An Overview of Specialized Textile Inspection Methods
This article provides a comprehensive overview of specialized textile inspection methods. It begins with an introduction to the importance of textile inspection in maintaining quality control and preventing defects from being introduced into finished products. The article then goes on to discuss various types of inspection methods used in the textile industry, including visual inspection, tensile testing, and mechanical tests. Additionally, it explores the role of modern technology such as computerized image processing and automated testing in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of textile inspection. Finally, the article concludes by highlighting the benefits of using specialized inspection methods to ensure the quality and safety of textile products.
Introduction: Textiles, as a fundamental component of human life, come into contact with various materials and environments. As such, it's crucial to ensure that these products are free from harmful substances or defects that could compromise their quality or safety. Specialized textile inspection methods are essential for identifying these issues and ensuring compliance with relevant standards and regulations. In this article, we will explore the various specialized techniques employed in textile testing. Let's dive into the world of specialised textile inspection.
-
Chemical Testing: Chemical testing is the primary method of examining textiles for harmful chemicals, dyes, pigments, or any other contaminants. The process involves analyzing the fabric's surface, ink, or dyes using various chemical agents. This can be done through spectrophotometry, chromatography, or solubility tests. For example, the presence of toxic heavy metals like lead or mercury can be detected using atomic absorption spectrophotometry, while the colorfastness of dyed fabrics can be evaluated using a dye test.

-
Biological Testing: Biological testing focuses on the examination of textiles for microbial growth, fungi, bacteria, and viruses. These tests assess the fabric's ability to resist biological degradation and ensure its hygiene and cleanliness. Common methods include microbial culture, colony counting, and bio-film formation tests. For instance, the presence of harmful bacteria or molds in a textile can be determined using a plate count or microscopic analysis.
-
Environmental Testing: Environmental testing evaluates the impact of textiles on the environment, including water pollution and soil contamination. It involves monitoring the release of chemicals during washing, dyeing, or dying processes. This helps identify potential hazards and guide sustainable practices. Examples of environmental tests include the determination of pH levels, organic content, and heavy metals in textiles.
-
Physical Examination: Physical examination involves visual assessment of the texture, color, pattern, weight, and other physical characteristics of textiles. This method provides an overview of the fabric's overall appearance and quality. For example, a visual inspection can reveal defects like fraying, loose threads, or discoloration. Additionally, texture tests like brush tests or scratch tests can help determine the fabric's wear resistance and durability.
-
Instrumental Tests: Instrumental testing employs specialized equipment to measure the properties of textiles. These tests are often more precise than manual inspections but require specialized knowledge and expertise. Some examples of instruments used in instrumented testing include tensile strength testers, elongation testers, and thermal conductivity testers. By measuring the mechanical properties of the fabric, these tests can assess its structural integrity and performance under different conditions.
-
Quality Control (QC) Checklist: A QC checklist is a systematic approach to ensuring the quality of textile products. It includes a set of standardized procedures that must be followed during the manufacturing process. This ensures consistency and traceability, which are critical when dealing with complex products like textiles. For example, QC checklists may include steps like pretreatment, dyeing, printing, finishing, and final inspection.
-
Sample Preparation: Sample preparation is a crucial step in textile testing, particularly in instrumental tests. It involves selecting representative samples that accurately represent the entire batch. This ensures that the results obtained are reliable and generalizable to the entire product. For instance, samples should be cut from various parts of the fabric, such as the warp and weft threads, to avoid biased results.
-
Compliance Assessment: Compliance assessment involves evaluating whether textile products meet established standards and regulations. This requires a thorough understanding of industry-specific requirements and guidelines. For example, some countries have specific standards for textile safety, such as the European Union's REACH regulation. To comply with these standards, textile manufacturers must undergo certification programs like the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS).
-
Case Study: To illustrate the practical application of specialized textile inspection methods, let's consider a case study involving a high-end fashion brand. The brand's fabrics were sourced from a supplier known for its eco-friendly practices. However, upon receiving samples for testing, the brand discovered traces of harmful chemicals in one of their fabrics. Using the company's QC checklist, they identified the source of the contamination and implemented measures to prevent future incidents. This case highlights the importance of thorough inspection and strict adherence to quality control protocols in maintaining brand reputation and consumer trust.
-
Conclusion: Specialized textile inspection methods play a vital role in ensuring that textile products meet stringent quality and safety standards. From chemical testing to instrumented testing, these methods provide comprehensive insights into the fabric's composition, structure, and performance. As consumers demand more sustainable and ethically produced products, the need for effective inspection methods only grows stronger. Ultimately, by adopting these specialized techniques, we can better safeguard our health and wellbeing while enjoying the beauty of textiles.
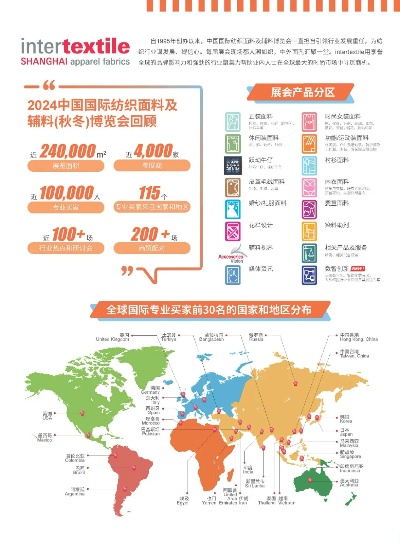
在探讨纺织品特种检测时,我们深入探讨其涵盖的领域和具体检测方法,以下是一篇关于纺织品特种检测的英文口语化内容,结合表格和案例说明,以便更好地理解。
纺织品特种检测概述
纺织品特种检测是确保纺织品质量、性能和安全的重要手段,它涵盖了多个方面,包括纤维性能检测、织物结构与性能检测、化学成分分析等,以下是关于纺织品特种检测的一些关键点:
纤维性能检测
纤维性能检测包括纤维的强度、弹性、耐磨性、抗皱性等指标的测试,这些指标直接关系到纺织品的耐用性和舒适度,通过使用各种测试仪器,可以检测纤维的拉伸强度、断裂伸长率等,以评估纤维的耐磨性。

案例说明:近年来,某品牌的新材料纺织品采用了先进的纤维技术,通过纤维性能检测,确保了其具有优异的耐久性和舒适度。
织物结构与性能检测
织物结构与性能检测包括织物的密度、织纹、透气性等指标的测试,这些指标直接关系到织物的舒适度、透气性和吸湿性,通过使用织物分析仪器,可以检测织物的透气性,以评估其在不同环境下的使用效果。
案例说明:某品牌的新款式纺织品采用了特殊的织物设计,通过织物结构与性能检测,确保了其具有优秀的透气性和舒适度。
化学成分分析
化学成分分析是对纺织品中的化学成分进行检测,包括纤维成分、染料成分、添加剂成分等,这些成分直接关系到纺织品的环保性、安全性以及穿着舒适度,通过使用化学分析仪器,可以检测纺织品中的有害物质含量,确保其符合相关标准和法规。
纺织品特种检测的具体方法与案例
纤维性能检测方法与案例
纤维性能检测方法主要包括纤维拉力测试、纤维断裂强度测试、纤维耐磨性测试等,某品牌的新材料纺织品采用了先进的纳米技术,通过纤维拉力测试和耐磨性测试,确保了其具有优异的耐久性和舒适度,该品牌还采用了多种环保染料,确保了纺织品的环保性。
织物结构与性能检测方法与案例
织物结构与性能检测方法主要包括织物密度测试、织物纹理分析、透气性测试等,某品牌的新款式纺织品采用了特殊的织物设计,通过织物结构与性能检测,确保了其具有优秀的透气性和舒适度,该品牌还采用了高科技面料处理技术,提高了织物的抗皱性和抗磨损性。
化学成分分析方法与案例
化学成分分析方法主要包括样品前处理、化学分析仪器使用等,某品牌的新材料纺织品在生产过程中严格控制了有害物质的含量,确保了其符合相关标准和法规,该品牌还采用了环保染料和添加剂,提高了纺织品的环保性和安全性。
纺织品特种检测是确保纺织品质量、性能和安全的重要手段,在具体实践中,我们可以根据不同的纺织品类型和需求,选择不同的检测方法和技术手段,我们还需要不断加强技术创新和研发能力,提高纺织品特种检测的准确性和可靠性。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Story of XiAn Citys New Districts黛美丝纺织品批发部
The Unique Connecting Citys Needlework Textiles Wholesale Market
Exploring the Future:The Journey of Zhejiang Hengsheng Textile Factory