The Essential Tools for Textile Chemistry
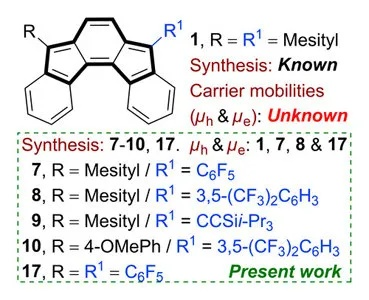
In the realm of textile chemistry, a diverse array of essential tools is necessary for the successful synthesis and manipulation of fibers, fabrics, and materials. These tools include chemical reactants, solvents, catalysts, and equipment such as stirrers, heating systems, and vacuum chambers. The use of these tools allows scientists and engineers to create new fibers with unique properties, modify existing ones to meet specific applications, and develop advanced fabrication techniques that enhance the performance and durability of textile products. As technology continues to advance, the importance of these tools in textile chemistry will only continue to grow, providing a powerful toolkit for researchers and practitioners alike.
Introduction: Textile chemistry is a fascinating field that involves the manipulation of materials used in clothing and textiles to improve their properties. It encompasses a wide range of techniques, including dyeing, finishing, and functionalization, all of which require precise measurement and control of chemicals and equipment. In this article, we will explore some of the essential tools used in textile chemistry, including instruments such as pH meters, spectrophotometers, and chromatographs. By understanding the importance of these tools, you can better appreciate the precision required in this field and how it contributes to the quality and performance of textile products.
-
pH Meter: A pH meter is an essential tool for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. In textile chemistry, pH measurements are crucial for determining the suitability of chemicals for use in dyeing and finishing processes. For example, pH values affect the stability of dyes and the rate of chemical reactions, so it is important to monitor the pH of solutions during these processes. A pH meter can be used to measure the pH of aqueous solutions, as well as non-aqueous solvents like alcohols and acetone.
-
Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometry is a technique that uses light to measure the absorption or emission of light by a sample. In textile chemistry, spectrophotometers are used to analyze the color of textile samples and to determine the concentration of various chemicals. This instrument allows for the measurement of absorbance, transmittance, and reflectance, which are critical parameters in determining the color and texture of fabrics. Spectrophotometers are particularly useful for analyzing dyed fabrics and for monitoring the progress of chemical treatments.
-
Chromatograph: Chromatography is a method used to separate complex mixtures based on their different physical or chemical properties. In textile chemistry, chromatographs are employed for the separation of different types of dyes and for the analysis of finished fabrics. These instruments use a stationary phase to separate molecules based on their size, shape, and charge. Chromatography is particularly useful for identifying impurities in dyes and for analyzing the distribution of dyes in fabrics.
-
Refractometer: A refractometer is a device used to measure the折射率 of a liquid or solid. In textile chemistry, refractometry is used to determine the refractive index of a solution, which is important for calculating the molecular weight of substances dissolved in water. Refractometry is particularly useful for analyzing the molecular structure of polymers and for determining the purity of synthetic fibers.
-
Karl Fischer Titrator: Karl Fischer titration is a method used to determine the amount of moisture in a sample. In textile chemistry, Karl Fischer titration is often used to measure the moisture content of fabrics and yarns. This instrument measures the amount of hydroxide ion released when a sample is treated with a strong acid. The amount of hydroxide ion released is directly proportional to the amount of moisture in the sample, allowing for accurate determination of moisture levels.
-
Dyeing Machine: Dyeing machines are essential tools for producing textile products with specific colors and patterns. They consist of a series of rollers and drums that apply dyes to fabrics while simultaneously removing excess dye. Dyeing machines are designed to handle a wide range of fabrics and dyes, allowing for consistent results every time. Some common dyeing machines include rotary drum dyeing machines, continuous flow dyeing machines, and digital printing machines.
-
Weaving Machine: Weaving machines are used to produce woven fabrics from multiple layers of yarn. They consist of a series of interlacing mechanisms that create a patterned surface. Weaving machines are designed to handle a variety of yarn types and weights, allowing for the production of a wide range of textile products. Some common weaving machines include ring combing machines, shuttleless weaving machines, and computerized weaving machines.
-
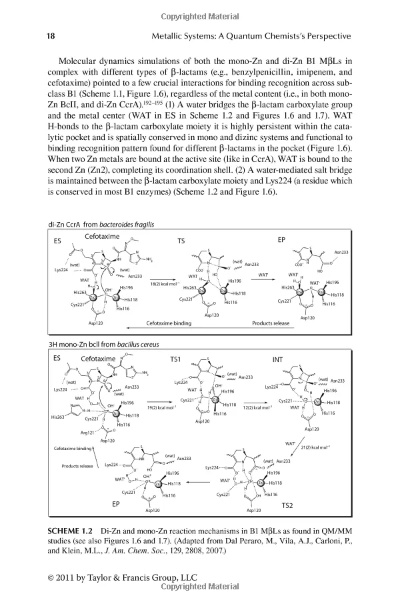
Stainless Steel Binder: Stainless steel binders are used to hold together the layers of yarn in a fabric. They are made of high-quality stainless steel and are resistant to corrosion and wear. Stainless steel binders are particularly useful for high-performance fabrics, such as sportswear and military uniforms, where durability and strength are critical.
