The Fabric of Overproduction:An Examination of the Global Textile Industry
This paper examines the global textile industry, focusing on its overproduction problem. The overproduction of textile products has become a major issue in recent years, leading to a decrease in market demand and increased competition among manufacturers. This paper analyzes the factors that contribute to this overproduction problem, including excessive investment in production facilities, lack of innovation in product design, and weak market demand forecasting. The paper also discusses the impact of these factors on the industry's competitiveness and sustainability. Finally, the paper proposes several strategies to address the overproduction problem, including reducing investment in production facilities, increasing innovation in product design, and strengthening market demand forecasting.
Introduction: In an era where technology has revolutionized the way we live, one industry that has not kept pace is the textile sector. Despite advancements in materials and manufacturing processes, the global textile industry continues to face challenges of overproduction, leading to a surplus of goods that often go unsold or end up in landfills. This essay aims to explore the causes of textile overproduction, its impact on the environment, and how it can be addressed through sustainable practices.
Causes of Overproduction: Textile overproduction is a complex issue that stems from various factors. Firstly, there is an overcapacity in the production process, resulting in excess inventory. This can be attributed to outdated machinery, labor shortages, and a lack of demand for certain types of textile products. Secondly, there is a trend towards producing low-quality goods at lower prices, which leads to consumers purchasing more than they need, further contributing to overproduction. Thirdly, globalization has led to increased competition among manufacturers, driving down prices and encouraging overproduction as a means of gaining market share. Finally, government policies and regulations have also played a role in driving overproduction by providing subsidies for producers and imposing minimum standards that encourage mass production.
Environmental Impact: The textile industry's overproduction has significant environmental consequences. One of the most pressing issues is the waste generated during the production process. Textile scraps, dyes, and other materials are often discarded without proper disposal, leading to pollution in waterways and soil. Additionally, excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture contributes to deforestation and soil degradation. Furthermore, the textile industry is responsible for a significant amount of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly from the energy required to produce raw materials and power machinery.
Sustainable Practices: To address the issue of textile overproduction, it is essential to adopt sustainable practices. One approach is to promote circular economy principles, where products are designed to be repaired, reused, and recycled rather than discarded. This can involve designing textiles with longer lifespans, implementing recycling programs, and using eco-friendly materials. Another approach is to increase demand for high-quality textiles, which can drive innovation and reduce waste. This can be achieved by promoting ethical consumption practices, such as fair trade and sustainable sourcing, and supporting small-scale producers who prioritize sustainability. Finally, governments and businesses can work together to implement policies and regulations that encourage sustainable practices within the textile industry. This could include setting targets for reducing carbon emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and providing incentives for producers who adopt sustainable practices.
Case Study: One example of a successful initiative that addresses textile overproduction is the Fair Trade Certified program. This program ensures that textile producers receive fair wages and working conditions, while also ensuring that they use sustainable practices in their production processes. By doing so, they can produce higher-quality goods that meet consumer demand without compromising the environment. Another example is the use of recycled materials in the production of textiles. Many companies are now incorporating recycled polyester into their fabrics, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Conclusion: In conclusion, textile overproduction is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach to address. While technological advancements have improved our ability to produce textiles, the industry still faces challenges related to overproduction, environmental impact, and sustainability. By promoting circular economy principles, increasing demand for high-quality textiles, and implementing sustainable practices, we can create a more sustainable future for the textile industry. As we move forward, let us remember that every step we take towards sustainability will contribute to a brighter tomorrow for our planet and its people.
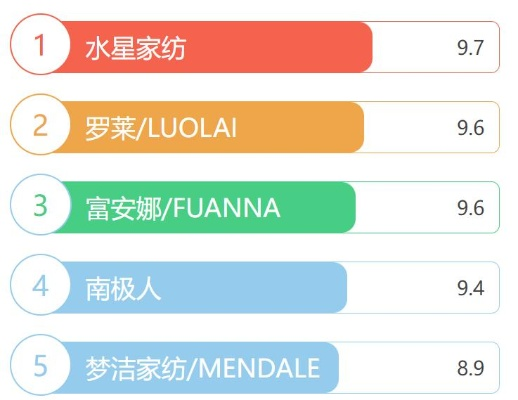
背景介绍
纺织品市场出现了一定程度的过剩现象,这主要是由于全球纺织品的生产与消费需求增长过快所致,随着人们生活水平的提高,对纺织品的需求日益多样化,但同时也导致了部分地区的纺织品库存积压。
过剩现象分析
-
纺织品种类繁多,需求量大增 随着科技的进步和人们生活方式的改变,纺织品种类繁多,从服装、家居装饰到户外用品等都有涉及,纺织品的需求量大幅增加。

-
地区差异明显,库存积压问题突出 由于不同地区的经济发展水平和纺织品的生产能力存在差异,纺织品过剩现象在不同地区呈现出不同的特点,某些地区的服装生产能力过剩,导致纺织品库存积压严重。
案例说明
为了更好地理解纺织品过剩现象,我们可以结合一些具体的案例进行分析。
某地区纺织品过剩情况
该地区近年来纺织品的生产能力持续增加,导致纺织品库存积压严重,许多商家和消费者都面临着纺织品过剩的问题,一些商家为了应对库存积压,不得不降价销售或寻找新的销售渠道,消费者则因为价格波动和供应过剩而感到困扰。
纺织品过剩对消费者的影响
纺织品过剩对消费者的影响是多方面的,消费者需要花费更多的金钱来购买相同或相似类型的纺织品,增加了他们的经济负担,由于市场供应过剩,部分纺织品的质量可能受到影响,消费者需要更加谨慎选择,纺织品过剩还可能导致一些不良商家利用市场机会进行欺诈行为,给消费者带来不必要的损失。
应对措施

针对纺织品过剩现象,我们可以采取以下措施。
-
优化生产与销售策略 政府和企业应加强合作,优化纺织品的生产与销售策略,提高纺织品的生产效率和质量,减少库存积压,加强市场监管,打击不良商家的欺诈行为。
-
促进循环利用和再利用 政府和企业可以鼓励循环利用和再利用纺织品,减少对环境的影响,推动绿色制造和可持续发展,促进纺织品的绿色生产。
-
加强国际合作与交流 在全球范围内加强纺织品市场的交流与合作,共同应对纺织品过剩问题,通过国际合作与交流,可以引进先进的生产技术和管理经验,推动纺织品的可持续发展。
纺织品过剩现象是一个复杂的问题,需要政府、企业和社会各方的共同努力来解决,通过优化生产与销售策略、促进循环利用和再利用、加强国际合作与交流等措施,可以有效地应对纺织品过剩问题,促进纺织品的可持续发展,消费者也需要更加理性地看待市场供应过剩问题,做出明智的购买决策。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Future of Textiles:An Overview of Silverdale Textiles
The Dynamics of Sustainable Fashion:An Exploration into Lichuang Textile