The Global Landscape of Textile Waste and Its Impact on the Environment
The global textile waste landscape is a significant environmental concern, with the amount of textiles generated annually reaching staggering figures. This issue has become increasingly pressing due to the extensive use of synthetic fibers in modern clothing and household products. The impact of textile waste on the environment is multifaceted, including pollution of waterways, soil, and air, as well as the depletion of natural resources. Additionally, the disposal of textile waste can lead to the release of toxic chemicals into the environment, posing a threat to both human health and wildlife. To address this issue, it is crucial to implement sustainable practices in textile production and consumption, such as using renewable materials and reducing textile waste through recycling and reuse. By taking action now, we can help mitigate the negative impacts of textile waste on the environment and ensure a healthier planet for generations to come.
Introduction: Textile waste, a significant environmental challenge, poses a formidable threat to our planet. It is estimated that textiles account for up to 10% of all municipal solid waste globally. In this talk, we will delve into the global landscape of textile waste, its sources, impacts, and potential solutions. We will also present an illustrative case study to highlight the challenges faced by textile industries in addressing their waste management responsibilities.
Global Landscape of Textile Waste: Textile waste is generated through various processes, including manufacturing, repair, and consumption. Manufacturing generates the bulk of textile waste, with synthetic materials like polyester and nylon being the most prevalent. Recycling and reusing these materials can significantly reduce textile waste. However, many textiles end up in landfills or are incinerated, releasing harmful pollutants into the environment.
Sources of Textile Waste:

- Manufacturing: This is the primary source of textile waste, accounting for about 80% of the total.
- Consumer Products: Clothes and other textiles that wear out over time become waste.
- Repair and Maintenance: Many textiles require frequent repairs, leading to increased waste.
- E-Waste: Textiles made from synthetic materials like nylon and polyester are often discarded as electronic waste.
- Industrial Processes: Textiles used in industrial settings, such as cleaning cloths and protective clothing, contribute to waste.
Impacts of Textile Waste on the Environment:
- Water Pollution: Textile waste, when disposed of improperly, can contaminate water bodies, leading to algal blooms and other ecological imbalances.
- Air Pollution: Burning textile waste releases toxic gases into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Soil Contamination: Textile waste can leach toxic chemicals into the soil, affecting plant growth and posing health risks to animals and humans.
- Biodiversity Loss: The decomposition of textile waste can lead to habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity.
Potential Solutions:
- Improved Design and Manufacturing: Encouraging the use of sustainable materials and designing products with longer lifespans can reduce textile waste generation.
- Regulations and Policies: Implementing strict regulations and policies to promote recycling and proper disposal of textile waste can help minimize its impact on the environment.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in technology can enable more efficient textile recycling and processing methods.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of textile waste management can encourage responsible behavior.
Case Study: Consider the story of Bangladesh's Textile Industry. For decades, Bangladesh was known for its thriving textile industry, producing some of the world's finest garments. However, this success came at a cost: a massive amount of textile waste accumulated in landfills, causing environmental damage and posing a threat to local ecosystems. To tackle this issue, Bangladesh implemented a comprehensive waste management plan that included innovative techniques like turning textile scraps into fuel pellets, reducing the need for landfill space. By 2020, Bangladesh had achieved a 70% reduction in textile waste, demonstrating the power of collective action and technological innovation in addressing a pressing environmental issue.
Conclusion: Textile waste management is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding its sources, impacts, and potential solutions, we can work towards a cleaner, greener future. As we move forward, let us embrace innovation, adopt responsible practices, and work together to protect our planet for generations to come.
大家好,今天我们来聊聊一个大家都可能遇到但又常常被忽视的话题——纺织品报废,随着纺织品的广泛应用,其报废处理也日益成为我们关注的焦点,让我们一起来探讨这个话题,并从中学习一些实用的技巧和经验。
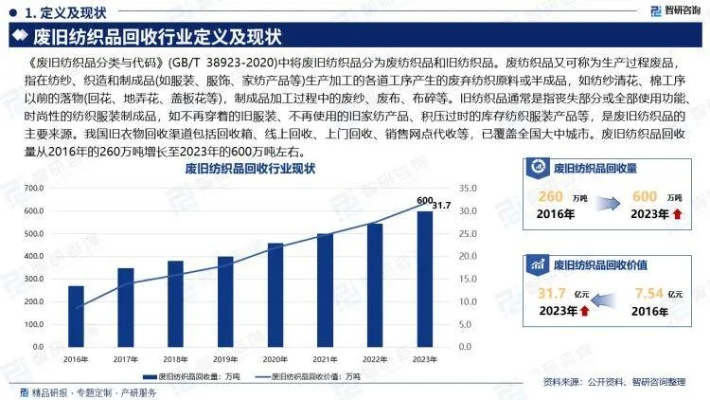
纺织品报废背景
纺织品在我们的日常生活中扮演着重要的角色,从日常衣物到工业生产中的关键材料,它们在我们的生产链中发挥着不可或缺的作用,随着纺织品的不断更新换代,其使用寿命有限,报废处理也成为了一个不可避免的问题。
纺织品报废原因及处理方式

纺织品报废的原因多种多样,包括但不限于产品质量问题、技术更新换代、市场需求变化等,在处理纺织品报废时,我们需要根据具体情况采取不同的方式。
- 直接报废处理:对于一些质量良好但寿命已到期的纺织品,我们可以选择直接报废,这通常涉及到与供应商协商处理方式,确保资源的有效利用和环保处理。
- 回收再利用:对于剩余的纺织品,我们可以采取回收再利用的方式进行处理,这不仅可以减少资源浪费,还可以降低生产成本,提高经济效益。
- 循环再造:对于一些可循环再造的纺织品,我们可以进行循环再造,将其转化为新的纺织品或材料,这不仅有利于环境保护,还可以促进可持续发展。
案例分析
下面我们将通过一个具体的案例来进一步说明纺织品报废的问题。
某纺织公司纺织品报废处理过程
某纺织公司在生产过程中发现了一批质量良好但寿命已到期的纺织品,经过与供应商协商,决定采取直接报废处理的方式,在报废过程中,公司采取了环保处理措施,确保报废资源得到有效利用,公司还积极推广循环再利用技术,将报废纺织品转化为新的纺织品或材料,实现了资源的循环利用。
纺织品报废的注意事项
在纺织品报废过程中,我们需要注意以下几点:
- 合理规划报废资源:在报废前,我们需要合理规划报废资源,确保资源的有效利用和环保处理。
- 重视产品质量和安全:在报废过程中,我们需要注重产品质量和安全,确保报废产品的质量和环保性能符合相关标准。
- 加强宣传教育:我们还需要加强宣传教育,提高公众对纺织品报废问题的认识和重视程度。
纺织品报废是一个不可忽视的问题,我们需要采取有效的措施和策略来处理纺织品报废问题,在处理过程中,我们需要注重产品质量和安全、加强环保处理、推广循环再利用技术等,我们还需要加强宣传教育,提高公众对纺织品报废问题的认识和重视程度,通过这些措施和策略的实施,我们可以更好地应对纺织品报废问题,实现资源的有效利用和环境保护。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
A Comprehensive Guide to the Price Range of Home Textiles in Jingan District
Free Textile Testing with Benefits for the Environment and Consumers