A Comprehensive Guide to Material Textiles
This comprehensive guide to material textiles offers a thorough overview of the various types of materials used in textile production. It covers topics such as fiber selection, yarn preparation, weaving techniques, and finishing processes. The guide also discusses the importance of sustainability and environmental concerns in textile production, emphasizing the need for responsible practices. Additionally, it provides insights into the history and evolution of textile technology, highlighting key milestones in the industry's development. Overall, this guide serves as an essential resource for anyone involved in the textile industry, whether they are professionals or enthusiasts.
Introduction: Textiles have been an integral part of human civilization for centuries, providing comfort, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Today, the field of material textiles is vast, encompassing a wide range of products that are designed to meet the diverse needs of modern society. In this guide, we will explore the various categories of material textiles, their characteristics, and how they are used in various industries.
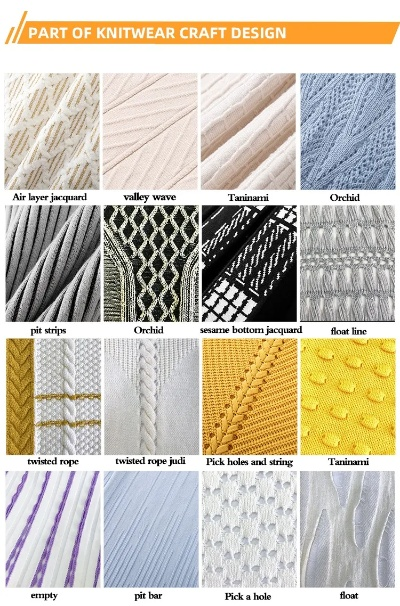
I. Textiles as Raw Materials A. Wool Wool is one of the most versatile materials used in textiles, offering warmth, softness, and breathability. It is widely used in clothing, bedding, and home furnishings. The production process involves carding, twisting, and spinning, with the final product being yarn or fabric.

B. Cotton Cotton is a popular choice for textiles due to its breathability, absorbency, and durability. It is commonly used in clothing, bed linens, and home textiles. The cotton industry is characterized by the use of natural fibers and sustainable farming practices.
C. Polyester Polyester is a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum, making it a popular alternative to natural fibers like cotton. It offers excellent wrinkle resistance, moisture management, and stain resistance. Polyester is commonly used in apparel, upholstery, and other textile applications.
D. Rayon Rayon is a type of silk-like fiber that is spun into yarn and then woven into fabric. It offers a soft, lightweight feel and a drapey texture. Rayon is commonly used in women's clothing, evening gowns, and accessories.
II. Textiles as Manufactured Products A. Clothing Clothing is a broad category that includes everything from casual wear to formal attire. It can be made from various materials, including cotton, polyester, and blends. Clothing manufacturers use advanced technology and processes to create high-quality garments that meet the demands of different industries and lifestyles.
B. Bedding Bedding is a crucial component of our daily lives, providing comfort and relaxation after a long day. It can be made from natural fibers like wool or cotton, or synthetic materials like polyester or rayon. Bedding manufacturers use techniques such as dyeing, printing, and finishing to create unique designs and patterns.
C. Home Textiles Home textiles refer to items used in the living space, such as curtains, rugs, and upholstery. They offer style, functionality, and protection for furniture and floors. Home textile manufacturers use a variety of materials and techniques to produce high-quality products that enhance the aesthetic appeal of homes.
III. Textiles as Consumer Goods A. Accessories Accessories are small, decorative items that complement clothing and home textiles. They can be made from a variety of materials, including leather, metal, and plastic. Accessory manufacturers use innovative design and manufacturing techniques to create trendy and functional products that cater to consumers' desires for fashion and functionality.
B. Decorative Textiles Decorative textiles are used in interior design to add color, pattern, and texture to spaces. They can be made from a variety of materials, including silk, velvet, and lace. Decorative textile manufacturers use a range of techniques to create unique designs and patterns that complement various decor styles and themes.
IV. Textiles as Employment Opportunity A. Textile Industry Jobs The textile industry provides a wide range of employment opportunities for individuals with diverse skill sets. From raw material processing to finished product manufacturing, there are numerous job roles available within the industry. These jobs include textile engineers, designers, weavers, spinners, and more.
B. Textile Technology Innovation The textile industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and consumer preferences. Textile technology innovations include automation, digital printing, eco-friendly manufacturing processes, and more. As a result, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can stay ahead of the curve and drive innovation within the industry.
V. Textiles as Environmental Impact A. Sustainable Textile Practices Sustainable textile practices aim to minimize environmental impact while still meeting the needs of consumers. This includes using renewable resources like bamboo and hemp, reducing water usage through efficient dyeing and finishing processes, and implementing recycling programs for waste reduction.
