The Revolutionary Approach of Adding Nanoparticles to Fibers in Textiles
The revolutionary approach of adding nanoparticles to textile fibers is a promising innovation in the field of textile science. This technique has been shown to enhance the performance and functionality of fabrics, making them more sustainable, durable, and eco-friendly. By incorporating nanoparticles into the fibers, we can create materials that are stronger, lighter, and more resistant to wear and tear. Additionally, these nanoparticles can also improve the breathability and moisture management of the fabrics, leading to better comfort and wicking properties. The use of nanoparticles in textiles is also an effective way to reduce waste and promote circular economy principles. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of nanoparticles in textiles, opening up new possibilities for creating high-performance, eco-friendly materials for a wide range of applications.
Introduction
Nanotechnology has emerged as a game-changer in the textile industry, revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with fabrics. The integration of nanoparticles into fibers is not only a technological advancement but also a significant step towards enhancing the performance, durability, and sustainability of textiles. In this article, we will explore the concept of adding nanoparticles to fibers in textiles, including the benefits, challenges, and practical applications. We will also present an illustrative table to help visualize the various types of nanoparticles and their effects on the properties of textiles.
Benefits of Adding Nanoparticles to Fibers
-
Enhanced Durability: Nanoparticles can significantly improve the resistance of textiles against wear and tear. For example, titanium dioxide nanoparticles can increase the scratch resistance of fabrics, making them more durable and resistant to damage caused by everyday use.
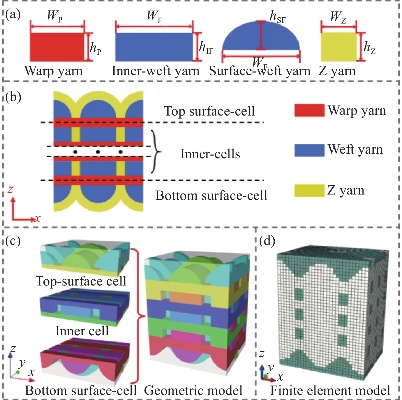
-
Improved Colorfastness: Adding nanoparticles to dyes can enhance the colorfastness of textiles, ensuring that colors remain vibrant for longer periods. This is particularly important in industries that require high levels of color consistency, such as fashion or hospitality.
-
Increased Water Repellency: Nanoparticles can be used to create hydrophobic coatings on textiles, reducing their tendency to absorb water. This is beneficial in applications where moisture control is crucial, such as in sportswear or outdoor gear.
-
Improved Air Permeability: By increasing the surface area of textiles, nanoparticles can enhance air permeability, allowing for better breathability and comfort. This is particularly useful in clothing for athletes or those working in hot environments.
-
Enhanced Light Reflectance: Titanium dioxide nanoparticles can increase the light reflectance of textiles, making them more aesthetically pleasing and visually appealing. This is especially important in industries that rely on visual appeal, such as fashion or interior design.
Challenges and Challenges
-
Environmental Impact: While nanoparticles have many benefits, they can also have negative environmental impacts. Some nanoparticles are toxic and can cause harm to ecosystems when released into the environment. Therefore, it is essential to consider the potential environmental consequences of using these materials in textiles.
-
Cost: The production of nanoparticles may be expensive, which could limit their use in textiles. Additionally, the cost of incorporating nanoparticles into existing fabrics may also be prohibitive for some businesses.
-
Regulation: There is currently no standardized regulation for the use of nanoparticles in textiles, which can make it challenging to ensure safety and compliance. It is important for stakeholders to work together to establish regulations that protect consumers and the environment.
Practical Applications
-
Sportswear: Adding nanoparticles to textiles can enhance the performance of sportswear. For example, titanium dioxide nanoparticles can improve the durability and resistance of sportswear against wear and tear, while also enhancing colorfastness and water repellency.
-
Fashion: Nanoparticles can be used to create unique textures and patterns on textiles, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. For example, adding silver nanoparticles to fabric can create a shinier and more luxurious look.
-
Hospitality: In the hospitality industry, nanoparticles can be used to create stain-resistant and moisture-wicking textiles that provide comfort and hygiene for guests.
Conclusion
Adding nanoparticles to fibers in textiles represents a significant advancement in the field of textile technology. While there are challenges and concerns surrounding the use of these materials, the potential benefits they offer in terms of durability, colorfastness, water repellency, and improved air permeability cannot be ignored. As research continues to explore the full potential of nanoparticles in textiles, we can expect to see innovative solutions that will transform the way we approach textile production and consumption.
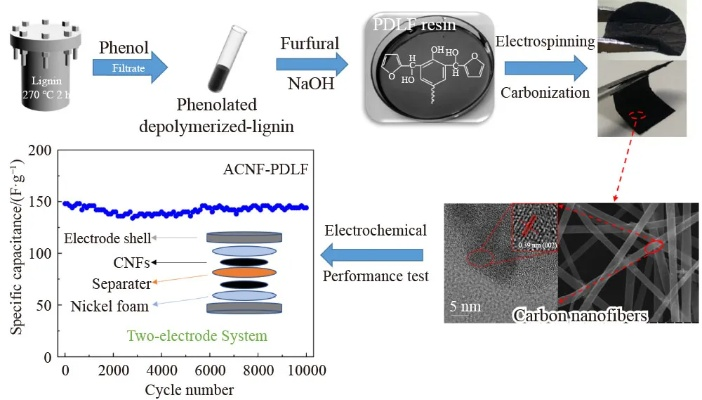
随着科技的飞速发展,纳米技术逐渐渗透到各个领域,包括化纤纺织品领域,纳米微粒的加入为化纤纺织品带来了新的可能性,不仅提升了其性能,还赋予了它们新的功能,本文将详细介绍化纤纺织品加入纳米微粒的过程及其应用案例。
纳米微粒在化纤纺织品中的作用
纳米微粒在化纤纺织品中发挥着重要作用,主要体现在以下几个方面:
- 提高纤维强度和耐磨性:纳米微粒可以增强纤维的力学性能,提高纤维的耐磨性和抗拉强度。
- 改善纤维透气性和吸湿性:纳米微粒可以改善纤维的透气性和吸湿性,提高纤维的使用舒适度。
- 增强纤维环保性:纳米微粒可以减少环境污染,提高纤维的环保性能。
纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品的工艺流程
纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品的工艺流程主要包括以下几个步骤:
- 材料准备:选择合适的纳米材料,制备出所需的纳米微粒。
- 纺丝工艺:将纳米微粒与化纤原料混合后,通过纺丝工艺制成纤维。
- 后处理:对制成的纤维进行必要的后处理,如干燥、定型等。
案例分析
以某知名化纤品牌为例,展示纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品的应用案例:
- 产品介绍:该品牌推出的新型化纤纺织品采用了先进的纳米技术,加入了特殊的纳米微粒,提高了纤维的强度和耐磨性。
- 生产过程:该品牌采用先进的纺丝工艺,将纳米微粒与化纤原料混合后制成纤维,在后处理过程中,通过特殊的工艺手段,使纤维具有更好的透气性和吸湿性。
- 应用效果:该产品广泛应用于服装、家居用品等领域,受到了消费者的热烈欢迎,其优良的性能和环保特性使其成为市场上的热销产品。
纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品的优势与挑战
纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品带来的优势包括:
- 提高纤维性能:纳米微粒可以显著提高纤维的强度、耐磨性、透气性和吸湿性等性能。
- 环保性提升:纳米微粒可以减少环境污染,符合现代环保理念。
纳米微粒加入化纤纺织品也面临一些挑战,如生产工艺的复杂性、成本问题等。
随着科技的不断发展,纳米技术将在化纤纺织品领域发挥更大的作用,我们可以期待更多的创新产品出现,为人们的生活带来更多的便利和舒适,我们也应该关注纳米技术的可持续发展问题,推动其在环保、节能等方面的发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Carbon Content of Textiles
The Advanced Textiles Factory in China:A Case Study
Preventing Textile Dyeing Issues with Strategies and Case Studies



