The Encompassing Nature of Textile Manufacturing
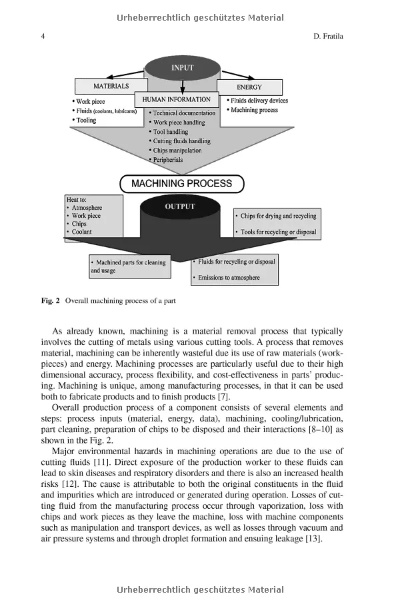
The textile manufacturing industry is characterized by its extensive nature, encompassing a wide range of processes and technologies. From the initial raw material procurement to the final product assembly, every stage of the production process involves complex operations that require precise control and coordination. The textile industry's extensive nature is evident in the diverse array of materials used, including cotton, polyester, and wool, each with their unique properties and processing requirements. The industry also employs a wide range of machinery and equipment, from simple hand tools to sophisticated automated systems, each designed to enhance efficiency and productivity. Additionally, the textile manufacturing process requires significant amounts of energy, both in terms of raw materials and labor, highlighting the industry's environmental impact. Despite these challenges, the textile industry remains a vital component of global commerce, providing essential products for clothing, home furnishings, and other applications.
In the realm of textile manufacturing, the term "encompassing" is aptly used to describe the vast array of products and processes involved in creating clothing, home goods, industrial fabrics, and more. From the raw materials to the final product, the textile industry spans across various stages, each contributing to the end-to-end process that shapes our world.
At its core, textile manufacturing involves the creation of fibers from natural or synthetic materials such as cotton, wool, silk, and polyester. These fibers are then processed into yarns, which can be woven, knitted, or crocheted into fabrics for use in a wide range of applications. For example, cotton is commonly used to produce linens, while wool is favored for warm winter wear.
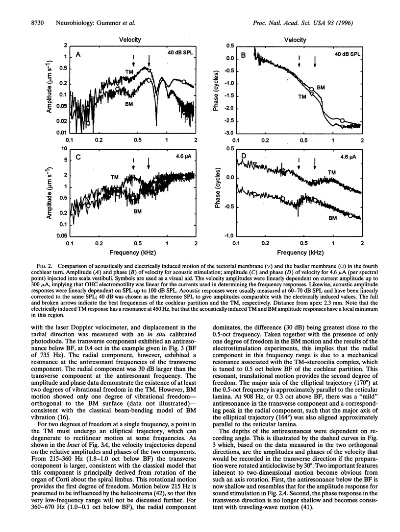
The process of weaving involves interlacing multiple threads to create a strong, durable fabric. This technique is used in the production of everything from tablecloths to sailcloths. Knitting, on the other hand, involves looping individual threads together to form a single fabric. This method is used in the production of sweaters and socks.
Crocheting, a less common but highly skilled technique, involves creating intricate patterns by manually pulling thread through a series of loops. It's often used in the production of delicate pieces like lace or shawls.
Once the fabric is produced, it undergoes further processing to enhance its properties. This may include treatments such as dyeing, printing, or finishing with embellishments like buttons, ribbons, or sequins. For instance, a company might use a combination of dyeing and printing techniques to create a unique pattern on their t-shirts.
Textile manufacturing also involves the assembly of components into complete products. This may involve cutting, sewing, or gluing together different parts to create a garment or piece of furniture. For example, a pair of jeans might start with raw denim fabric, which is cut into strips and sewn together along the seams to form the legs.
