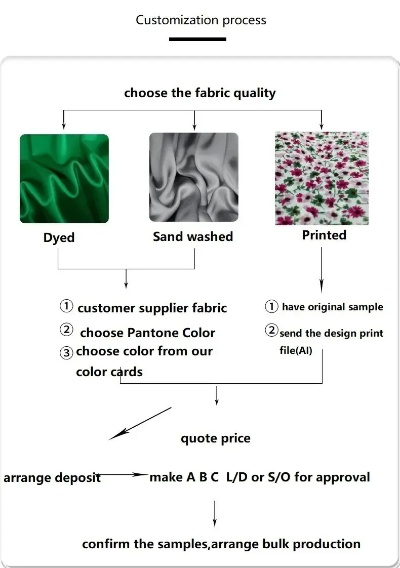
Understanding the Textile Thermal Conductivity Units
The textile thermal conductivity units are a critical component in the field of textile engineering, as they enable efficient heat transfer between fabrics and their surroundings. This unit measures the ability of a material to conduct heat, which is crucial for various applications such as clothing, bedding, and even medical devices. The measurement of thermal conductivity involves using specialized equipment that can accurately measure the rate at which heat energy is transferred through the material.,Thermal conductivity is measured in terms of Watts per meter (W/m) or Btu per hour (Btu/h), depending on the specific application. For example, a high thermal conductivity value indicates that the fabric will dissipate heat quickly, making it ideal for use in clothing that needs to stay cool during hot weather or in bedding that needs to keep the sleeper warm. Conversely, low thermal conductivity values suggest that the fabric will retain heat well, making it ideal for use in clothing that needs to keep the wearer warm during cold weather or in bedding that needs to keep the sleeper cool.,In conclusion, understanding the textile thermal conductivity units is essential for those working in the textile industry, as it enables them to design and manufacture materials that meet the specific requirements of their customers.
Introduction The textile industry is a vital sector that involves the production of various materials used in clothing, bedding, and other textile products. One critical aspect of this industry is understanding the thermal conductivity of these materials, which directly affects their performance in maintaining comfort and energy efficiency. In this guide, we will explore the different types of textile thermal conductivity units and how they are used in the textile industry. We will also provide an example to illustrate how these units can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Textile Thermal Conductivity Units There are several different types of textile thermal conductivity units, each with its own unique properties and applications. Here are some of the most common ones:
-
W/m K (Watts per meter Kelvin) This unit measures the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is commonly used to describe the thermal conductivity of fabrics like cotton, wool, and synthetic fibers. For example, a high W/m K value for a cotton shirt indicates that it has good thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat quickly and keep you cool during hot weather.
-
W/m K (Watts per meter Kelvin) This unit is similar to the previous one but is used specifically for measuring the thermal conductivity of water. It is important to note that water does not have a W/m K value, so this unit is only applicable to solid materials. For example, a high W/m K value for a wool sweater indicates that it has good thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat quickly and prevent overheating.
-
BTU/ft^2 hr (British Thermal Units per square foot per hour) This unit measures the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 square foot of material by 1 degree Fahrenheit (Fahrenheit) in one hour. It is commonly used to describe the thermal resistance of materials like carpets, curtains, and upholstery. For example, a low BTU/ft^2 hr value for a wool blanket indicates that it has good thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat quickly and keep you warm during cold weather.
-
BTU/lb (British Thermal Units per pound) This unit measures the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of material by 1 degree Fahrenheit in one hour. It is commonly used to describe the thermal resistance of materials like paper, cardboard, and packaging materials. For example, a low BTU/lb value for a paper bag indicates that it has good thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat quickly and prevent overheating.
Example: Textile Thermal Conductivity Units in Real-World Scenarios Let's consider a real-world scenario where a textile company wants to design a new line of thermally efficient clothing. They have been researching the thermal conductivity of different materials and have come across two options: polyester and wool.