-
Electronic Weighing Scale: Electronic weighing scales are used to accurately measure the weight of textile samples. They are designed to provide precise readings with minimal errors due to temperature variations or air resistance. Electronic weighing scales are commonly used in laboratories and research facilities for the accurate measurement of small quantities of materials.
-
Thermometer: Thermometers are used to measure the temperature of a sample, which is important for controlling the conditions under which chemical reactions occur. In textile chemistry, thermometers are particularly useful for monitoring the temperature of dye baths and finishing solutions. Some common thermometers include mercury thermometers, digital thermometers, and infrared thermometers.
Case Study: Let's take a look at a case study involving the use of a pH meter in textile chemistry. Suppose a textile company is developing a new fabric that requires the use of a specific dye that has a narrow pH range. To ensure that the dye is properly applied and does not cause any adverse effects on the fabric, the company needs to monitor the pH value of the dye bath throughout the process. The pH meter is used to measure the pH value of the dye bath before and after application, allowing the company to adjust the pH if necessary. By using the pH meter, the company can ensure that the fabric meets the desired color and texture requirements, ultimately leading to a higher quality product.
Conclusion: Textile chemistry is a complex field that requires precise measurement and control of chemicals and equipment. From pH meters to chromatographs, there are numerous tools available for researchers and professionals working in this field. By understanding the importance of each instrument and its role in achieving optimal results, you can better appreciate the precision required in textile chemistry and how it contributes to the quality and performance of textile products.
在纺织品科学领域,各种仪器发挥着至关重要的作用,这些仪器不仅帮助我们深入了解纺织材料的性质,还推动了纺织技术的进步,本文将详细介绍纺织品化学中常用的仪器及其应用。
主要仪器介绍
- 原子吸收光谱仪(Atomic Absorption Spectrometer):这是一种用于快速、精确测定纺织品中特定元素含量的仪器,它通过测量样品中的元素吸收光谱来确定其含量,广泛应用于纺织材料的成分分析。
- 红外光谱仪(Infrared Spectrometer):这是一种用于分析纺织品纤维结构、化学成分和物理特性的仪器,红外光谱可以提供纤维内部化学键、官能团等信息,有助于我们了解纤维的物理性质和化学反应。
- 扫描电子显微镜(Scanning Electron Microscope):这是一种用于观察纺织品微观结构的仪器,可以提供纤维的表面形貌、元素分布等详细信息,它广泛应用于纺织材料的结构分析、材料性能研究等领域。
- 恒温干燥箱:这是一种用于干燥样品的仪器,对于纺织品化学实验中样品处理至关重要,它可以控制恒定的温度环境,确保样品在处理过程中不受外界环境影响。
案例说明
以纺织品化学为例,我们可以看到这些仪器在实际应用中的具体案例。
原子吸收光谱法分析纺织品成分
某公司使用原子吸收光谱仪对一批纺织品进行了成分分析,通过分析结果,他们可以确定纺织材料的种类和含量,为生产提供了重要的参考依据。
红外光谱法研究纺织纤维结构与性能
某研究机构使用红外光谱仪对纺织纤维进行了深入研究,通过分析红外光谱图,他们可以了解纤维的化学成分、官能团等信息,进而研究纤维的结构与性能,这些信息对于优化纺织材料和提高纺织产品的性能具有重要意义。
仪器使用说明
- 使用原子吸收光谱仪时,需要先准备好待测样品,并将其放入样品池中,根据样品类型和需求选择合适的测量参数和波长范围,按下开始按钮进行测量。
- 使用红外光谱仪时,需要先对样品进行预处理,如干燥、粉碎等,将样品放入光谱仪的样品室中,进行扫描和分析,根据分析结果得出结论。
- 在使用恒温干燥箱时,需要先设定好温度参数,然后将样品放入干燥箱中进行干燥处理,干燥过程中需要定期检查温度和湿度,确保样品在恒定的温度环境下处理。
纺织品化学中常用的仪器种类繁多,每种仪器都有其独特的用途和特点,在实际应用中,我们需要根据实验需求选择合适的仪器,并正确使用它们,我们还需要不断学习和掌握新的仪器技术,以适应纺织品科学领域的发展需求。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:



