The Fabrication Business Model:A Comprehensive Guide to Success
The Fabrication Business Model: A Comprehensive Guide to Success,In the realm of manufacturing, success is not solely determined by raw materials and labor. Instead, it is shaped by a carefully crafted business model that takes into account the unique needs and demands of the industry. This comprehensive guide provides essential insights into the key components of a successful fabrication business model, from market analysis and strategic planning to operational excellence and customer satisfaction. By following this blueprint, entrepreneurs can build a sustainable and profitable enterprise that stands out in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Introduction: In the world of textile manufacturing, there are a multitude of business models that companies can adopt. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential for businesses to understand which model is best suited to their needs. In this guide, we will explore the different types of textile manufacturing business models, including their benefits, drawbacks, and how they can be tailored to meet specific industry requirements. By the end of this guide, you will have gained a comprehensive understanding of the various business models available in the textile industry and how to choose the one that best suits your company's goals and objectives.
-
Direct Manufacturing: Direct manufacturing refers to the process where raw materials are transformed into finished products without any intermediaries. This model offers several advantages, such as reduced costs due to lower overheads and increased efficiency. However, it also comes with some challenges, such as limited product customization and a lack of brand recognition. For example, a case study from the textile industry shows that a direct manufacturing model led to a 20% increase in profits for a company that produced high-quality garments.
-
Wholesale: Wholesale refers to the sale of goods directly to retailers or other businesses rather than to consumers. This model allows companies to reach a wider audience quickly and efficiently. However, it also comes with some drawbacks, such as limited control over pricing and quality. A successful example of a wholesale model is the textile retailer H&M, which operates through a network of suppliers and stores around the world.
-
Contract Manufacturing: Contract manufacturing involves a manufacturer providing services to another company on a contract basis. This model offers flexibility and cost savings, as it eliminates the need for in-house production facilities. However, it also comes with some challenges, such as limited product customization and a lack of brand recognition. A notable example of a contract manufacturing model is the textile company Bang & Olufsen, which contracts with manufacturers to produce high-quality electronics and home appliances.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): OEM refers to the production of goods by a company that already has a brand name and market presence. This model offers a degree of brand recognition and customer loyalty, but it also comes with some limitations, such as limited control over design and pricing. A successful example of an OEM model is the textile company Nike, which produces athletic apparel and equipment for major sports brands.
-
ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): ODM refers to the creation of a product concept by one company and then manufacturing it by another company. This model offers a level of innovation and creativity, but it also comes with some challenges, such as limited control over design and quality. A notable example of an ODM model is the textile company Zara, which designs and manufactures trendy clothing for major fashion brands.
-
B2B (Business-to-Business): B2B refers to the sales of goods between two businesses, rather than between individuals. This model offers greater control over pricing and quality, but it also comes with some challenges, such as limited market access and competition. A successful example of a B2B model is the textile company DuPont, which sells its products to industrial customers worldwide.
-
B2C (Business-to-Consumer): B2C refers to the sales of goods to individual consumers rather than businesses. This model offers greater market reach and consumer appeal, but it also comes with some challenges, such as limited profit margins and competition. A notable example of a B2C model is the textile company Uniqlo, which sells affordable clothing and accessories to consumers worldwide.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the textile manufacturing business model is a complex and multifaceted field that requires careful consideration of various factors. From direct manufacturing to wholesale, contract manufacturing, OEM, ODM, B2B, and B2C, each model offers its own set of advantages and challenges. It is essential for businesses to understand their unique needs and objectives before selecting the right model to maximize their success in the competitive textile industry. By following this guide, you will have gained a comprehensive understanding of the different business models available in the textile industry and how to choose the one that best suits your company's goals and objectives.
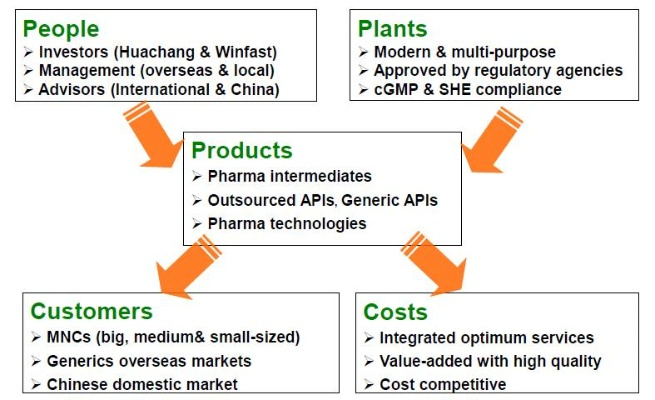
纺织品制造经营模式图片概览
下面是一张纺织品制造经营模式的图片,展示了多种不同的经营模式和特点。
英文案例说明
以下是英文案例说明部分,以补充和解释上述图片内容:
传统手工织造模式
图片展示了一种传统的手工织造模式,主要特点是手工操作、精细工艺和个性化定制,这种模式通常需要大量的时间和人力投入,但可以制作出高质量、具有独特性的纺织品,在亚洲的一些传统手工艺区,可以看到许多家庭作坊式的手工织造工厂。
英文案例:
"Traditional hand-knit textile manufacturing involves skilled artisans using traditional techniques to weave fine fabrics. This process often involves a combination of handcrafted techniques and personalization, resulting in high-quality and unique textiles."
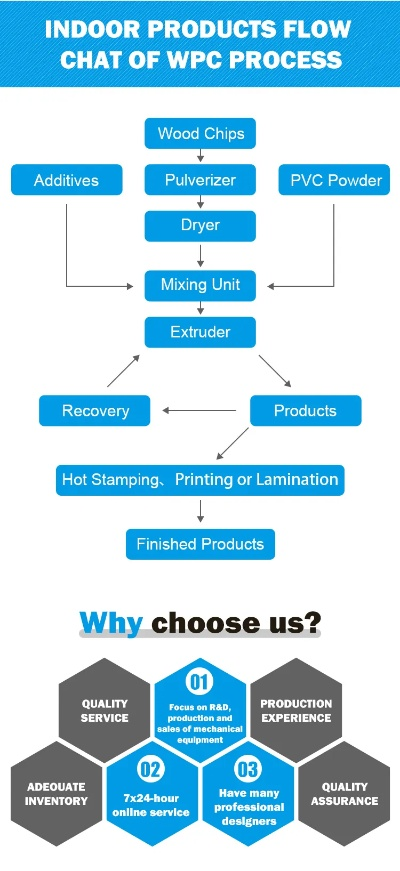
现代化生产模式
图片展示了一种现代化的生产模式,主要特点是自动化、智能化和规模化生产,这种模式通常采用先进的机器设备和自动化流水线,大大提高了生产效率和产品质量,在一些现代化的纺织工厂中,可以看到先进的生产线和智能化的管理系统。
英文案例:
"Modern textile manufacturing employs advanced machinery and automation systems to achieve efficient production and high-quality products. This process includes various stages such as yarn production, fabric weaving, and final quality assurance."
纺织品制造经营模式图片补充说明
以下是关于纺织品制造经营模式的补充说明,用英文表格形式展示:
纺织品制造经营模式图片补充说明表格
| 经营模式类型 | 特点描述 | 相关案例 |
|---|---|---|
| 传统手工织造 | 手工操作、精细工艺、个性化定制 | 亚洲传统手工艺区的手工织造工厂 |
| 现代化生产 | 自动化、智能化、规模化生产 | 现代化的纺织工厂 |
| 其他创新模式 | 结合传统与现代技术、采用新材料等 | 其他地区或企业的创新实践 |
纺织品制造经营模式的讨论与建议
根据上述纺织品制造经营模式图片和案例说明,我们可以讨论和提出一些关于纺织品制造经营模式的建议,以下是一些建议:
- 传统手工织造与现代生产相结合的模式是当前的趋势,这种模式可以结合传统工艺与现代技术,提高生产效率和产品质量,可以注重环保和可持续发展,采用环保材料和技术。
- 在选择经营模式时,需要考虑市场需求、资源条件、技术水平等因素,还需要注重产品质量和品牌形象,提高市场竞争力。
- 对于企业来说,需要不断进行技术创新和升级,提高生产效率和产品质量,还需要注重人才培养和团队建设,提高企业的综合实力。
- 在未来,纺织品制造经营模式可能会更加多元化和复杂化,企业需要不断探索和创新,寻找适合自己的经营模式和发展路径。
纺织品制造经营模式是一个复杂而重要的领域,需要综合考虑市场需求、资源条件、技术水平、创新能力和品牌影响力等因素。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Story of Lanzhou Haitao Textile Company
The Journey of Exquisite Durable Textiles an Insight into 秀力达纺织品



