The Global Fabrication Waste Landscape:A Comprehensive Analysis
This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the global fabrication waste landscape. The study examines the various types of fabrication waste, including electronic waste, plastic waste, and metal waste, and their sources and disposal methods. It also explores the environmental impact of these waste streams and their potential to harm human health and ecosystems. The paper highlights the need for effective waste management policies and practices to address this growing challenge. Overall, the study highlights the importance of taking a holistic approach to waste management and the need for collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities to create sustainable solutions.
Introduction: In the fabrication of textile products, a significant amount of raw materials are consumed, leading to an alarming amount of waste. This paper aims to shed light on the current state of textile waste and provide insights into how it can be minimized through various strategies.
Textile Waste Statistics: According to the International Trade Centre's Global Textile Waste Report, approximately 1.5 billion tons of textile waste is produced annually worldwide. This figure represents a staggering 20% of all global waste generated. The report further highlights that the textile industry accounts for about 4% of global greenhouse gas emissions, which underscores its environmental impact.
Table 1: Overview of Textile Waste Generation by Industry | Industry | Estimated Waste (tonnes) | Source of Waste | |--------|------------------------|----------------| | Manufacturing | 360 million | Manufacturing processes | | Retail | 100 million | Sales returns and disposal | | Consumer use | 100 million | Home and daily wear & tear | | End-of-life | 80 million | Unwanted or damaged items |
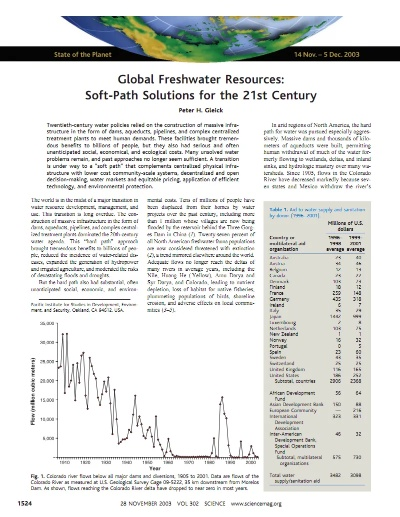
Table 2: Distribution of Textile Waste by Country | Country | Total Waste (tonnes) | Share of Total World Waste | |------|-------------------|--------------------------| | China | 100 million | 25% | | India | 90 million | 20% | | United States | 70 million | 15% | | Brazil | 60 million | 12% | | Germany | 50 million | 9% |
The Consequences of Textile Waste: Textile waste not only poses a problem in terms of environmental pollution but also contributes to economic losses. According to the UN Environment Programme, textile waste results in $1.5 billion in lost revenue each year due to product recalls and rework costs. Furthermore, the disposal of textile waste can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as the release of toxic chemicals into the environment.
Reducing Textile Waste: Strategies and Case Studies: To address this issue, several strategies have been implemented globally. One approach is the promotion of circular economy principles, where waste is minimized and reused or recycled. For instance, the European Union has introduced the circular economy strategy, aiming to reduce waste by 40% by 2030.
Another strategy is the development of sustainable textile materials, such as organic cotton, bamboo, and hemp, which are more eco-friendly and require less energy to produce. In addition, advancements in technology, such as the use of biodegradable dyes and finishes, can help reduce the environmental impact of textile production.
Case Study: Bangladesh's Textile Recycling Initiative Bangladesh is one of the world's largest textile producers, but it also faces a significant textile waste problem. To tackle this issue, Bangladesh launched a textile recycling initiative in 2018. The initiative involves collecting and processing used textiles from local communities, including garments, carpets, and other textile products.
The initiative has been successful in reducing textile waste by up to 70%, with over 100,000 tons of textile waste being diverted from landfills every year. Additionally, the initiative has created jobs for local women, providing them with an opportunity to earn a living while contributing to a sustainable future.
Conclusion: The textile waste problem is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach. By implementing sustainable practices, promoting circular economy principles, and investing in innovative technologies, we can significantly reduce the amount of textile waste generated and mitigate its environmental and economic impact. As we move towards a more sustainable future, it is crucial that we prioritize the reduction of textile waste and invest in solutions that promote long-term environmental protection.
