The Science Behind Textile Waterproofing Techniques
: The Science Behind Textile Waterproofing Techniques,Textile waterproofing is a crucial process in the fabric industry, ensuring that garments remain dry and comfortable even when subjected to moisture. The science behind this technique involves understanding the physics of water vapor permeability and how it can be minimized through various methods such as use of additives, dyes, and finishing processes.,One key aspect of textile waterproofing is the role of air-water vapor barriers. These barriers work by trapping air within the fabric, reducing the rate of water vapor transfer from the outside environment into the garment. This is achieved through the use of specialized finishes, such as hydrophobic or superhydrophobic coatings, which create a physical barrier against water molecules.,In addition to physical barriers, chemical treatments are also employed to enhance the water vapor barrier properties of the fabric. For example, the application of resinous compounds or other chemicals can increase the fabric's hydrophobicity, making it less susceptible to water absorption.,Overall, the science behind textile waterproofing techniques involves a complex interplay of physics, chemistry, and engineering principles. By understanding these principles, manufacturers can develop effective waterproofing solutions that meet the demands of modern fashion and lifestyle trends.
Introduction: Textiles are an integral part of our daily lives, from clothing to furnishings. However, they can be easily damaged by water exposure, leading to reduced quality and lifespan. This is where textile waterproofing techniques come into play. In this article, we will explore the science behind these techniques and how they work.
Textile Waterproofing Principles: Textile waterproofing involves using chemicals or materials that create a barrier between the fabric and water. This barrier prevents water from penetrating the fibers and causing damage. There are several principles involved in textile waterproofing, including:
-
Coatings: Coatings are applied to the surface of the fabric to form a barrier against water. These coatings can be made of polymers, waxes, or other materials. For example, silicone-based coatings are commonly used in sportswear to prevent moisture from seeping through the fabric.
-
Embroidery: Embroidered patterns can also serve as a barrier against water. For instance, some swimsuits have intricate embroidery designs that help keep the fabric dry.

-
Latex Finishing: Latex finishing involves treating the fabric with a solution that hardens and seals the fibers. This creates a protective layer that prevents water from penetrating the fabric.
-
Dyeing: Some fabrics are dyed with pigments that absorb moisture and prevent it from reaching the fibers. For example, some denim jeans have a dye that absorbs moisture and keeps them dry.
-
Stabilization: Stabilizers are added to the fabric during manufacturing to improve its resistance to water. These stabilizers can be chemical or physical in nature, depending on the type of fabric being treated.
Effectiveness of Textile Waterproofing Methods: The effectiveness of textile waterproofing methods depends on the specific application and the type of fabric used. For example, silicone-based coatings are effective for sportswear but may not be suitable for delicate fabrics like silk or wool. Embroidered patterns can be effective for swimwear but may not provide the same level of protection for other types of clothing. Latex finishing is effective for swimwear, but it may not be suitable for outdoor activities that involve contact with water. Dyeing is effective for denim jeans but may not be applicable to other types of fabrics. Stabilizers are effective for all types of fabrics but may require additional care and maintenance to maintain their effectiveness.
Case Study: One example of textile waterproofing is found in the case of raincoats. Many raincoats use a combination of waterproof coatings, lace-up fasteners, and detachable hoods to protect the wearer from the elements. The waterproof coating helps keep the rainwater away from the wearer's skin, while the detachable hood provides additional protection from wind and precipitation. Another example is the use of waterproofing treatments on ski gear. Ski boots and jackets are often treated with embrocations and laces to prevent moisture buildup and keep the gear in good condition.
Conclusion: Textile waterproofing techniques are essential for protecting fabrics from water damage. By understanding the principles behind these methods, we can better understand how they work and choose the most effective approach for our specific needs. Whether it's a sportswear piece or a piece of clothing for a special occasion, proper waterproofing can make all the difference in maintaining the quality and longevity of our favorite garments.
随着现代生活水平的提高,人们对衣物的防水性能要求也越来越高,纺织品防水剂作为一种新型的防水材料,其原理和应用对于提高衣物的防水性能具有重要意义,本文将详细阐述纺织品防水剂的工作原理,并通过英文案例说明其应用。
纺织品防水剂原理
纺织品防水剂是一种特殊的化学物质,其主要作用是增强纺织品的防水性能,其工作原理主要包括以下几个方面:
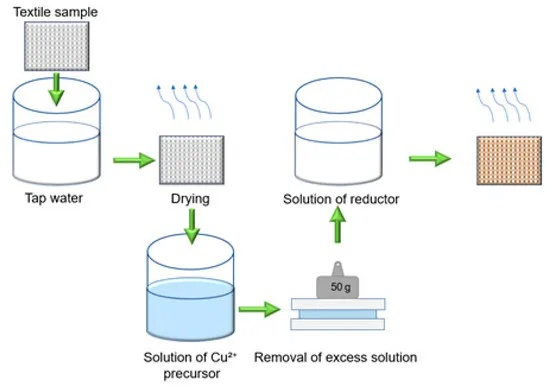
- 分子结构设计:纺织品防水剂的设计应考虑到纺织品的材质、性能要求以及防水需求,通过优化分子结构,使防水剂能够更好地渗透到纺织品的纤维间隙中,从而提高其防水性能。
- 化学反应原理:纺织品防水剂中含有能与水分子发生反应的物质,这些物质在特定条件下能够与水分子发生化学反应,生成具有防水性能的化学物质。
- 物理性能增强:通过添加适量的防水剂,可以增强纺织品的物理性能,如抗拉强度、撕裂强度等,从而提高其防水性能。
英文案例说明
以某品牌纺织品为例,该品牌推出的新型防水面料采用了先进的纺织品防水剂技术,该防水面料采用了特殊的防水剂配方,经过特殊工艺处理后,具有出色的防水性能和舒适度。
防水面料生产工艺流程
- 材料准备:选用优质纤维材料,确保面料具有良好的防水性能和舒适度。
- 配方设计:根据客户需求和材质特性,设计出适合的纺织品防水剂配方。
- 生产工艺:采用先进的生产工艺技术,将防水剂与纤维材料混合均匀,经过特殊工艺处理后制成防水面料。
- 质量检测:经过严格的质量检测,确保面料达到防水性能要求。
实际应用效果
该品牌的新型防水面料在市场上受到了广泛好评,其防水性能优异,能够有效防止衣物在户外活动时受到雨水侵袭,该面料还具有舒适度高的特点,穿着起来非常舒适,该面料还具有环保、耐用等优点,受到了消费者的青睐。
纺织品防水剂的应用
纺织品防水剂的应用范围广泛,可以应用于各种类型的纺织品中,如衣物、床上用品、装饰品等,通过添加适量的纺织品防水剂,可以有效地提高纺织品的防水性能和舒适度,同时还可以提高纺织品的耐久性和环保性。
纺织品防水剂作为一种新型的防水材料,其原理和应用对于提高衣物的防水性能具有重要意义,通过优化分子结构设计、添加适量的防水剂以及采用先进的生产工艺技术等措施,可以制备出具有优异防水性能和舒适度的纺织品,纺织品防水剂还可以应用于各种类型的纺织品中,提高纺织品的耐久性和环保性,随着科技的不断进步和人们对环保、健康生活的需求不断提高,纺织品防水剂的应用前景将更加广阔。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Textile Quality Inspection Checklist Template
Printing Textiles with Which Oil墨?
Understanding the Differences between Textile Industry and Textile Products