B. Textile Waste Management Textile waste management is a critical aspect of the textile industry's sustainability efforts. Manufacturers must adopt responsible waste management practices, including proper disposal of hazardous materials and reducing the amount of waste generated during production. Additionally, consumers can play a role in promoting sustainable textile practices by choosing products made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials.
VI. Case Studies: Successful Textile Industries A. Nike's Apparel Production Nike is a leading sportswear brand that uses innovative textile technologies to create high-performance apparel. The company's success can be attributed to its commitment to sustainability and quality manufacturing processes. Nike's apparel production relies on advanced knitting machines and dyeing techniques that ensure maximum performance and minimal environmental impact.
B. Bang & Olufsen's Bedding Production Bang & Olufsen is a luxury electronics brand that also produces high-quality bedding products. The company's success can be seen in its focus on sustainable sourcing and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Bang & Olufsen's bedding production utilizes organic cotton and recycled materials, while also incorporating sustainable packaging methods to reduce its environmental footprint.

Conclusion: Textiles are an essential part of our daily lives, offering comfort, functionality, and style. With a wide range of materials and manufacturing processes available, textiles have become an integral part of the global economy. By exploring the various categories of material textiles and understanding their characteristics and uses, we can gain insights into the future of this industry and the opportunities it presents for innovation and sustainability.
纺织品作为人类生活中不可或缺的组成部分,种类繁多,涵盖了从日常服装到特殊工艺品的各个领域,本文将围绕综合材料纺织品展开讨论,包括其涵盖的种类及其应用场景。
综合材料纺织品概述
综合材料纺织品是指采用多种材料混合、再加工而成的纺织品,这些材料可以是天然纤维、合成纤维、金属材料、塑料等,它们具有独特的性能和特点,广泛应用于服装、家居装饰、工艺品等领域。
以下是综合材料纺织品的一些主要种类及其特点:
天然纤维与合成纤维混合纺织品
天然纤维如棉、麻、丝等,具有天然、环保、舒适等优点,而合成纤维则具有轻便、耐用、易洗等优点,两者结合,可以制作出既具有天然纤维的舒适性,又具有合成纤维耐用的纺织品,纯棉与涤纶混纺的衣物既保暖又透气。
金属材料与纺织品的结合
金属材料如铜、铝等,具有独特的视觉效果和质感,它们可以与纺织面料进行巧妙地结合,制作出具有现代感和时尚感的纺织品,金属线条装饰的服装或家居用品。
塑料与纺织品的结合
塑料以其轻便、耐用、易加工等优点,在纺织品制造中也有广泛应用,它们可以与各种纺织工艺相结合,制作出各种具有独特风格的纺织品,塑料仿皮面料制成的服装,既环保又时尚。
案例说明
以纺织品为例,我们可以看到综合材料纺织品的实际应用案例,以下是一个具体的英文案例:
新型环保面料
近年来,随着环保意识的提高,新型环保面料逐渐受到市场欢迎,这种面料采用天然纤维与合成纤维的混合,同时结合了金属和塑料等材料,某公司研发的新型环保面料,采用竹纤维与聚酯纤维的结合,既环保又具有透气性,这种面料被广泛应用于服装、家居装饰等领域。
金属装饰布艺
金属装饰布艺是一种新兴的纺织品类型,它结合了金属材料的光泽和质感,以及纺织工艺的精湛工艺,某品牌推出的金属装饰窗帘,采用铜丝编织而成,具有独特的视觉效果和质感,这种窗帘不仅美观大方,而且易于清洁和维护。
表格说明
以下是关于综合材料纺织品的一些表格说明:
综合材料纺织品种类列表
| 材料种类 | 描述 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|
| 天然纤维 | 棉、麻、丝等 | 服装、家居装饰 |
| 合成纤维 | 涤纶、尼龙等 | 服装、家居用品 |
| 金属材料 | 铜、铝等 | 服装、家居装饰、工艺品 |
| 塑料 | 其他塑料材料 | 服装、家居装饰、工艺品等 |
综合材料纺织品实际应用案例示例(具体产品)
新型环保面料产品介绍(具体产品)
产品名称:新型环保面料服装 产品特点:采用天然纤维与合成纤维混合,结合金属和塑料等材料,环保且具有透气性,适用于服装领域。 产品应用场景:环保时尚服装、家居装饰等。
金属装饰窗帘产品介绍(具体产品)
产品名称:金属装饰窗帘家居用品 产品特点:采用金属材料编织而成,具有独特视觉效果和质感,适用于家居装饰领域。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article: