Understanding the Chemical Classification of Textiles
This study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the chemical classification of textiles. Textiles can be classified based on their composition, structure, and functional properties. The chemical composition of textiles includes natural fibers such as cotton, wool, silk, and linen, as well as synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic. These fibers are then woven or knitted into fabrics that are further processed to create various types of textiles, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial materials. The chemical classification of textiles is important for understanding their properties, such as strength, durability, and comfort. For example, natural fibers like cotton and wool have unique chemical properties that make them ideal for certain applications. Additionally, the use of chemicals during the production process can affect the chemical composition of textiles and ultimately their performance. Overall, this study provides a detailed overview of the chemical classification of textiles, highlighting the importance of understanding their composition and function in order to optimize their use and performance.
In the world of textiles, there is a vast array of materials used in creating fabrics that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. From the basic cotton to the luxurious silk, each material has its unique chemical composition that determines its properties. In this article, we will explore the various categories of textile chemicals and how they impact the final product. Let's dive into the world of textile chemicals and their classification!
Natural Fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, linen, wool, and silk are derived from plants or animals. They have unique chemical structures that give them their distinct properties. For example, cotton is a cellulose-based material that absorbs water and dries quickly, making it ideal for clothing. Linen, on the other hand, has a higher degree of strength and durability due to its protein content. Wool, another natural fiber, is softer and warmer than synthetic fibers but requires more care to maintain its quality. Silk, with its lustrous texture and high tensile strength, is prized for its beauty and elegance.
Synthetic Fibers
Synthetic fibers, on the other hand, are man-made and are made by combining chemicals to create new materials. These fibers are often cheaper and easier to produce than natural fibers, making them popular in industries such as apparel and home textiles. Some common synthetic fibers include polyester, nylon, and acrylic. Polyester is known for its strong durability and ability to resist stains, while nylon is lightweight and breathable. Acrylic is a blend of two different types of polymers that provides good flexibility and moisture absorption.
Cotton Dyestuffs
Cotton dyestuffs play a crucial role in the dyeing process of cotton fabrics. These substances help bind the dye molecules to the fibers, ensuring even coverage and preventing bleeding. Common cotton dyestuffs include chlorine, sodium carbonate, and potassium permanganate. Chlorine is commonly used for fast dyeing and bright colors, while sodium carbonate is preferred for producing softer, more natural-looking fabrics. Potassium permanganate is used for dark colors and can be toxic if not handled properly.
Finishing Agents
Finishing agents are essential for enhancing the appearance of textiles. These chemicals can be applied to fabrics before or after dyeing to add shine, smoothness, and color stability. Examples of finishing agents include waxes, resins, and pigments. Waxes provide gloss and luster, while resins enhance the bond between fibers and dye. Pigments add color and can be used alone or in combination with other agents to achieve specific effects.
Latex
Latex is a type of latex paint that is commonly used in the production of carpets and upholstery. It is a mixture of natural rubber latex and water, which gives it excellent elasticity and resistance to wear and tear. Latex also provides a soft feel underfoot and is highly resistant to mold and mildew. However, latex is not biodegradable and can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Case Study: The Rise of Recycled Textiles
In recent years, the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly textiles has increased significantly. This trend has led to the rise of recycled textiles, which are made from old clothes and other discarded materials. By using recycled materials, manufacturers can reduce waste and save resources without compromising on quality. For example, a company may use leftover fabric scraps from previous seasons to create new garments. This not only reduces the amount of waste generated but also helps to reduce the environmental impact of textile production.
In conclusion, understanding the chemical classification of textiles is crucial for anyone looking to purchase high-quality products. By exploring the different categories of textile chemicals, consumers can make informed decisions about the materials used in their clothing and home textiles. Whether you're looking for natural fibers like cotton or synthetic fibers like polyester, there's a wide range of options available to suit your needs. So why not explore the world of textile chemicals today? You might be surprised at what you find!
