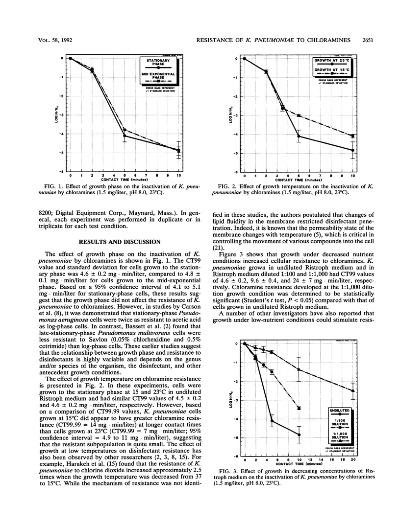
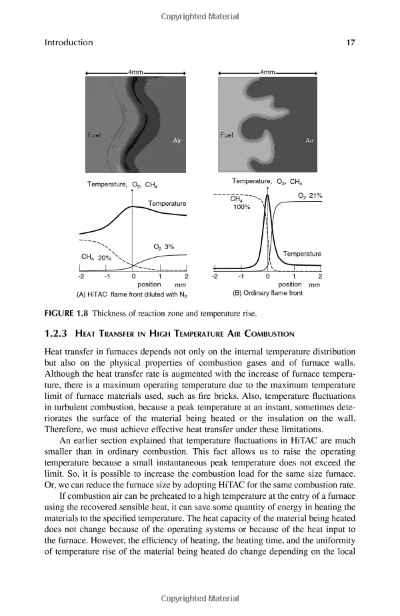
Understanding and Measuring the Softness of Textiles
This paper discusses the concept and methods of measuring the softness of textiles. The softness of textiles is a key factor influencing their comfort and wearability, and can be measured using various techniques such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and tear resistance. The paper also explores the relationship between the softness of textiles and their physical properties, such as yarn structure, weaving pattern, and fabric construction. Additionally, it examines the impact of different processing methods on the softness of textiles, including dyeing, printing, and finishing. Overall, this research provides a comprehensive understanding of the factors that affect the softness of textiles and offers valuable insights for improving their comfort and durability.
Introduction: Textiles are an integral part of our lives, from everyday clothing to high-end fashion. One of the most important properties for textiles is their softness, which affects how they feel against the skin and how well they perform in various applications. In this article, we will explore the different ways to measure textile softness, including using a textile testing machine, conducting sensory tests, and comparing different fabrics. We will also provide some examples of how softness can impact the performance of textiles in practical applications.
Measuring Textile Softness: There are several methods to measure textile softness, each with its own advantages and limitations. Here are three common methods:
-
Textile Testing Machine (Tensile Testing): The tensile testing method involves stretching a sample of the textile material under controlled conditions until it breaks. The force required to break the sample is measured and converted into a unit of measurement called "grams per square centimeter" or "g/cm²." This value represents the textile's resistance to being stretched, which is inversely proportional to its softness. Higher g/cm² values indicate greater softness.
-
Sensory Testing: Sensory testing involves evaluating the texture and feel of a textile by touching it directly. Participants rate the fabric on a scale of 1 to 10, where 1 is very stiff and rough, and 10 is very soft and smooth. This method provides subjective data that can be difficult to quantify but is often used as a complementary tool in measuring textile softness.

