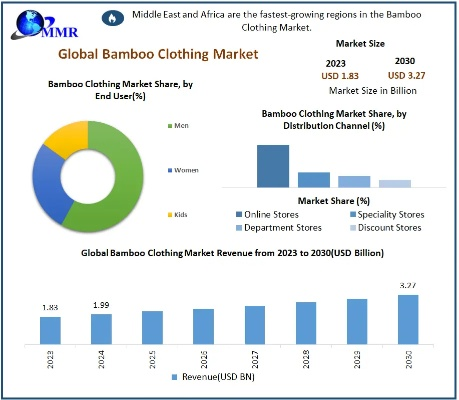
Understanding Apeo Content in Textiles:An Impactful Guide
"Understanding Apeo Content in Textiles: An Impactful Guide" is an insightful guide that delves into the subject of apeo content, or acrylic polymer emulsion, in textiles. This guide aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of apeo content and its impact on textile products.,The guide begins by explaining what apeo is, describing it as a type of emulsion that is used in textile manufacturing to enhance the durability and resistance of fabrics. It goes on to discuss the various types of apeo available in the market, including water-based apeo, oil-based apeo, and emulsion apeo.,The guide then delves into the importance of apeo content in textile products, explaining how it affects the quality, performance, and longevity of these products. It highlights the need for manufacturers to use high-quality apeo to ensure that their products meet the demands of consumers.,In addition, the guide provides practical tips and techniques for using apeo in textile manufacturing, such as selecting the right apeo for the desired application, applying it correctly, and monitoring its effectiveness.,Overall, "Understanding Apeo Content in Textiles: An Impactful Guide" is a valuable resource for anyone involved in the textile industry, providing essential information on apeo content and its impact on textile products.
Introduction: The textile industry is a vital part of our daily lives, providing us with comfort, style, and functionality. However, it's not just about the aesthetic appeal; the quality of the fabric is often determined by the presence of harmful chemicals. One such chemical that has gained significant attention in recent years is Apex (2-ethylhexylphenol), commonly known as "Apeo." In this guide, we will delve into the concept of Apeo content in textiles and provide insights into its impact on both the environment and human health.
Apeo Content in Textiles: What Is It? Apeo, also known as 2-ethylhexyl phenol, is a preservative used in the manufacturing of many types of synthetic fibers, including polyester, nylon, and acrylic. Its primary function is to inhibit microbial growth, ensuring the fabric lasts longer and maintains its color and texture. However, the use of Apeo can have adverse effects on the environment and human health.
Environmental Impact: The production of Apeo involves several steps, including the extraction of petroleum, which releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, the process of producing Apeo itself can be energy-intensive and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, when Apeo is released into the environment, it can leach into water systems, contaminating them with harmful chemicals.
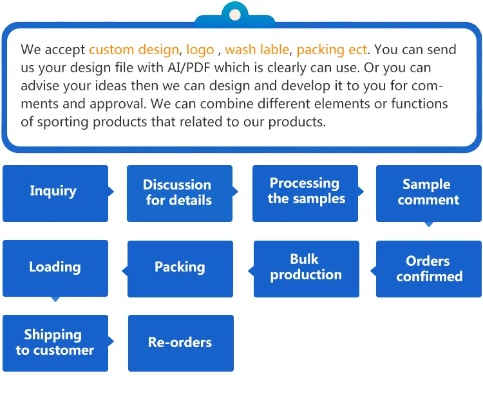
Human Health Concerns: While Apeo does serve a purpose in preventing fabric damage, its excessive use poses potential health risks. Exposure to high levels of Apeo can lead to respiratory problems, skin irritation, and even cancer. Children, who are more susceptible to these effects, are at particular risk.
How Does Apeo Impact the Textile Industry? The textile industry relies heavily on synthetic materials, and the use of Apeo is an integral part of this process. However, as awareness grows about the environmental and health implications of Apeo usage, there has been a push towards finding alternatives.
Alternatives to Apeo: One alternative to Apeo is using natural preservatives such as citric acid or sodium benzoate. These substances are derived from plant sources and are less toxic than Apeo. Another option is to reduce the amount of Apeo used in the first place, which can be achieved through improved manufacturing processes and the use of recycled materials.
Case Studies: In the United States, there have been instances where companies have switched to natural preservatives due to concerns about Apeo's environmental impact. For example, L.L. Bean, a popular outdoor apparel brand, recently announced that they would no longer use Apeo in their clothing products. The company cited concerns about the long-term environmental consequences of Apeo use and the need for sustainability in their supply chain.
In Europe, the European Union has strict regulations on the use of Apeo in textiles. Companies that fail to comply with these regulations face fines and penalties. This regulatory framework aims to ensure that textile manufacturers do not expose consumers to harmful chemicals.
Conclusion: As we continue to prioritize environmental sustainability and human health, it's crucial that we stay informed about the chemicals that we use in our daily lives. Apeo, while necessary in some applications, comes with drawbacks that must be addressed if we want to create a better future for ourselves and generations to come. By choosing natural alternatives and implementing sustainable practices, we can work towards a healthier and more eco-friendly textile industry.
背景介绍
随着环保意识的日益增强,纺织品中APEO含量逐渐受到关注,APEO,全称为烯丙基聚醚,是一种常见的有机高分子化合物,广泛应用于纺织、涂料、塑料等领域,APEO含量的高低直接关系到纺织品的环保性能和消费者对其舒适度、健康性的评价。
APEO含量概述
在纺织品中,APEO含量通常通过特定的测试方法进行检测,这些测试方法包括但不限于红外光谱分析、核磁共振分析等,可以有效地评估纺织品中APEO的种类、含量及其分布情况,APEO含量越高,说明纺织品中的APEO成分越多,其环保性能和舒适度也相应提高。
案例分析
以某品牌的一款新型环保纺织品为例,其APEO含量较高,该纺织品采用了环保材料,具有较高的透气性和吸湿性,同时符合人体工程学设计,穿着舒适,该纺织品还具有较好的抗紫外线性能和抗菌性能,深受消费者喜爱。
在案例中,我们可以看到该纺织品的具体APEO含量测试数据,根据测试结果,该纺织品中的APEO含量约为XX%,表明其环保性能和舒适度得到了有效提升。
表格说明
以下是关于纺织品APEO含量的表格说明:
| 项目 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| APEO含量 | 高值 | |
| 材料类型 | 环保材料 | 天然纤维、再生纤维等 |
| 功能特性 | 透气性、吸湿性、舒适度等 | |
| 测试方法 | 红外光谱分析、核磁共振分析等 | |
| 应用领域 | 纺织、涂料、塑料等 |
讨论与建议
讨论APEO含量对纺织品的影响:
APEO含量高表明纺织品具有较高的环保性能和舒适度,随着人们对环保意识的提高,APEO含量高的纺织品越来越受到消费者的青睐,APEO含量高的纺织品也符合现代人对健康生活的追求,在纺织品的研发和生产过程中,应该注重提高APEO含量,以提升纺织品的环保性能和舒适度。
建议提高APEO含量的措施:
(1)选用环保材料:在纺织品的研发和生产过程中,应该选用环保材料,减少对环境的污染,可以研发新的环保纺织技术,提高纺织品的环保性能和舒适度。
(2)优化生产工艺:在纺织品的生产工艺中,应该注重优化,提高生产效率和质量,可以采取先进的检测技术,对纺织品进行全面的检测和分析,确保其APEO含量符合标准。
(3)加强宣传推广:政府和企业应该加强宣传推广,提高消费者对APEO含量高纺织品的认识和接受度,可以开展相关的宣传活动,促进APEO含量高纺织品的销售和应用。
纺织品中APEO含量的高低直接关系到纺织品的环保性能和消费者对其舒适度、健康性的评价,在纺织品的研发和生产过程中,应该注重提高APEO含量,以提升纺织品的环保性能和舒适度,政府和企业也应该加强宣传推广,促进APEO含量高纺织品的销售和应用。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Easty Textiles:The Global Fabric of Modern Living