The Varied Dimensions of Textile Testing Standards:A Comparative Analysis
The paper aims to explore the diverse dimensions of textile testing standards through a comparative analysis. The standard tests are divided into three categories: physical, chemical and mechanical properties tests. Physical tests mainly include yarn and fabric strength, elongation and flexibility tests, while chemical tests focus on colorfastness, water absorption, shrinkage, etc. Mechanical properties tests involve breaking strength, tearing strength, compression set, etc. These tests aim to evaluate the quality of textile products and provide scientific basis for product design and production.
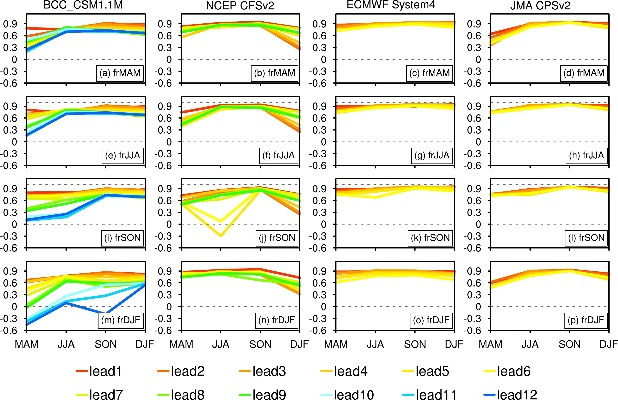
In the world of textiles, there is a vast array of standards that dictate how fabrics are tested and evaluated for quality, functionality, and safety. These standards vary significantly from one region to another, often reflecting cultural norms, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements. In this talk, we will explore the differences in testing methods and criteria between various textile standards, including international standards like ISO, ASTM, and ANSI, as well as local and regional standards. We will also examine how these differences impact the design, production, and consumer use of textiles.
Let's start with some basic information about textiles and their testing. Textiles are materials made from natural or synthetic fibers that are woven, knitted, or spun into fabrics. They serve a wide range of purposes, including clothing, home furnishings, and industrial applications. When it comes to testing, textiles undergo various tests to ensure they meet specific performance criteria, such as strength, durability, comfort, and environmental friendliness.
Now let's take a closer look at the different testing standards used in the textile industry. Here is an example table summarizing some of the most common textile testing standards:
| Textile Testing Standard | Criteria | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 16043 | Tensile strength | Fabric test specimens subjected to tensile force until failure |
| ISO 5072 | Tear strength | Fabric sample torn along a perpendicular line |
| ISO 19082 | Water absorption | Measurement of water absorbed by fabric samples over time |
| ASTM D417 | Shrinkage | Measurement of fabric shrinkage during drying |
| ASTM D418 | Crease recovery | Measurement of fabric's ability to regain its shape after being creased |
| ANSI/ASHRAE 90.1-2010 | Flame resistance | Testing of fabrics for resistance to flame propagation |
Now let's consider the implications of these differences on the textile industry. For example, the ISO standard is widely adopted globally and emphasizes uniformity across different countries. However, some regions may have unique requirements or preferences that affect the testing process. For instance, ASTM standards are more focused on practical applications and are often used in industries where durability and ease of use are critical factors.
Another important factor to consider is the impact of testing standards on the design and production processes of textiles. Different standards require different types of testing, which can influence the choice of materials, manufacturing techniques, and final product features. For example, if a fabric must pass a high-tear strength test, it may be necessary to use stronger fibers or more complex weaving patterns. Conversely, if a fabric must conform to a low water absorption standard, it may be designed with a higher percentage of moisture-absorbent materials.
Finally, let's look at how these differences affect consumers. Consumers have varying expectations and concerns when it comes to textile products. Some may prioritize durability and longevity, while others may focus on comfort and aesthetics. The testing standards used in the textile industry can help manufacturers tailor their products to meet these diverse needs. By understanding the differences in testing methods and criteria, consumers can make informed decisions about the products they purchase.
In conclusion, the testing standards used in the textile industry can vary significantly depending on the region and the industry's specific needs. These differences not only impact the design and production processes of textiles but also affect consumer choices and expectations. As technology continues to evolve and new materials become available, it will be essential for textile manufacturers to stay up-to-date with the latest testing standards and adapt their practices accordingly. By doing so, they can continue to offer high-quality products that meet the needs of their customers while adhering to the evolving standards of the global textile industry.
随着纺织品行业的快速发展,不同标准的差异成为了行业关注的焦点,本篇文章将探讨纺织品测试中不同标准的差异,并通过案例分析来说明这些差异。
纺织品测试标准概述
- 国际标准:主要涵盖纺织品的质量、安全、环保等方面的规定,ISO 14001、ASTM等。
- 国家标准:各国家和地区根据自身实际情况制定的一系列纺织品标准,中国国家标准、欧盟纺织品标准等。
不同标准的差异分析
- 测试方法与测试仪器:不同标准的测试方法、测试仪器和测试流程存在明显差异,国际标准通常采用更加严格和全面的测试方法,而国家标准的测试方法可能更加注重实用性。
- 测试标准的应用范围:不同标准的适用范围也有所不同,国际标准通常适用于全球范围内的纺织品生产、销售和贸易,而国家标准可能更侧重于特定地区或行业的特定要求。
- 案例分析:以纺织品测试为例,我们可以看到不同标准的差异在实际应用中的体现,某国际知名品牌的产品在经过严格的质量检测后,其出口到不同国家和地区时,需要满足不同的标准要求,在某些地区或国家,可能更注重产品的环保性能和安全性能,而忽略了其他方面的要求;而在其他地区或国家,可能更加注重产品的功能性、舒适性和美观性。
纺织品测试案例说明
- 国际标准案例:某国际知名品牌的一款纺织品产品,经过严格的质量检测后,需要满足多个国际标准的检验要求,其中包括ISO 14001环境管理体系认证、ASTM纤维含量测试等,该品牌的产品在出口到不同国家和地区时,需要确保符合当地环保法规和安全法规的要求。
- 国家标准案例:某国内知名品牌的一款纺织品产品,其质量标准和适用范围可能更加注重实用性,该品牌的产品在满足国家安全性能和环保性能的同时,也注重产品的功能性、舒适性和美观性,该品牌的产品在市场上受到了消费者的广泛好评。
纺织品测试中不同标准的差异是不可避免的,但通过合理的测试方法和标准应用,可以更好地保证纺织品的质量和安全性能,在实际应用中,我们需要根据不同地区或国家的实际情况,选择合适的测试标准和适用范围,以确保纺织品符合当地法规和要求,我们也需要不断加强纺织品的质量检测和认证工作,提高纺织品的质量和安全性能,满足消费者的需求。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Legacy of Textiles:An Inspiring Story of Heritage Preservation
The Fabrics of Seamless Luxury