在纺织品的大家族中,根据其化学成分和性质,我们可以将其进行多种分类,本篇文章将详细介绍纺织品化学分类的相关知识,并结合实际案例进行说明。
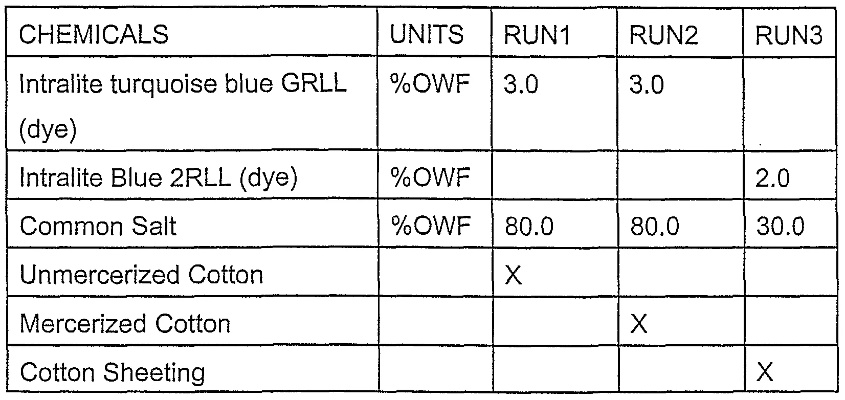
纺织品化学分类概述
-
天然纤维:天然纤维是指由自然界中直接获取的纤维,如棉花、羊毛、麻等,这些纤维具有天然的化学组成和结构,因此可以根据其化学性质进行分类。
-
合成纤维:合成纤维是通过化学合成方法制备的纤维,具有优良的性能和广泛的应用领域,根据其化学组成和结构,可以将其分为聚酯纤维、聚酰胺纤维、聚丙烯纤维等。
-
纺织材料的分类依据:纺织材料的化学分类主要依据其化学成分、物理性能和用途,棉织物可以根据其纤维类型分为纯棉、混纺等;丝绸织物则因其独特的化学组成和物理性能而具有较高的档次。
纺织品化学分类案例说明
天然纤维案例:棉花
棉花是一种天然纤维,其化学组成主要是纤维素和少量的其他化合物,棉花织物具有吸湿性好、透气性强、柔软舒适等特点,广泛应用于服装、家居用品等领域,根据其化学性质,可以将棉花织物分为纯棉织物和混纺织物。
纯棉织物是由天然棉花纤维经过纺织加工而成,具有天然的纤维素成分和良好的吸湿性,在纺织过程中,可以通过添加其他化学物质来改善其性能,如染色、印花等,纯棉织物还具有环保、可降解等优点,符合现代人们对环保的需求。
合成纤维案例:聚酯纤维
聚酯纤维是一种合成纤维,其化学组成主要是聚酯分子,聚酯纤维具有高强度、高弹性、耐腐蚀等优点,广泛应用于服装、家居用品等领域,根据其化学性质,可以将聚酯纤维分为不同的种类,如涤纶、锦纶等。
涤纶是一种常用的合成纤维,具有较高的强度和耐磨性,在纺织过程中,可以通过添加其他化学物质来改善其染色性能和柔软性,涤纶还具有较好的抗皱性和抗紫外线性能,适用于各种服装面料。
纺织品化学分类的具体应用
纺织品化学分类的应用广泛且多样,在服装领域,根据不同的化学性质和用途,可以制作出各种款式和风格的服装;在家居用品领域,纺织品可以用于制作床单、毛巾、地毯等家居用品;在工业领域,纺织品也可以用于制作过滤材料、绝缘材料等。
纺织品化学分类是根据其化学成分、物理性能和用途进行分类的,根据不同的纺织材料和用途,我们可以将其进行多种分类,在实际应用中,纺织品化学分类的应用广泛且多样,可以满足不同领域的需求,随着科技的不断进步和应用领域的不断扩大,纺织品化学分类也将不断发展和创新。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Top Ten Textile Import Dyeing Agents in the Chinese Market
The Dynamics of Sustainable Fashion:An Exploration into Lichuang Textile