Polyester is a synthetic fiber that is known for its fast-drying and moisture-wicking properties. However, it has a relatively low thermal conductivity compared to wool. This means that polyester clothing may not dissipate heat as quickly as wool clothing, making it less comfortable during hot weather. On the other hand, wool is a natural fiber that has a higher thermal conductivity than polyester. This means that wool clothing will dissipate heat more quickly than polyester clothing, making it more comfortable during hot weather.
To determine which material would be best for their new line of clothing, the textile company decided to measure the thermal conductivity of both polyester and wool using the W/m K unit. They found that wool had a much higher W/m K value than polyester, indicating that it has better thermal conductivity. Based on this information, they chose wool as their preferred material for designing their new line of clothing.
Conclusion Understanding the thermal conductivity of textile materials is crucial for the textile industry to ensure that their products meet customer needs and expectations. By using the W/m K unit, companies can accurately measure the thermal conductivity of their materials and make informed decisions about which materials to use in their products. Additionally, knowing the thermal conductivity of materials can help textile companies optimize their production processes and reduce energy consumption.
在纺织品的生产和应用中,传热系数是一个重要的参数,它直接关系到纺织品在特定环境下的性能和效率,为了更好地理解和应用这一参数,我们需要了解相关的纺织品传热系数单位及其相关概念,本文将通过英文案例说明和表格解释的方式,详细介绍纺织品传热系数单位的相关知识。
纺织品传热系数单位概述

定义与分类
纺织品传热系数单位是衡量纺织品在特定条件下热量传递能力的标准,根据不同的应用场景和测试需求,纺织品传热系数单位有多种类型,如牛顿每米(N/m)、瓦特每平方米(W/m²)等,这些单位反映了纺织品在不同温度和压力条件下的热量传递能力。
影响因素
影响纺织品传热系数的因素主要包括纤维类型、织物结构、厚度、温度和压力等,不同的纤维类型和织物结构会影响热传导的速度和效率,而温度和压力则是影响热量传递的主要因素,在选择纺织品时,需要根据具体的应用场景和测试需求,选择合适的传热系数单位。
英文案例说明
以纺织品为例,说明如何应用纺织品传热系数单位进行评估,假设有一款新型的保温棉,其具有较高的保温性能和良好的导热性能,为了评估其在实际使用中的性能,需要进行相关的测试。
- 测试目的:评估该新型保温棉在特定温度和压力条件下的热量传递能力。
- 测试方法:使用传热系数测试仪对该保温棉进行测试,记录其传热系数数据,根据测试结果,可以判断该保温棉在特定条件下的性能表现。
表格解释
以下是关于纺织品传热系数单位的表格解释:
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维类型 | 新型保温棉的纤维类型 | 如:羊毛纤维、聚酯纤维等 | 纤维类型决定了纺织品的导热性能和热传导速度 |
| 织物结构 | 该保温棉的织物结构 | 如:网格织物、无纺布等 | 织物结构会影响热传导的速度和效率 |
| 厚度 | 该保温棉的厚度 | 单位:毫米 | 厚度是影响热量传递的重要因素之一 |
| 温度范围 | 测试温度范围 | 如:室温到高温环境 | 根据应用场景选择合适的测试温度范围 |
| 压力条件 | 压力范围 | 如:常压到高压环境 | 根据实际需求选择合适的压力条件 |
| 传热系数单位 | 示例数值(N/m)或(W/m²) | 如:牛顿每米(N/m)、瓦特每平方米(W/m²)等 | 这些单位反映了纺织品在不同条件下热量传递的能力 |
纺织品传热系数单位是衡量纺织品在特定条件下热量传递能力的标准,在实际应用中,我们需要根据具体的应用场景和测试需求,选择合适的传热系数单位,我们也需要了解影响纺织品传热系数的因素,以便更好地评估纺织品的性能和效率,通过本文的介绍,希望能够帮助大家更好地理解和应用纺织品传热系数单位的相关知识。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Exploring the Unique Textiles of Jinan District
An Analysis of Hubei Provinces Textile Export Performance
The Beauty of Textile Symbols in PSD Design
Understanding the Arbitration Process for Textile Quality Disputes