In addition to these traditional methods, there are also emerging technologies that are transforming the textile industry. For instance, the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software enables designers to create complex patterns and designs that would have been impossible to achieve using traditional techniques. Similarly, automation and robotics are being used to streamline the production process and increase efficiency.
One particularly noteworthy case study is the development of sustainable textiles. Many companies are now striving to reduce their environmental impact by using eco-friendly materials and processes. For example, some manufacturers are switching from traditional petroleum-based dyes to plant-based alternatives that are biodegradable and non-toxic. Others are implementing recycling programs to reuse or repurpose waste materials.
Another area where textile manufacturing is making significant strides is in the field of smart textiles. These fabrics are engineered to respond to changes in temperature, moisture, or pressure, providing wearers with customized comfort and functionality. For instance, some shirts have built-in sensors that adjust the amount of airflow based on the user's body heat, providing an extra layer of warmth without adding weight.
In conclusion, the textile manufacturing industry is a vast and diverse field that encompasses a wide range of products and processes. From the creation of raw materials to the final product, every stage contributes to the end-to-end process that shapes our world. As technology continues to advance and sustainability becomes increasingly important, we can expect to see even more innovative and sustainable solutions emerge in this field.
In this article, we will explore the scope of textile manufacturing, providing an overview in English with tables and case studies to illustrate.
纺织品制造范围简介
纺织品制造范围涵盖了各种类型的纺织品生产,包括但不限于各种面料、纱线、服装、家居装饰品等,这些产品广泛应用于服装、家居装饰、纺织配件、工业用布等领域。
具体制造领域
- 面料制造:这是纺织品制造的主要领域之一,涵盖了各种类型的面料,如棉布、丝绸、麻布等,这些面料经过精细的加工和工艺处理,可以制作出各种质地、颜色和图案的纺织品。
- 纱线制造:纱线是纺织品的骨架,是纺织生产的基础材料,纱线的种类和品质直接影响到纺织品的性能和质量,从细线到粗线,从纯纺到混纺,纱线的制造工艺和技术不断进步,满足不同领域的需求。
- 服装制造:纺织品在服装领域的应用非常广泛,包括衬衫、T恤、裤子、外套等,这些纺织品需要经过特殊的工艺处理,以适应不同的穿着环境和使用需求。
- 家居装饰品制造:纺织品在家居装饰领域也有着广泛的应用,包括窗帘、地毯、壁挂等,这些纺织品可以满足不同风格和需求的家居装饰需求。
案例说明
- 面料制造案例:某知名纺织品制造商,专注于生产各种类型的面料,包括高档棉布、丝绸面料等,该制造商采用先进的生产工艺和技术,不断推出新产品,满足不同领域的需求。
- 纱线制造案例:某大型纱线生产企业,专注于生产各种类型的纱线,包括高强度纱线、环保纱线等,该企业采用先进的生产工艺和技术,不断提高产品质量和性能,满足不同领域的需求。
纺织品制造范围的技术特点
- 高品质:纺织品制造范围注重品质控制,采用先进的生产工艺和技术,确保产品质量稳定可靠。
- 环保性:随着人们对环保意识的提高,纺织品制造范围越来越注重环保性,采用环保材料和技术,减少环境污染和资源浪费。
- 多功能性:纺织品具有多种功能,如保暖、透气、防潮等,纺织品制造范围的产品种类繁多,可以满足不同领域的需求。
未来发展趋势
随着科技的不断进步和人们生活水平的提高,纺织品制造范围将继续发展壮大,纺织品制造范围将更加注重绿色环保、智能化、个性化等方面的发展,纺织品制造范围还将不断推出新产品和新工艺,满足不同领域的需求。
纺织品制造范围涵盖了各种类型的纺织品生产,包括面料、纱线、服装、家居装饰品等,随着科技的不断进步和人们生活水平的提高,纺织品制造范围将继续发展壮大,产品种类将更加丰富多样,纺织品制造范围还将注重品质控制、环保性、智能化等方面的发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:



