Fabrication Plants Recycling Inventory Challenges and Solutions
Fabrication and recycling plants face a significant challenge in accurately tracking and managing their inventory due to the complexity of materials used and the variability of production processes. This issue can lead to inefficiencies in inventory management, increased costs for material handling, and a lack of transparency in supply chain operations. To overcome these challenges, several solutions have been proposed. One approach is the implementation of advanced inventory management systems that utilize sensors and data analytics to monitor inventory levels and predict demand accurately. Another solution involves the use of blockchain technology, which can provide secure and transparent record-keeping of inventory details. Additionally, collaboration between manufacturers and distributors can streamline inventory management by sharing information about stock levels and demand patterns. Finally, training and education programs can help employees better understand the importance of accurate inventory management and how it relates to overall plant efficiency. Ultimately, effective inventory management is crucial for ensuring a stable supply chain and reducing waste while maximizing profits.
Introduction: In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing, sustainability has become an essential pillar for many companies. This means that it's more crucial than ever to properly manage and optimize our inventory. One way to achieve this is through recycling, which involves taking old, unsold fabrics and transforming them into new products. However, this process comes with its own set of challenges, including managing different types of textile scrap, ensuring proper sorting and processing, and dealing with the logistics involved in transporting these materials back to factories. Let’s explore how textile manufacturers are addressing these issues.
Challenges: Textile manufacturers often encounter several challenges when it comes to recycling their stock. Here's a breakdown:
-
Types of Textile Materials: Different types of fabrics require different treatments to be repurposed. For example, cotton and polyester are easier to recycle than synthetic fibers like nylon or acrylic.
-
Quality Control: The quality of the reclaimed fabrics significantly affects the final product's performance and appearance. Therefore, it’s critical to maintain strict quality control measures.

-
Logistical Challenges: Recycling requires careful planning and coordination between the production and shipping departments. It’s important to ensure materials reach their destination on time and without damage.
-
Regulations and Compliance: Depending on the country or region, there could be strict regulations around waste management and disposal. Manufacturers need to comply with these laws and regulations to avoid penalties or legal issues.
-
Technological Advances: As technology advances, so does the ability to sort, recycle, and reprocess textile scrap. New technologies can make recycling more efficient and cost-effective, but they also come with their own set of challenges.
-
Cost Considerations: Recycling can be more costly than disposing of waste at landfills or incinerators. Manufacturers need to balance the environmental benefits against the financial implications.
-
Market Demand: There may not always be a market for recycled products due to consumer preferences or economic factors. Factories need to find ways to meet market demand while still prioritizing sustainability.
-
Supply Chain Management: A well-organized supply chain can make recycling more streamlined. Poor management can lead to lost or damaged materials, further complicating the process.
Solutions: Despite the challenges, textile manufacturers are finding innovative solutions to tackle the recycling challenge:
-
Adopting Advanced Technology: Many factories have invested in advanced sorting and recycling technologies that allow them to better manage and recycle their stock. For example, using machine learning to classify textile scrap based on its type and quality, or investing in robotic systems for automated handling of large quantities of textile waste.
-
Collaborating with Recyclers and Suppliers: Some manufacturers form partnerships with recycling companies or suppliers who specialize in textile recycling. This helps them get access to specialized equipment, knowledge, or even raw materials needed for recycling.
-
Engaging with Regulatory Agencies: By staying informed about local and global regulations, manufacturers can ensure compliance and avoid potential fines or penalties. They can also seek out opportunities for regulatory exemptions or incentives.
-
Improving Logistics Systems: By implementing robust logistics strategies, manufacturers can ensure that materials arrive at recycling facilities on-time and without damage. This includes optimizing transportation schedules, developing effective warehouse management systems, and implementing predictive maintenance for machinery.
-
Diversifying Markets: To counteract the risk of market saturation, manufacturers can explore new markets for their recycled products. This might involve developing unique designs, creating niche products, or entering into new partnerships with consumers who value sustainable fashion or eco-friendly products.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Rather than blindly pursuing recycling, manufacturers should conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses before committing to it. They should consider not only the initial costs of setting up a recycling facility but also the long-term savings, such as lower energy bills, reduced water consumption, and decreased dependence on non-renewable resources.
Case Study: One company that has made significant strides in the field of textile recycling is the Swedish manufacturer of sportswear brand Umbro. Umbro has implemented a comprehensive system for sorting, recycling, and reprocessing textile scrap into new products. The company's recycling program involves partnering with specialized recycling facilities that specialize in textile recycling. By doing so, Umbro ensures that their textile scrap is processed in a manner that minimizes harm to the environment and maximizes the value of the materials. The company also invests heavily in research and development to improve the quality of recycled products and develop new uses for existing textiles.
Conclusion: Recycling textile scrap is not just a necessary step towards sustainability; it's also a powerful tool for reducing costs and increasing profits for manufacturers. Through technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and rigorous logistics planning, textile manufacturers can successfully transition from one phase of their product life cycle to another, ultimately creating a circular economy that benefits both the environment and society as a whole.
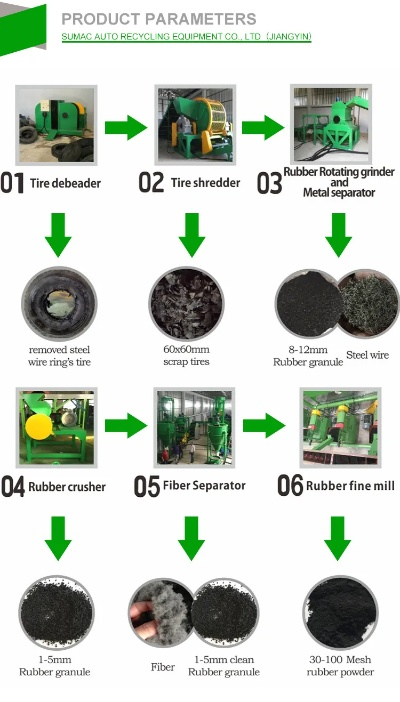

纺织厂库存回收现场
【员工A】(走进纺织厂,看到大量库存需要处理)
员工A:大家好,这里是纺织厂库存回收现场。
【同事B】(介绍情况)
同事B:纺织厂最近有一些库存需要处理,我们正在进行库存回收工作。
库存概述与分类
【员工A】(展示库存清单)
员工A:这里有一些旧纺织品、布料、纱线等库存,有些是生产过程中的剩余品,有些是过季或积压的商品。
【表格1】(库存分类举例)
表格1:库存分类说明
| 类别 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 旧纺织品 | 经过使用后剩余的纺织品 |
| 布料 | 生产过程中产生的布料 |
| 纱线 | 用于生产各种产品所需的原材料 |
案例分析:成功回收库存的例子
【案例一】成功回收案例分析
纺织厂成功回收纱线库存
员工A:我们注意到有一批纱线库存量很大,我们可以尝试进行回收,我们联系了一家专业的回收公司,他们经过评估后同意接收这些库存,经过协商,回收公司按照市场价格进行了合理的处理,这不仅减少了库存积压,还为公司节省了成本。
【表格2】(成功回收案例分析)
表格2:成功回收纱线库存的表格分析
| 措施 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| 回收公司选择 | 专业且信誉良好的公司 |
| 处理方式 | 按照市场价格进行回收处理 |
| 节约成本 | 减少了库存积压和浪费 |
讨论与建议
【讨论】关于库存回收的建议与讨论
员工B:对于纺织厂的库存回收工作,我们可以考虑以下几点建议,应该定期对库存进行盘点和评估,以便更好地了解库存状况,可以与专业的回收公司合作,以确保回收工作的顺利进行,对于过季或积压的商品,可以考虑进行合理的处理和销售,以实现资源的有效利用。
【建议】加强库存管理,提高回收效率
员工A:我们可以通过加强库存管理,提高回收效率,应该建立完善的库存管理制度,确保每一项库存都有明确的标识和记录,可以定期进行库存盘点和评估,以便及时发现和处理问题,可以与专业的回收公司合作,以确保回收工作的顺利进行和高效性。
总结与展望
【纺织厂库存回收工作的总结与展望
员工A:通过这次库存回收工作,我们不仅减少了库存积压和浪费,还为公司节省了成本,我们也看到了加强库存管理的重要性,我们可以在继续加强库存管理的基础上,积极寻求更多的创新和改进措施,以实现资源的有效利用和企业的可持续发展。
【展望】未来纺织厂库存回收工作的展望
员工B:我们可以在继续加强库存管理的基础上,积极探索更多的回收途径和方法,可以尝试与其他行业的企业合作,开展废旧纺织品和其他废物的回收工作,我们也可以考虑引入更多的科技手段,以提高回收工作的效率和准确性。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Disaster at Qidong Textile Factory
The Story of Linhai Dafeng Textile Factory
The Story of Nanyang Textile Factory
The Transformative Journey of the Ouqiao Textile Factory



