纺织品燃烧鉴别指南
: Textile Fire Detection Guidelines,Abstract: This paper presents a comprehensive guide on the identification of fire hazards in textile products. The guidelines focus on understanding the characteristics of different types of textile materials, including cotton, synthetic fibers, and blends, which can be susceptible to fire. The text provides a step-by-step process for detecting potential fire hazards through visual inspection, testing methods such as burning tests, and chemical analysis. Additionally, it outlines the importance of proper storage conditions, labeling, and disposal practices to minimize fire risks. By following these guidelines, consumers and manufacturers can effectively identify and prevent fire hazards in textile products.
Introduction: In the world of textiles, understanding how to identify and assess the quality and safety of materials is crucial for both consumers and manufacturers. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the methods and considerations involved in identifying the characteristics of different types of textiles through their burning behavior. By following this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to safely evaluate the materials you come across.
Textile Compositions: Textiles can be classified based on their composition into natural fibers (such as cotton, wool, silk) and synthetic fibers (polyester, nylon, acrylic). Each type has unique characteristics that affect its burning behavior.
Natural Fibers:
- Cotton: Burns with a soft flame, producing a smoldering ash that can be easily brushed off.
- Wool: Burns with a hard flame, producing a white ash that may contain some combustible oils.
- Silk: Burns quickly, producing a bright yellow flame and a fine ash.
Synthetic Fibers:

- Polyester: Burns with a fast flame, producing a bright orange or red glow and a thick black ash.
- Nylon: Burns with a fast flame, producing a bright yellow or orange glow and a fine gray ash.
- Acrylic: Burns with a fast flame, producing a bright blue or green glow and a fine gray ash.
Classification by Type: To further categorize the various textiles, they can be classified based on their melting point and chemical makeup.
Melting Point:
- Low-melting point fibers (e.g., cellulose) burn more slowly and produce a less intense flame.
- High-melting point fibers (e.g., polyester) burn more quickly, producing a brighter and hotter flame.
Chemical Composition:
- Natural fibers are generally composed of long chains of carbon atoms, which burn at lower temperatures compared to synthetic fibers.
- Synthetic fibers are made from polymers that burn at higher temperatures, resulting in a more intense and rapid fire.
Fire Safety Tips: When evaluating the burning properties of textiles, it's important to consider factors such as temperature, duration, and oxygen content. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
Temperature:
- High temperatures can cause damage to the fabric and potentially release harmful chemicals.
- Low temperatures may not produce a strong flame but can still cause significant damage if left unchecked.
Duration:
- The length of time a fire persists can indicate the material's durability and potential for re-ignition.
- Long-lasting fires may indicate poor construction or materials used in the production process.
Oxygen Content:
- Oxygen helps fuel the fire, so reducing the amount of oxygen available can slow down the burning process.
- Closing off windows and doors can help create an oxygen-deficient environment that may extinguish the fire more quickly.
Case Study: Let's examine the case of a textile company that was accused of using low-quality synthetic materials in their clothing line. Upon investigation, the company's products were found to have high melting points and quick burning characteristics, indicating that they contained high amounts of polyester and other synthetic fibers. This led to concerns about the safety of the products and prompted the company to implement stricter controls and testing procedures to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion: Understanding the characteristics of different textiles through their burning behavior is essential for ensuring product safety and consumer protection. By following this guide, you will be able to confidently evaluate the materials you come across and make informed decisions about their suitability for use. Remember, when in doubt, always err on the side of caution and choose materials that meet your highest standards for safety and quality.
在纺织品鉴别过程中,燃烧鉴别是一种重要的手段,通过观察纺织品在燃烧过程中的特性,我们可以初步判断其材质、成分以及是否存在潜在的安全隐患,本文将围绕纺织品燃烧鉴别展开讨论,并提供相关案例分析。
纺织品燃烧鉴别方法
观察火焰颜色与形状
观察纺织品燃烧时火焰的颜色和形状是初步鉴别纺织品燃烧性能的重要方法,优质的纺织品通常具有稳定的火焰颜色,燃烧时不会产生过多的黑烟或异味,相反,劣质的纺织品在燃烧时可能火焰颜色不稳定,伴有黑烟或异味。
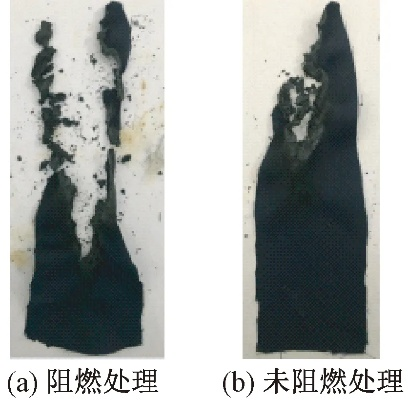
使用仪器检测
除了观察火焰颜色和形状外,还可以使用专业的仪器进行检测,红外线光谱仪可以检测纺织品中的化学成分,从而判断其材质和成分,一些专业的纺织品燃烧鉴别设备还可以提供温度、时间等参数,帮助我们更准确地判断纺织品燃烧性能。
案例分析
纺织品燃烧鉴别——天然纤维与合成纤维的区分
某客户收到一件疑似天然纤维的纺织品,询问是否可以进行燃烧鉴别,根据燃烧后的观察,我们可以初步判断该纺织品为天然纤维,通过使用红外线光谱仪进行检测,可以进一步确认其材质和成分,如果检测结果显示该纺织品为合成纤维,那么就需要进一步进行其他鉴别手段。
纺织品安全性能的判断
近期市场上出现了一些疑似含有有害物质的纺织品,消费者对此非常关注,我们可以使用燃烧鉴别的方法来判断这些纺织品的安全性能,对于含有有害物质的纺织品,如果其在燃烧过程中产生异味或产生大量黑烟,那么就可能存在安全隐患,在这种情况下,我们还可以结合其他检测手段,如气味测试、化学成分分析等,来进一步确认纺织品的真实安全性能。
纺织品燃烧鉴别注意事项
选择合适的鉴别方法
在进行纺织品燃烧鉴别时,我们需要根据具体情况选择合适的鉴别方法,对于天然纤维的鉴别,我们可以观察火焰颜色和形状;对于合成纤维的鉴别,我们可以使用仪器检测等方法,我们还需要注意选择可靠的仪器和设备,以确保检测结果的准确性。
注意安全防护
在进行纺织品燃烧鉴别时,我们需要注意安全防护,操作人员需要佩戴适当的防护用品,如防火服、防火眼镜等,在操作过程中需要注意防火安全,避免引发火灾事故,对于疑似含有有害物质的纺织品,我们还需要进行进一步的检测和处理。
纺织品燃烧鉴别是纺织品质量鉴别的重要手段之一,通过观察火焰颜色和形状、使用仪器检测等方法,我们可以初步判断纺织品的材质、成分以及是否存在潜在的安全隐患,在实际操作中,我们需要选择合适的鉴别方法,并注意安全防护,我们还需要不断学习和掌握新的鉴别技术和方法,以提高纺织品质量鉴别的准确性和效率。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Effectiveness of Textile Stains in Fabric Treatment
The Global Fabric of Anglo-American Trade:An Analysis of Anglophile Textiles



