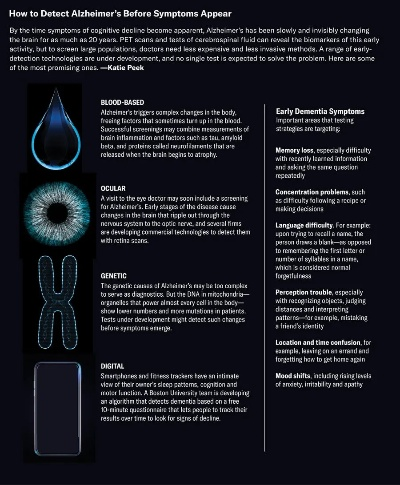
Embracing Essentials:The Art and Science of Textile Antibacterial Treatment
Introduction to Textile Antimicrobial Treatment
The textile industry is a crucial sector, responsible for producing clothing, furnishings, and other materials that touch our skin, comfort us, and protect us from harmful pathogens. In recent years, the demand for antibacterial treatments in textiles has grown exponentially, driven by an increasing awareness of hygiene concerns and the potential risks associated with bacterial infections such as MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus), E. coli, and Clostridium difficile. Textile antimicrobial technology not only enhances product performance but also plays a vital role in promoting public health and safety.
Types of Antibacterial Agents
The variety of antimicrobial agents used in textiles is vast, ranging from naturally occurring compounds like silver and copper ions, to synthetic chemicals like quaternary ammonium salts and organic amines. Each type of agent has its own unique properties and efficacy against different bacteria.
Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
Among the most widely used antimicrobials, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are particularly effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including MRSA. These tiny silver particles have a high surface area, allowing them to penetrate bacterial cell walls more effectively than larger silver ions. However, they can also be toxic to some types of cells, leading to undesired side effects.
Quaternary Ammonium Salts (QAS)
QAS are another popular choice for textile antibacterial treatment because of their broad-spectrum activity and low cytotoxicity. They work by disrupting the cell membrane of microorganisms, causing leakage of intracellular components and ultimately leading to death. However, QAS can also interact with other molecules, potentially affecting their efficacy or introducing new issues.
Organic Amine Antibacterial Agents (OAAs)
OAAs are derived from natural sources and have been shown to be relatively safe and effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. They function by forming complexes with proteins on the bacterial cell wall, disrupting normal cellular processes and ultimately leading to death. OAAs are generally considered to be less toxic than QAS, making them a preferable option for many applications.
Application Techniques in Textiles
The application techniques for textile antimicrobial treatments are essential for ensuring consistent efficacy across various products. Here are a few common methods:
Dyestuff Application
Dyestuffs, especially those containing AgNPs, can be added to dye baths during printing or dying stages to impart antibacterial properties to the fabric. This method is often employed for printed textiles, especially those intended for healthcare or hygiene applications.
Direct Addition
Antimicrobial compounds can be directly added to fiber preparations, such as cotton, wool, or silk, before spinning or weaving. This technique allows for precise control over the concentration and distribution of the antimicrobial agent throughout the fibers.
Chemical Immersion
Textiles undergo chemical immersion in an antimicrobial solution, which may include QAS or OAAs, to achieve a uniform coating on the fabric's surface. This process typically involves soaking the fabric in a solution for a specific period of time.
Membrane Coating
In this technique, a thin layer of antimicrobial material is coated onto the surface of the fabric using a solvent or emulsion. This method can provide longer-lasting protection against bacterial growth compared to simple dipping.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Textile Antimicrobial Technology
One example of successful application of textile antimicrobial technology is found in the production of disposable hospital gowns. Many hospitals use textiles that have been treated with AgNPs to prevent cross-contamination and infection among patients. Another instance is in the development of sportswear that uses antimicrobial finishing treatments to reduce the risk of bacterial infections in athletes. Such products are designed to be hygienic, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing while maintaining their protective properties.
