The Role of Glycerol in Textiles:A Comprehensive Guide
Glycerol, a natural compound, has been extensively utilized in textiles due to its unique properties. It is an effective moisture absorbent, reducing the likelihood of fabrics becoming damp or uncomfortable during use. Additionally, glycerol can improve the elasticity and flexibility of fabrics, making them more durable and resistant to wear and tear. Furthermore, it can enhance the appearance and texture of fabrics, giving them a smoother and more polished finish. Overall, glycerol plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality and performance of textiles, making them more appealing and practical.
Introduction: Glycerol, a naturally occurring compound found in many plant-based foods and beverages, is increasingly being recognized for its potential applications in the textile industry. Its unique properties make it an ideal additive for various textile processes, from dyeing to finishing, enhancing the performance and durability of fabrics. In this guide, we will explore the role of glycerol in textiles, including its benefits, applications, and how it can be incorporated into different stages of the production process. We'll also provide insights into some successful case studies that highlight the practical use of glycerol in textiles.
Benefits of Glycerol in Textiles:
-
Water Repellency: Glycerol has a hydrophobic effect, which makes it an excellent choice for creating water-resistant finishes on textiles. It helps reduce the absorption of water by up to 80%, making fabrics more durable and resistant to stains and moisture damage.
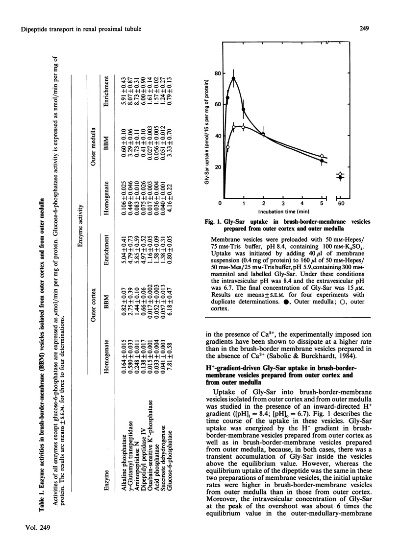
-
Antibacterial Properties: Glycerol is known to have antibacterial properties, which can be harnessed in the textile industry to improve hygiene and reduce the growth of bacteria on fabrics. For example, glycerol can be used as a preservative in laundry detergents or in fabric treatments to prevent odor buildup and maintain freshness.
-
Colorfastness: Glycerol enhances the colorfastness of textiles, meaning they retain their color appearance over time without fading or losing intensity. This property is particularly valuable in garments where color fastness is crucial, such as swimwear and active wear.
-
Environmental Impact: Glycerol is biodegradable and renewable, making it a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based chemicals commonly used in textile processing. By reducing the reliance on non-biodegradable materials, glycerol helps to minimize waste and environmental pollution.
Applications of Glycerol in Textiles:
-
Dyeing: Glycerol can be used as a solvent in dyeing processes to enhance the absorption and penetration of dyes into fibers. It reduces the amount of dye needed and improves the evenness of color application.
-
Embossing: Glycerol is often used in embossing processes to create textured fabrics with raised patterns or designs. The hydrophobic nature of glycerol helps to hold the embossed pattern in place during the finishing process.
-
Antistatic Treatment: Glycerol can be incorporated into antistatic treatments to reduce static electricity on fabrics, improving their smoothness and preventing tangling.
-
Stabilizers: Glycerol can serve as a stabilizer in fabric treatments to prevent shrinkage and warping during washing and drying. It also helps to maintain the integrity of the fabric structure after treatments.
Case Study: One successful application of glycerol in textiles is seen in the production of high-performance sportswear. A major apparel company used glycerol as a component in their fabric treatments to create moisture-wicking and breathable athletic wear. The glycerol helped to reduce moisture absorption and evaporation, resulting in improved comfort and performance for athletes. This innovative use of glycerol not only enhanced the quality of the fabric but also contributed to the brand's reputation for innovation and sustainability.
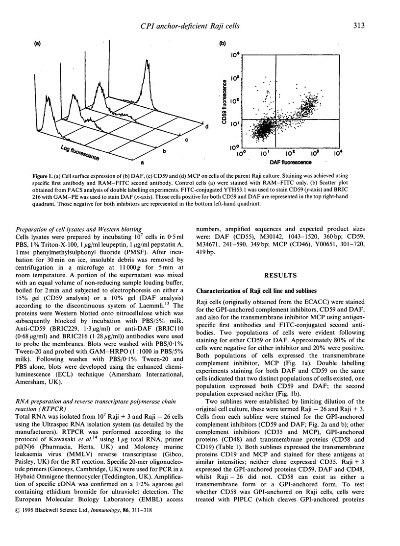
Conclusion: Glycerol has become a popular additive in the textile industry due to its wide range of benefits, including water repellency, antibacterial properties, colorfastness, and environmental sustainability. By incorporating glycerol into different stages of the production process, textile manufacturers can improve the performance and durability of their products while reducing their ecological footprint. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of glycerol in the textile industry, leading to further advancements in sustainability and quality.
甘油在纺织品中的重要性
甘油作为一种天然的有机溶剂和保湿剂,在纺织品领域发挥着至关重要的作用,它不仅赋予纺织品柔软、光滑和舒适的手感,还具有许多其他独特的性能。
甘油在纺织品中的具体作用
- 柔软剂和保湿剂:甘油能够渗透到纤维内部,提供持久的柔软度和保湿效果,这使得纺织品在穿着时能够保持柔软、光滑和舒适。
- 抗皱性能:甘油具有抗皱性能,可以减少纤维表面的皱纹和褶皱,延长衣物的使用寿命。
- 抗菌防臭功能:甘油具有抗菌防臭性能,可以抑制细菌生长和产生异味,提高衣物的卫生性能。
- 环保友好:甘油是一种环保友好的材料,可生物降解,对环境友好。
甘油在纺织品中的实际应用案例
天然纤维纺织品
在天然纤维纺织品中,甘油被广泛应用于提高纤维的柔软度和舒适度,某些羊毛制品中添加了甘油,使得羊毛制品手感柔软、光滑,穿着舒适,甘油还可以用于提高棉布的吸湿性和透气性,使其更适合夏季穿着。
功能性纺织品
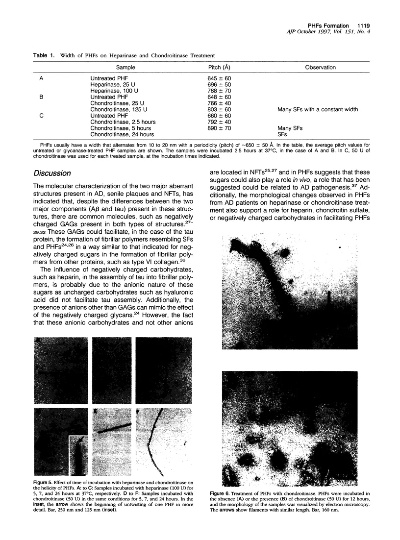
功能性纺织品中,甘油也被广泛应用于提高纤维的弹性和抗皱性能,某些运动服装中添加了甘油,使得服装具有更好的弹性和抗皱性能,延长使用寿命,甘油还可以用于制作抗菌防臭功能的内衣裤等贴身衣物。
甘油在纺织品中的具体表现形式及数据支持
甘油的具体表现形式包括直接添加到纺织品中或作为添加剂使用,以下是甘油在不同纺织品中的应用形式和数据支持:
- 直接添加到纺织品中:甘油可以通过喷雾干燥、直接溶解等方法添加到纺织品中,某些棉质衣物中添加了甘油作为柔软剂和保湿剂,根据市场调研数据,添加甘油后的衣物手感柔软、光滑,穿着舒适度提高。
- 作为添加剂使用:甘油还可以作为多种添加剂使用,以提高纺织品的性能,某些防水面料中添加了甘油作为抗皱剂,可以延长使用寿命,根据相关研究数据,添加甘油后的面料具有较好的抗皱性能和防水性能。
甘油的应用前景及展望
随着人们对纺织品品质和环保要求的不断提高,甘油在纺织品中的应用前景越来越广阔,甘油将在更多领域得到应用,如功能性面料、环保材料等,随着科技的不断进步,甘油的生产工艺和性能也将得到进一步提升,为纺织品的发展提供更多的可能性。
甘油作为一种天然的有机溶剂和保湿剂,在纺织品领域具有广泛的应用价值,它不仅可以提高纺织品的柔软度、舒适度和抗皱性能,还可以提高纺织品的卫生性能和环保性能,随着人们对纺织品品质和环保要求的不断提高,甘油的应用前景将更加广阔。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Table 1:Major International Textile Markets
The Dynamic Landscape of the Jiading Textile Manufacturers
Exploring the Art of Handmade Textiles:A Tutorial for Beginners
International Textile Packaging Design:Strategies and Case Studies