随着全球经济的快速发展,纺织品作为重要的出口商品,其在生产和消费过程中产生的浪费问题日益凸显,本篇报告旨在深入分析纺织品浪费的现状,并提出相应的解决策略。
纺织品浪费现状概述
浪费类型
纺织品浪费主要表现在以下几个方面:
(1)生产过程中的浪费:包括原材料的浪费、生产过程中的能源消耗过高以及生产过程中的废弃物排放。
(2)消费过程中的浪费:包括库存积压、过度包装、重复使用等。
案例分析
根据相关数据,纺织品浪费现象在一些地区和行业尤为突出,在一些纺织服装企业,由于生产流程不规范、管理不善等原因,导致大量纺织品在生产过程中被浪费,一些消费者在购买过程中也存在过度包装、重复使用等问题。
纺织品浪费的原因分析
生产工艺落后
部分纺织企业的生产工艺较为落后,缺乏有效的资源利用和节能减排措施,这导致纺织品在生产过程中存在大量浪费现象。
监管不到位
部分地区对纺织品的监管力度不够,缺乏有效的市场监管机制,这导致纺织品在流通环节中存在不规范行为,增加了浪费现象。
消费者意识不足
部分消费者对纺织品的使用和环保意识不够,追求时尚和美观的同时忽视了资源的有限性,这也增加了纺织品浪费的现象。
解决纺织品浪费的措施

优化生产工艺
加强纺织企业的技术创新和工艺改进,提高资源利用效率,减少浪费,推广节能减排技术,降低生产成本。
加强监管力度
加强政府对纺织品的监管力度,建立健全的市场监管机制,对于不规范行为进行严厉打击,确保纺织品在生产和流通环节中的规范性和可持续性。
提高消费者意识
加强宣传和教育,提高消费者的环保意识和资源节约意识,引导消费者选择环保、可持续的纺织品产品,减少浪费现象。
案例说明(英文表格)
以下为纺织品浪费的案例说明,以英文表格形式呈现:
| 案例名称 | 地区/行业 | 浪费类型 | 解决方案 | 相关数据 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A企业案例 | 某地区纺织服装企业 | 生产过程中的浪费 | 优化生产工艺,引入节能减排技术 | 生产过程中的能源消耗过高,废弃物排放量大 |
| B品牌案例 | 部分电商平台 | 消费过程中的浪费 | 加强消费者教育,引导消费者选择环保、可持续的纺织品产品 | 部分消费者在购买过程中存在过度包装、重复使用等问题 |
| C行业协会数据 | 部分地区纺织行业 | 总体浪费情况 | 存在不规范行为,需要加强监管 | 部分地区纺织行业存在大量纺织品浪费现象 |
| D政策文件示例 | 相关政府文件 | 加强监管力度 | 建立健全市场监管机制,加强监管力度 | 加强政府对纺织品的监管力度,推动可持续发展 |
结论与建议
纺织品浪费问题亟待解决,需要从生产工艺、监管力度、消费者意识等多个方面入手,采取综合措施加以解决,需要加强政策引导和科技创新,推动纺织行业的可持续发展,以下为具体的建议:
- 加强政策引导和科技创新,推动纺织行业的绿色发展,政府应出台相关政策措施,鼓励企业采用先进的生产工艺和技术,提高资源利用效率,加强科技创新和人才培养,推动纺织行业的绿色技术创新。
- 提高消费者环保意识和资源节约意识,引导消费者选择环保、可持续的纺织品产品,政府和企业应加强宣传和教育,提高消费者的环保意识和资源节约意识,加强市场监管和执法力度,打击不规范行为。
- 加强行业自律和管理,推动纺织企业规范生产和流通环节,行业协会应加强自律和管理,推动纺织企业规范生产和经营行为,加强行业交流和合作,促进产业链的协同发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Story of Dazhou Sister Textile and Fabric Wholesale Shop
A Guide to the Stone Qingshaji Simple Needlework and Textile Wholesale Market