Benefits of Textile Antimicrobial Treatments
Textile antimicrobial treatments offer several advantages over traditional cleaning methods:
-
Enhanced Hygiene: By killing or inhibiting bacterial growth on fabric, textiles treated with antimicrobial agents become safer and healthier.
-
Reduced Bacterial Resistance: Properly implemented antimicrobial treatments can help prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, thereby preserving the effectiveness of existing antibiotics.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: While initial investments may be higher upfront, antimicrobial textiles can significantly reduce maintenance costs due to reduced need for frequent sterilization and laundry services.
-
Environmental Impact: Textile antimicrobial treatments can contribute to reducing water pollution caused by excessive washing of textiles, which in turn helps mitigate the negative environmental impacts associated with textile production.
Conclusion

The integration of textile antimicrobial technologies is increasingly becoming a key factor in enhancing the overall hygiene and performance of textiles. As demand grows, it is crucial for manufacturers to balance cost-effectiveness, efficacy, and sustainability when selecting antimicrobial agents and application methods for their fabrics. With continued research and innovation, textiles will continue to play an integral role in protecting public health while also adhering to ethical standards and environmental responsibility.
随着全球抗菌需求的增长,纺织品行业对抗菌整理技术的需求也日益增加,本文将深入探讨纺织品常用的抗菌整理方法及其在实践中的应用。
抗菌整理技术概述
抗菌整理原理
抗菌整理技术主要通过添加特定的化学物质或采用特殊的表面处理工艺,使纺织品具有抗菌性能,这些物质能够抑制或杀死细菌,从而达到抗菌效果。
抗菌整理方法
(1)粉末涂料整理:通过在纺织品表面喷涂抗菌粉末涂料,达到抗菌效果。 (2)活性印花:利用活性印花技术,在纺织品纤维表面形成抗菌涂层。 (3)织物后整理:在纺织品生产过程中,通过添加特定的后处理工艺,实现抗菌效果。
案例分析
抗菌纤维的生产与应用
某知名纺织品牌采用先进的粉末涂料整理技术,生产出具有抗菌性能的纺织品,该品牌生产的衣物采用特殊配方,能够有效地抑制细菌生长,提高穿着舒适度。
抗菌印花技术的创新应用
近年来,新兴的抗菌印花技术逐渐受到市场欢迎,该技术通过在印花过程中添加抗菌剂,使印花图案具有抗菌性能,同时保持了纺织品的舒适度和美观度。
纺织品常用抗菌整理技术的应用实例
粉末涂料整理的应用实例
(1)产品描述:某品牌的高档西装外套,采用粉末涂料整理技术,衣物表面光滑细腻,具有抗菌性能。 (2)使用效果:该产品能够有效抑制细菌生长,提高穿着舒适度。
活性印花技术的应用实例
(1)产品描述:某品牌的女式连衣裙,采用活性印花技术,图案设计独特,具有抗菌性能。 (2)市场反馈:该产品受到了消费者的热烈欢迎,抗菌性能得到了广泛认可。
抗菌整理技术的未来发展趋势
新型抗菌材料的开发与应用
随着科技的不断进步,新型抗菌材料的开发与应用将成为未来纺织品抗菌整理的重要趋势,这些新型材料具有更好的抗菌性能、更好的生物相容性和更优异的环保性能。
智能化抗菌整理技术的应用
未来纺织品抗菌整理将更加智能化,通过智能化技术,可以实现纺织品抗菌性能的实时监测和控制,提高纺织品的使用效果和安全性。
纺织品常用的抗菌整理技术是提高纺织品使用效果和安全性的重要手段,随着科技的不断进步和人们对健康生活的需求增加,纺织品抗菌整理技术将得到更加广泛的应用和发展。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Chinas Textile Market Overview and Recent Trends
The Role of Textile Testing Laboratories in the Fashion Industry
The Role of China Health Textiles Association in Promoting Healthy Living
Exploring the Rich Tapestry of Cotton Textiles in Shaoxing
The Fabric of Innovation:A Look at Wenzhou Huanhong Textiles