-
Comparative Testing: Comparative testing involves comparing the softness of two or more textile samples side by side. This can be done by placing one sample on a surface and another on top, or by using a fabric comparison chart to compare textures visually. This method is useful for identifying differences in softness between different fabrics and brands.
Example: Consider a case study involving a new line of athletic wear made from recycled polyester. The company wanted to ensure that the fabric was soft enough to provide comfort and reduce chafing during intense workouts. To evaluate the softness of the fabric, the manufacturer used both tensile testing and sensory testing. They found that the fabric had a high g/cm² value, indicating strong resistance to stretching, which could potentially lead to discomfort during physical activity. However, sensory testing showed that the fabric was still quite soft and comfortable overall. Based on this information, the company decided to adjust the fabric's design and manufacturing process to improve its softness without compromising its strength and durability.
Practical Applications: The softness of textiles has a significant impact on their performance in various applications, such as clothing, home furnishings, and sportswear. For example, a soft fabric can provide a more comfortable fit and feel, while a stiff fabric may be more durable but less comfortable. In the fashion industry, soft fabrics are often preferred for clothing because they create a more luxurious and inviting look. In the healthcare industry, soft fabrics can be used for medical garments like surgical gowns and hospital gowns, which need to be comfortable and easy to clean. In the automotive industry, soft fabrics are often used for upholstery and interior materials, as they provide a comfortable ride and a pleasant aesthetic.
Conclusion: In conclusion, measuring textile softness is crucial for ensuring that textiles meet the needs of their intended users. Using different methods to measure softness allows manufacturers to gain insight into the properties of their products and make informed decisions about design and production. By understanding the softness of textiles, we can create products that are not only functional but also enjoyable to use.
大家好,今天我们来聊聊纺织品柔软度的话题,柔软度是衡量纺织品舒适度和贴肤感的关键指标,对于我们日常穿着体验有着至关重要的影响,在选购纺织品时,了解其柔软度是非常必要的。

柔软度指标mn及其影响因素
柔软度指标mn主要包括触感柔软度、弹性柔软度和纤维材质柔软度三个方面。
- 触感柔软度:反映了纺织品表面触感是否舒适,是否能够让人感到柔软和舒适,可以通过手感、触感反馈等方式来评估。
- 弹性柔软度:反映了纺织品在拉伸、压缩等物理性能方面的表现,以及纤维材料的弹性,可以通过拉伸测试、压缩回复率等方式来评估。
- 纤维材质柔软度:纤维材质的种类、含量以及纺织工艺等因素都会影响其柔软度,天然纤维如棉、麻的柔软度通常优于合成纤维。
案例分析
下面我们通过一个具体的案例来说明纺织品柔软度的重要性。
选择合适的纺织品
小明最近购买了一件新衣服,他非常关心这件衣服的柔软度,他注意到衣服的柔软度指标mn显示为“较高”,说明这件衣服的舒适度和贴肤感较好,他进一步询问店员,得知这件衣服使用了高质量的天然纤维,具有较高的柔软度。

讨论与建议
-
提高纺织品柔软度的建议: (1)选择优质纤维:选择含有较高柔软度的天然纤维或合成纤维,可以大大提高纺织品的柔软度。 (2)注意纺织工艺:纺织工艺的不同也会影响纺织品的柔软度,例如使用先进的织造技术可以大大提高纺织品的柔软度和舒适度。 (3)注意面料设计:面料的设计也会影响纺织品的柔软度,例如采用合理的褶皱处理和纹理设计可以使纺织品更加贴合皮肤。
-
实际应用与注意事项: (1)在购买纺织品时,消费者可以根据自己的需求和喜好选择合适的柔软度指标mn,对于需要长时间穿着的衣物,可以选择更高柔软度的纺织品。 (2)在购买时,消费者还可以注意观察纺织品的外观、手感、弹性等指标,以便更好地了解其柔软度。 (3)消费者在购买时也可以咨询专业人士或店员,了解更多关于纺织品柔软度的信息。
总结与展望
纺织品柔软度是衡量纺织品舒适度和贴肤感的关键指标,对于我们日常穿着体验有着至关重要的影响,在选购纺织品时,消费者可以根据自己的需求和喜好选择合适的柔软度指标mn,同时也可以注意观察纺织品的外观、手感、弹性等指标,以便更好地了解其柔软度,随着科技的不断进步,纺织品行业也在不断发展和创新,未来纺织品柔软度的提升也将是一个重要的研究方向。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Transformative Apparel:The American Retro Look in Fashion
Prenatal Detection of Weaponry in Fabrics:A Review and Case Studies