The Fabric of Future:The Impact and Innovation of Textile Waste Management
"The Fabric of Future: The Impact and Innovation of Textile Waste Management",In the realm of sustainable development, textile waste management has emerged as a critical challenge. This paper explores the fabric of future, examining the impact and innovation in this field. The paper highlights the growing significance of textile waste, which is not only a significant contributor to environmental pollution but also a significant source of economic revenue for many countries.,The paper discusses the various methods used to manage textile waste, including recycling, composting, and reusing. It also examines the challenges faced by these methods, such as the lack of infrastructure, low efficiency, and high costs. However, the paper also highlights some innovative solutions being developed, such as the use of biodegradable materials and the integration of technology into the process.,The paper concludes by emphasizing the importance of investing in textile waste management, both for environmental and economic reasons. It argues that by adopting innovative solutions and developing infrastructure, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and our planet.
Introduction: The textile industry, with its vast array of fabrics and materials, has been a pillar of human civilization for centuries. However, as the demand for these products continues to surge, so too does the volume of textile waste that accumulates. This challenge not only poses environmental concerns but also presents opportunities for innovation in waste management. In this article, we will explore the various facets of textile waste management, highlighting the importance of responsible practices and exploring potential solutions.
Textile Waste Generation: Textile waste is generated through various processes, including production, repair, and reuse. The production process involves the use of synthetic fibers such as polyester, acrylic, and nylon, which are difficult to break down and can take hundreds of years to decompose. Retailers generate textile waste by discarding used clothing, while repair shops often end up with scraps from old garments.
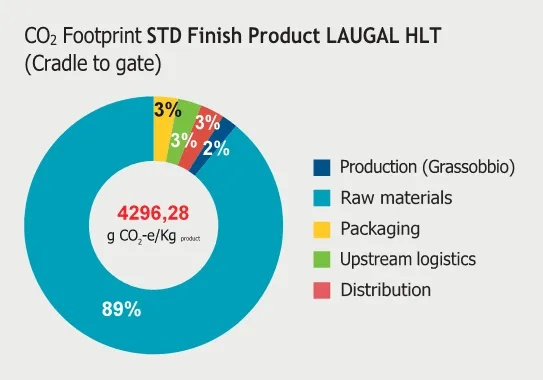
Environmental Impact: Textile waste poses significant environmental challenges, including pollution, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, the production of synthetic fibers releases toxic chemicals into the environment during the manufacturing process, leading to water pollution and harm to wildlife. Additionally, textile waste requires large amounts of energy to be transported and processed, contributing to climate change.
Innovation in Textile Waste Management: To address these issues, innovative solutions are being developed worldwide. One approach is the use of circular economy principles, where textile waste is transformed into new products or resources. For example, textile scraps can be turned into carpet fibers, yarns, or even biodegradable plastics. Another strategy is the development of advanced technologies for textile recycling, such as mechanical recycling machines that separate different types of fibers and convert them into usable materials.
Case Study: One company that has made significant strides in textile waste management is Patagonia. The company's commitment to sustainability extends beyond just reducing their own environmental impact; they also aim to reduce the amount of textile waste generated in their supply chain. Patagonia uses a system called "Renew" that allows customers to choose between two options for their clothing: a sustainable option that includes recycled materials and a traditional option that uses organic cotton. The company's success in this area is due in part to their strong brand identity and marketing efforts that emphasize their commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion: The textile industry faces numerous challenges related to waste generation, but there are also opportunities for innovation and growth. By adopting circular economy principles and investing in advanced technologies, companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while creating new revenue streams. As consumers become more aware of the impact of their purchasing decisions, it is essential that businesses prioritize responsible practices and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. The future of textile waste management lies in finding innovative solutions that balance economic growth with environmental responsibility.
随着全球纺织业的快速发展,纺织品废料问题日益凸显,为了更好地处理纺织品废料,我们成立了“纺织品废料网”,这个网络汇集了各种废旧纺织品资源,为纺织品的回收、再利用和资源化提供了有效的平台。
纺织品废料种类与处理方法
废旧纺织品种类
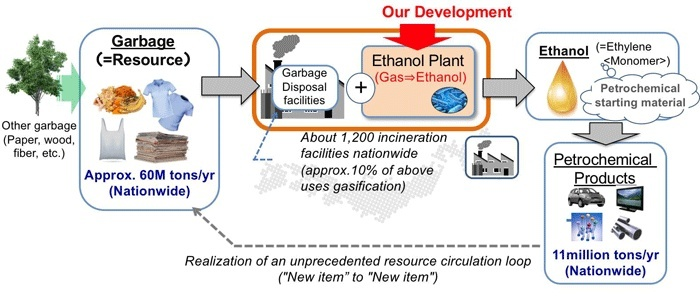
纺织品废料主要包括旧衣物、旧纺织品面料、旧纤维制品等,这些废料主要来源于生产过程中的边角料、残次品以及废弃纺织品等。
处理方法
对于废旧纺织品的处理,我们采用了多种方法,通过专业的回收机构进行分类和回收,利用化学处理、物理处理等方式进行再生利用,还有一部分废旧纺织品通过艺术再利用的方式转化为艺术品或工艺品。
案例分析
以某知名服装品牌为例,其纺织品废料处理过程如下:
回收渠道
该品牌设立了专门的回收站点,收集消费者退回的旧衣物和纺织品面料,与当地的再生资源回收企业合作,将废旧纺织品送往专业的再生利用工厂进行处理。
处理过程

在处理过程中,回收站点的工作人员对废旧纺织品进行分类和检测,确保其符合再生利用的标准,经过化学处理、物理处理等方式,将废旧纺织品转化为新的面料、纤维制品等,该品牌还注重废旧纺织品的艺术再利用,将其转化为艺术品或工艺品,提升产品的附加值。
网络运作与优势
网络运作模式
“纺织品废料网”通过建立完善的回收体系、提供专业的回收服务、开展广泛的宣传推广等方式运作,与政府、企业、研究机构等多方合作,共同推动纺织品的循环利用和资源化。
网络优势
网络汇集了各种废旧纺织品资源,为纺织品的回收提供了丰富的资源,网络通过专业的回收和处理服务,提高了废旧纺织品的利用率和再利用率,网络还注重环保和可持续发展,推动纺织业的绿色发展,网络通过宣传推广和合作共赢的方式,提高了品牌的社会责任感和公众认可度。
随着全球纺织业的快速发展和环保意识的提高,纺织品废料处理和网络化运作将成为未来纺织业的重要趋势。“纺织品废料网”将继续发挥其作用,推动纺织品的循环利用和资源化,为环保事业做出更大的贡献,网络还将积极探索新的处理方式和资源化途径,推动纺织业的绿色发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Exploring the Future of Textiles:A Comprehensive Analysis of Haian Textiles



