide
In this comprehensive guide on textile fiber particle size testing, we will delve into the various methods and techniques used to measure the size of textile fibers. The first step in this process is to select the appropriate testing method based on the type of textile fiber being tested. This can range from simple visual inspection to more complex laboratory tests that require specialized equipment and expertise. Once the method has been selected, the next step is to collect samples of the textile fibers in question. These samples should be representative of the entire population of fibers being tested, and they should be carefully handled to avoid contamination or damage during the testing process. After obtaining the samples, the next step is to analyze them using a variety of techniques, including microscopic examination, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). These techniques allow for a detailed analysis of the size and shape of the fibers, as well as any irregularities or defects that may be present. Finally, the results of the testing are interpreted and reported in a clear and concise manner, providing both technical and practical information to those involved in the textile industry. Overall, this guide provides a thorough overview of the various methods and techniques used for textile fiber particle size testing, helping researchers and practitioners alike to accurately assess the quality and performance of their materials.
Introduction: Textile fiber particle size testing is an essential quality control measure for assessing the uniformity and cleanliness of textile materials. The process involves measuring the size of individual fibers or particles that may be present in the fabric, either naturally occurring or introduced during manufacturing. This information is crucial for ensuring product consistency, enhancing appearance, and reducing potential defects such as pilling or irritation. In this guide, we will explore the various methods used for particle size testing, including their applications, advantages, and limitations. Additionally, we will provide a case study to illustrate how these tests can impact the end-use performance of a textile product.
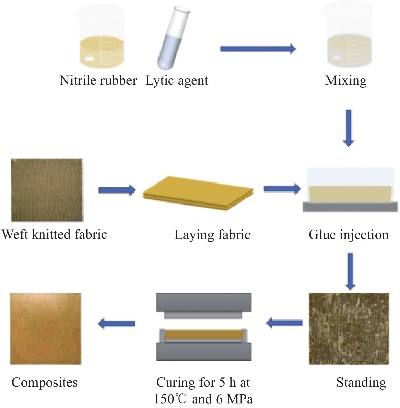
Methodology: Textile particle size testing can be performed using several techniques, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Here are some commonly used methods:
-
Sieving Tests: A sieving test involves passing a sample through a series of screens with different mesh sizes. The weight of the material falling on each screen is recorded, allowing for the calculation of the percentage of fibers larger than a given size. This method is simple but can be time-consuming and subject to human error.
-
Mechanical Tests: These involve physically crushing or rubbing the sample against a surface to remove particles. The resulting residue is then weighed to determine the size of the remaining particles. While mechanical tests are less time-consuming than sieving tests, they can damage fragile samples and require specialized equipment.
-
Light Transmission Tests: This technique uses a light source to illuminate the sample and measure the amount of light that passes through it. By comparing the transmission rate with a reference standard, the size of the particles can be estimated. This method is fast and non-destructive, making it ideal for large-scale production.
-
Microscopy: Using a microscope, researchers can visually examine the sample under high magnification. This allows for the identification of individual fibers and their size distribution. However, microscopy requires specialized equipment and expertise, and it is not suitable for routine quality control.
Applications: The choice of particle size testing method depends on the specific requirements of the textile industry. For example, if a garment manufacturer wants to ensure that their clothing does not pill or cause discomfort, they may opt for a sieving test that measures the percentage of larger particles. On the other hand, if a textile company is concerned about environmental sustainability, they may choose a method that minimizes waste and preserves natural resources.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Each method has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. For example, sieving tests are quick and easy to perform, but they can be affected by human error and require specialized equipment. Mechanical tests are more accurate but can damage fragile samples and require specialized training. Light transmission tests are fast and non-destructive but may not be suitable for all types of textile samples. Microscopy is highly accurate but requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Case Study: Consider a textile company that produces high-end fashionwear. To meet the demands of consumers who value sustainability and ethical practices, the company decided to implement a particle size testing program that focused on minimizing the use of synthetic materials. They chose a combination of sieving tests and microscopies to evaluate the fabric's fiber composition and size distribution.
