The Global Fabrics:An In-Depth Analysis of Textile International Trade
This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the global textile trade, examining its evolution, current trends, and future prospects. The study traces the historical development of textile trade, highlighting key periods of expansion and contraction. It also explores the various factors that have contributed to the growth of the industry, including technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and geopolitical dynamics.,The paper analyzes the structure of the textile market, examining the distribution of production across different regions and the role of major players in shaping the industry's dynamics. It also discusses the challenges faced by emerging economies, such as low-cost producers, and the need for policy interventions to promote sustainable practices and protect intellectual property rights.,The study concludes by outlining potential strategies for enhancing the competitiveness of the textile industry, including investment in research and development, diversification of product lines, and increased focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility. Overall, it provides a valuable insight into the complex interplay between economic, technological, and political forces that shape the global textile trade.

In the world of textiles, the fabrics of the future are woven together by an intricate web of global trade. As we delve into the intricacies of this industry, let us explore the current state of textile international trade and its implications for both producers and consumers around the globe.
Textiles have long been a vital part of human civilization, from the simple loincloths of ancient Egypt to the sophisticated garments of modern society. Today, the global textile industry is a multibillion-dollar market, with countries like China, India, and Bangladesh leading the way as major players in the production and export of textiles.
To illustrate this, consider the case of China, which accounts for over half of the world's cotton output. From the vast plains of Guangdong to the bustling cities of Shanghai, Chinese factories specialize in producing a wide range of textile products, including cotton, silk, and polyester. These products are then exported to countries around the world, where they meet with varying levels of demand and acceptance.
India, on the other hand, is known for its high-quality woolen goods. With a rich history dating back to ancient times, Indian textiles have become synonymous with luxury and sophistication. Today, Indian textiles are sought after not only for their quality but also for their unique cultural significance.
Bangladesh, another significant player in the global textile industry, is famous for producing affordable and stylish clothing. With a population of over 160 million people, Bangladesh has become a major supplier of apparel to the Middle East, Europe, and North America.
The global textile industry is also characterized by significant trade imbalances. While some countries produce more textiles than they can export, others rely heavily on imports. For example, while China produces over 30 million tons of textiles annually, it also imports over 20 million tons of textiles from other countries. This creates a complex web of trade relationships that are shaped by factors such as political stability, economic growth, and technological advancements.
One of the main drivers of this trade is the demand for textiles from emerging markets. As these markets grow and develop, they become increasingly important players in the global textile industry. For example, the Chinese economy is projected to grow at an annual rate of 6.5% over the next decade, making it one of the largest economies in the world. This growth will undoubtedly fuel further demand for Chinese textiles, which will in turn drive up prices and create new opportunities for investors in this industry.
However, the global textile industry is also facing challenges that threaten its sustainability and longevity. One of these challenges is climate change, which is causing rising sea levels and changing weather patterns that could negatively impact crop yields and production costs. Additionally, there is growing concern about the environmental impact of textile production, with concerns about water pollution, air pollution, and waste disposal.
Despite these challenges, the global textile industry remains resilient, driven by innovation and investment in technology and infrastructure. For example, advances in digital printing and automation are allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality textiles with greater efficiency and cost savings. Additionally, there is ongoing research into sustainable and eco-friendly production methods that can help minimize the environmental impact of textile production.
Looking ahead, the global textile industry faces many exciting opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, there is continued demand for textiles from emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa. On the other hand, there is increasing pressure to reduce waste and improve sustainability, which will require innovative solutions and collaboration between manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers.
In conclusion, the global textile industry is a complex and dynamic sector that plays a crucial role in shaping the world economy. From the vibrant cultures of ancient civilizations to the cutting-edge technologies of modern manufacturing, textiles have always been a symbol of human creativity and adaptability. As we continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by this industry, it is clear that the future of textiles lies not just in their ability to meet our needs but also in their ability to inspire and connect us to each other across the globe.
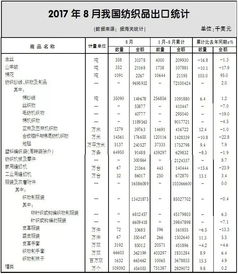
随着全球化的加速,纺织品国际贸易日益成为各国经济贸易的重要领域,本篇报告将深入探讨纺织品国际贸易的现状、趋势以及案例分析,旨在为相关企业和政策制定者提供参考。
纺织品国际贸易现状
市场规模与增长
全球纺织品市场规模不断扩大,各国之间的贸易往来日益频繁,特别是在新兴市场国家,纺织品贸易呈现出强劲的增长势头。
主要贸易伙伴与地区分布

纺织品主要贸易伙伴包括亚洲、欧洲、北美等地区,不同地区的纺织品贸易呈现出不同的特点和发展趋势,亚洲地区的纺织产品主要出口到欧美等发达国家,而欧洲地区的纺织品则主要出口到非洲、拉丁美洲等地区。
贸易政策与法规
各国政府对纺织品贸易的政策和法规不断调整和完善,以适应国际贸易形势的变化,一些国家实施了严格的环保标准,以保护生态环境和消费者权益。
纺织品国际贸易趋势
绿色、环保成为主流
随着全球环保意识的提高,绿色、环保成为纺织品国际贸易的重要趋势,各国政府和企业纷纷加大环保投入,推广绿色纺织产品,以降低环境污染和保护生态环境。
智能化、个性化成为新趋势
随着科技的不断发展,智能化、个性化成为纺织品国际贸易的新趋势,越来越多的纺织品开始采用智能化技术,提高生产效率和质量,满足消费者对个性化产品的需求。
区域合作与联动发展
区域合作与联动发展是纺织品国际贸易的重要方向,各国之间加强合作,共同推动纺织品贸易的发展,实现互利共赢,亚洲地区的纺织产品出口合作不断加强,推动了区域内的经济发展和贸易增长。
案例分析
亚洲地区纺织品贸易案例
亚洲地区的纺织品贸易近年来呈现出强劲的增长势头,中国作为亚洲最大的纺织品出口国之一,其纺织品出口量逐年增加,主要出口到欧美等发达国家,亚洲地区的纺织产品也开始向智能化、个性化方向发展,满足消费者对个性化产品的需求,亚洲地区的纺织产业还加强了与非洲、拉丁美洲等地区的合作,共同推动区域内的经济发展和贸易增长。
欧洲地区纺织品贸易案例
欧洲地区的纺织品贸易也呈现出良好的发展态势,欧洲的一些国家实施了严格的环保标准,推广绿色纺织产品,以降低环境污染和保护生态环境,欧洲地区的纺织产业也开始向智能化、个性化方向发展,采用先进的纺织技术,提高生产效率和产品质量,欧洲地区的纺织产业还加强了与亚洲地区的合作,共同推动纺织品的进口和出口合作。
纺织品国际贸易已经成为全球经济贸易的重要领域,在未来的发展中,纺织品国际贸易将继续呈现出市场规模扩大、贸易伙伴增多、绿色环保成为主流、智能化、个性化成为新趋势等特点,各国之间的合作与联动发展也将成为纺织品国际贸易的重要方向,对于企业和政策制定者来说,了解纺织品国际贸易情况,把握发展趋势,制定合理的贸易策略和政策,将有助于促进纺织品国际贸易的发展和繁荣。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Textiles Smoke Dyeing Durability Testing Standards