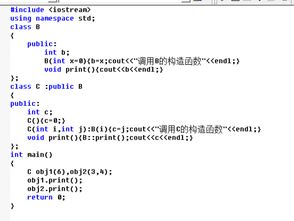
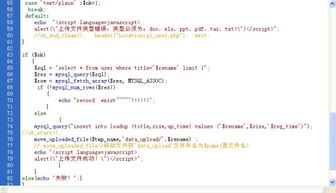
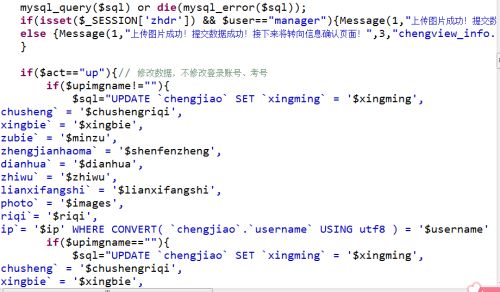
Graphical Guide to Textile Parameters
This paper presents a graphical guide to textile parameters. The guide includes various parameters such as yarn count, weave type, fabric weight, and more. It also provides information on how to measure these parameters and how they affect the quality of the textile product. Additionally, the guide includes tips on how to use these parameters in different applications, such as clothing, upholstery, and home decor. Overall, this guide is an essential resource for anyone working with textiles and wants to ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and functionality.
Introduction: Textiles are an essential part of our daily lives and play a significant role in the fashion, construction, and comfort industries. To understand how textiles function and their properties, it's crucial to have a clear understanding of the parameters that define them. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the key textile parameters that you need to know to make informed decisions when selecting or using textile products.
-
Fabric Weight Fabric weight refers to the amount of yarn used to create a fabric. It determines the thickness and softness of the fabric. The higher the weight, the thicker and denser the fabric.
-
Yarn Count Yarn count is the number of threads per square inch (or yard) of fabric. It is measured by counting the number of loops formed by the yarn as it passes over a fixed length of thread. A higher yarn count means a stronger and more durable fabric.
-
Weave Type Weave type refers to the pattern of threads crossing each other in the fabric. There are several types of weaves, including plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, and plaid weave. Each weave has its own unique characteristics and uses.
-
Denier Denier is a unit of measurement used to describe the strength of a yarn. It is based on the weight of one gram of yarn. The higher the denier, the stronger and more durable the yarn.
-
Tencel Tencel is a type of synthetic fiber that is derived from wood pulp. It is known for its breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and natural feel. Tencel is commonly used in clothing and bedding due to its antibacterial and antifungal properties.
-
Polyester Polyester is a synthetic fiber that is made from petroleum. It is known for its durability, resistance to wrinkles, and high heat resistance. Polyester is commonly used in sportswear, swimwear, and outdoor wear due to its performance properties.
-
Cotton Cotton is a natural fiber that is derived from the seeds of the cotton plant. It is known for its breathability, softness, and comfort. Cotton is commonly used in clothing, bedsheets, and home decor due to its eco-friendly and sustainable properties.
-
Lycra Lycra is a synthetic fiber that is made from polyamide. It is known for its stretchiness and recovery ability. Lycra is commonly used in athletic wear, swimwear, and undergarments due to its performance properties.
Case Study: Let's take a look at a real-life example to illustrate how these textile parameters can be used in practice.
Mr. Smith is looking for a new pair of jeans for his weekend outing. He wants to find a pair that is comfortable, durable, and stylish. He decides to visit a local store and ask the salesperson for recommendations.
The salesperson introduces Mr. Smith to a pair of jeans that are made from 100% cotton. They explain that the jeans are lightweight, breathable, and comfortable to wear. However, they also mention that they are not very durable and may wrinkle easily.
Mr. Smith is interested in finding a pair of jeans that is both comfortable and durable. He asks if there is a way to combine the benefits of cotton with the strength of denim. The salesperson suggests that he try a pair of jeans made from a blend of cotton and denim.
The salesperson explains that the blended jeans have a higher denier than the original cotton jeans, making them stronger and more durable. They also mention that the blended jeans have a higher yarn count, which makes them more breathable and moisture-wicking.
After trying on the blended jeans, Mr. Smith is impressed with the combination of comfort and durability. He purchases the pair and enjoys wearing them for his weekend outing.
Conclusion: Understanding textile parameters is crucial when selecting or using textile products. By understanding fabric weight, yarn count, weave type, denier, tencel, polyester, cotton, lycra, and other parameters, you can make informed decisions about the quality and performance of textile products. Incorporating these parameters into your purchasing decision-making process will help you choose the right textile product for your needs.
今天我们将一起探讨纺织品参数的重要性及其讲解图解的方法,纺织品是日常生活中不可或缺的物品,其参数的准确性和合理性对于产品的质量和性能至关重要,本文将通过图表和案例分析的方式,详细讲解纺织品的主要参数及其意义。
纺织品主要参数介绍
密度
密度是衡量纺织品厚薄程度的参数,通常以克/厘米²表示,密度越高,纺织品越厚实;反之,密度越低,纺织品则相对轻薄。
密度参数图解如下:
密度参数图解(示例)
织物类型
织物类型包括纯棉、涤纶、亚麻等,每种织物都有其独特的性能和特点,纯棉织物柔软舒适,适合制作内衣和外衣;涤纶织物耐磨、抗皱,适合制作运动服装等。
织物类型参数图解如下:
织物类型参数表(示例)
纱线类型
纱线类型包括单纱、双纱等,纱线的质量直接影响到纺织品的强度和弹性,高强度的单纱适用于制作高要求的产品,如运动鞋垫等。
纱线类型参数图解如下:
纱线类型参数表(示例)
纺织品参数讲解图解案例分析
纯棉衬衫面料讲解
纯棉衬衫面料是常见的纺织品之一,其参数讲解可以如下进行:
- 密度:纯棉衬衫面料密度较高,手感柔软舒适,根据不同的工艺和配方,纯棉衬衫面料的吸湿性、透气性等性能也有所不同。
- 织物类型:纯棉织物因其天然纤维的特点,具有吸湿性好、透气性强、柔软舒适等优点,适合制作夏季轻薄透气服装。
- 纱线类型:纯棉衬衫面料的纱线质量主要取决于纺纱工艺和原料质量,优质的纯棉纱线可以提高面料的强度和弹性,使其更加耐用。
羊毛混纺毛衣讲解
羊毛混纺毛衣是一种常见的纺织品,其参数讲解可以如下进行:
- 密度:羊毛混纺毛衣的密度较高,手感柔软舒适,根据不同的羊毛含量和工艺,羊毛混纺毛衣的保暖性能、吸湿性等也有所不同。
- 织物类型:羊毛混纺织物的特点是兼具羊毛的柔软性和化纤的强度和耐磨性,适合制作保暖性能要求较高的冬季服装。
- 纱线类型:羊毛混纺毛衣的纱线质量主要取决于所用化纤的种类和质量,优质的化纤可以增加毛衣的强度和耐磨性,使其更加耐用,合理的工艺也可以提高纱线的柔软性和舒适性。
纺织品参数讲解要点总结
纺织品参数是衡量纺织品质量和性能的重要指标,其讲解需要结合图表和案例进行分析,在讲解过程中,需要注意以下几点:
- 准确标注参数名称和数值,以便读者了解纺织品的主要参数及其意义。
- 通过图表和案例分析,帮助读者更好地理解纺织品参数的重要性及其应用场景。
- 在讲解过程中,需要注意结合纺织品的实际性能和应用场景,进行有针对性的讲解。
- 随着纺织技术的不断发展,新的纺织品参数和性能指标不断涌现,需要不断更新和完善讲解内容。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Fabric of Future:Embracing the 21st Century Textile Revolution
The Global Trends and Influence of British Textile Sales in India
The Fabric of Education:Defining the Materiality of School Bags
The Truth About Formaldehyde in Textiles
Exploring the Evolution and Impact of Xuequan Textiles in Shaoxing,China