The company found that while the majority of the fabric was composed of natural fibers, there were small amounts of synthetic materials present. These synthetic particles were too small to detect with traditional sieving tests, but they could be seen clearly under a microscope. As a result, the company made adjustments to their production process to reduce the use of synthetic materials and improved their overall sustainability rating.
Conclusion: Textile particle size testing is an essential tool for ensuring product quality and meeting consumer expectations. By understanding the different methods available and their respective advantages and disadvantages, textile manufacturers can optimize their testing programs to achieve the best results. Additionally, incorporating sustainable practices into their production processes can lead to long-term success and positive brand reputation.
大家好,今天我们将围绕纺织品毛羽测试这一主题展开讨论,毛羽是纺织品中常见的问题,对于纺织品的品质和性能有着至关重要的影响,了解毛羽测试的方法和标准对于确保纺织品的质量至关重要,下面我们将通过英文案例和表格详细介绍纺织品毛羽测试的相关内容。
毛羽测试的重要性
毛羽测试是纺织品质量检测的重要环节,它可以帮助我们了解纺织品在生产过程中的质量状况,及时发现并解决潜在问题,毛羽测试的结果也可以作为纺织品性能评估的重要依据。
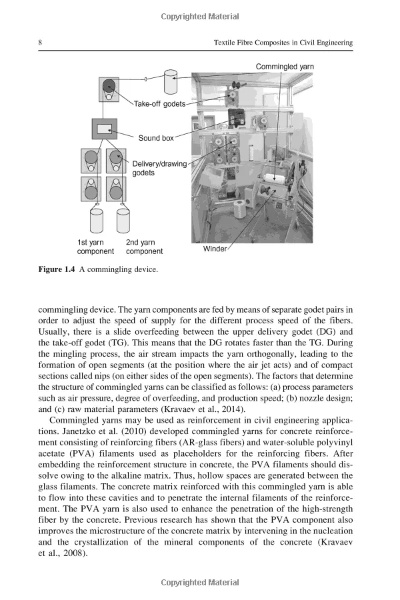
毛羽测试的方法和标准
方法:
(1)静态法:通过测量纺织品在静止状态下的毛羽长度和密度,评估纺织品的毛羽状况。 (2)动态法:通过测量纺织品在动态状态下的毛羽变化情况,评估纺织品的抗起球性能。
标准:
(1)静态法标准:根据国际标准ISO 16699-1,毛羽长度应小于一定数值,以保证纺织品具有良好的抗起球性能。 (2)动态法标准:根据实际生产需求和纺织品性能要求,制定相应的动态法测试标准。
案例分析
某品牌纺织品毛羽测试报告
某品牌在生产过程中发现其纺织品存在毛羽问题,经过检测发现其主要原因是生产过程中的某些环节出现了问题,针对这一问题,该品牌采取了相应的措施进行了改进,并成功解决了毛羽问题,通过毛羽测试,该品牌得到了满意的检测结果,证明其纺织品具有良好的抗起球性能。
毛羽测试的实际应用案例
近年来,随着人们对纺织品品质要求的提高,毛羽测试在纺织品生产中的应用越来越广泛,一些高端服装品牌在生产过程中采用了先进的毛羽测试设备和技术,确保了纺织品的品质和性能,一些纺织行业协会也制定了相应的毛羽测试标准和规范,为纺织品的生产和质量控制提供了有力的保障。
表格说明
以下是关于纺织品毛羽测试的表格说明:
| 项目 | 描述 | 示例数据 |
|---|---|---|
| 方法 | 静态法、动态法 | 根据实际需求选择合适的测试方法 |
| 标准 | 毛羽长度、密度等指标 | 根据国际标准或行业标准制定相应的标准 |
| 重要性 | 确保纺织品质量、性能评估 | 对于纺织品的品质和性能至关重要 |
| 应用领域 | 服装、家纺等 | 在服装、家纺等领域的生产和质量控制中广泛应用 |
纺织品毛羽测试是确保纺织品质量的重要环节,通过了解毛羽测试的方法和标准,我们可以更好地了解纺织品在生产过程中的质量状况,及时发现并解决潜在问题,在实际应用中,我们也需要根据实际需求和纺织品性能要求制定相应的测试标准和规范,希望本文的内容能够帮助大家更好地了解纺织品毛羽测试的相关知识。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:



