The Textile Inspection Process
The Textile Inspection Process is a comprehensive and rigorous process that involves the examination of textile products for defects, inconsistencies, or flaws to ensure their quality meets standards. This process begins with an initial visual assessment of the product, followed by more detailed inspections such as measuring, weighing, and testing various aspects of the fabric. The inspection team uses specialized tools and equipment to identify any potential issues, which may include fraying, pilling, color variations, shrinkage, or other defects. Once identified, the team works to determine the cause of the defect and develop a plan to address it. This may involve reprocessing the fabric or replacing it with a new piece if necessary. Finally, the inspected textile is returned to the manufacturer for further processing or discarded if it fails to meet quality standards. Overall, the textile inspection process is critical in ensuring that products meet consumer expectations and are safe for use.
Introduction: The textile industry is a vital sector that contributes significantly to global economic growth and employment. However, as the industry becomes more competitive, it has become increasingly important for countries to ensure that their textile products meet international standards and regulations. This is where the textile inspection process comes into play. In this article, we will explore the various steps involved in the textile inspection process and provide an example of how it works.

-
Pre-inspection: Before any inspection can take place, the product must undergo a pre-inspection phase. This involves checking the product's quality and ensuring that it meets the necessary standards. This could include inspecting the product's dimensions, weight, and color consistency. In some cases, the manufacturer may also conduct a visual inspection of the product to identify any defects or issues before the product is sent for inspection.
-
Inspection by Customs: Once the product has passed the pre-inspection phase, it is ready for inspection by customs officials. Customs officials will carefully examine the product and compare it to the relevant standards and regulations. They may also test the product for certain materials or components that are required to be present.
-
Inspection by Laboratories: In addition to customs officials, the product may also be inspected by laboratories specializing in textile testing. These laboratories use advanced equipment and techniques to analyze the product's composition, structure, and performance. They may test the product for specific materials such as polyester or cotton, or for certain properties such as durability or softness.
-
Inspection by Experts: If the product fails any of the above tests, it may be sent to experts for further analysis. These experts may specialize in a particular area of textile science, such as dyeing or weaving. They will use specialized equipment and techniques to determine the cause of any defects and suggest ways to improve the product's quality.
-
Reporting and Retesting: After the inspection process is complete, a report will be generated detailing the findings of the inspection. If any defects were found, they will be reported along with recommendations for improvement. The manufacturer may then retest the product to ensure that it meets all necessary standards and regulations.
Example: Let's consider a case study of a textile company that produces clothing. The company was required to submit its products for inspection by customs and laboratories. During the pre-inspection phase, the company identified several issues with the fabric's thickness and color consistency. The company decided to conduct a visual inspection of the product to identify any additional defects.
Upon inspection by customs officials, they found that the product did not meet all necessary standards and regulations. Specifically, the fabric was too thin and had noticeable color variations across different sections of the garment. The company was instructed to send the product for further testing by laboratories.
During the laboratory testing, the fabric was found to have low levels of polyester and high levels of cotton. Additionally, the fabric's structure was weak and prone to tearing. Based on these findings, the laboratory recommended that the company use a higher percentage of polyester in the fabric to improve its strength and durability.
The company implemented these recommendations and resubmitted the product for inspection. After the final inspection, the product was found to meet all necessary standards and regulations. The company successfully passed the inspection process and continued to produce high-quality textile products for its customers.
Conclusion: The textile inspection process is crucial for ensuring that textile products meet international standards and regulations. By following a pre-inspection phase, customs officials, laboratories, and experts can identify and address any defects or issues with the product. This ensures that the product is safe for consumers and promotes fair trade practices. As the textile industry continues to grow and evolve, it is essential that manufacturers continue to invest in quality control measures to meet the demands of global markets.
纺织品检验检疫是确保纺织品质量安全的重要环节,其流程涉及多个环节和步骤,本篇文章将详细介绍纺织品检验检疫的流程,并结合实际案例进行说明。
纺织品检验检疫流程概述
原料检验
原料检验是纺织品检验检疫的第一步,主要检查原料的质量和规格是否符合标准,包括对原料的外观、尺寸、重量、成分等各项指标进行检测。
样品采集
样品采集是检验检疫过程中的重要环节,需要按照规定的方式和时间采集样品,样品应具有代表性,能够反映整个纺织品的质量情况。
实验室检测
实验室检测是检验检疫的核心环节,包括化学分析、物理性能测试、微生物检测等,通过实验室检测,可以确定纺织品的各项性能指标是否符合标准。
出证检验
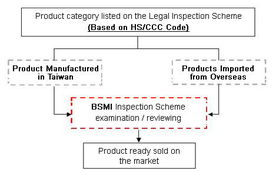
出证检验是对检验结果进行最终确认的过程,需要出具检验报告,报告应详细记录检测结果、结论以及处理意见等。
具体流程说明
原料检验流程
(1)外观检查:检查原料的外观是否符合标准,有无瑕疵、污渍等。
(2)尺寸测量:测量原料的尺寸是否符合标准,有无偏差。
(3)成分检测:对原料进行成分检测,确定其成分是否符合标准。
样品采集流程
(1)样品采集方式:根据实际情况选择合适的样品采集方式,如随机抽样、代表性抽样等。
(2)样品采集时间:按照规定的时间进行样品采集。
实验室检测流程
(1)化学分析:对原料进行化学分析,包括纤维类型、含量、杂质等指标的检测。
(2)物理性能测试:对纺织品的物理性能进行测试,如拉伸强度、弹性等指标。
(3)微生物检测:对纺织品进行微生物检测,确保其卫生安全。
出证检验流程
(1)出具检验报告:根据实验室检测结果,出具详细的检验报告,报告应包含检测结果、结论以及处理意见等。
(2)审核报告:对检验报告进行审核,确保报告的真实性和准确性,如有需要,可以进行复检或补充实验。
案例说明
以某纺织品出口为例,简要说明纺织品检验检疫流程,该纺织品出口到某个国家,需要进行检验检疫,原料检验环节中,需要对原料进行外观检查和尺寸测量,确保其符合出口标准,样品采集环节中,按照规定的方式和时间采集样品,实验室检测环节中,需要进行化学分析和物理性能测试,以确保纺织品的各项性能指标符合出口要求,出证检验环节中,出具详细的检验报告,并进行最终确认,该案例表明,纺织品检验检疫流程需要严格按照规定进行,确保纺织品质量安全。
纺织品检验检疫流程包括原料检验、样品采集、实验室检测和出证检验等多个环节和步骤,在实际操作中,需要严格按照规定进行,确保纺织品质量安全,在实际操作中,还需要结合实际情况进行灵活运用,确保检验检疫流程的顺利进行。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Progress and Challenges of Textile Dyes in the Global Fashion Industry
The Magic of Gua Xi Textile Factory Towels
Exploring the Dynamics of Chargong Textiles by Road in Guangdong A Case Study