Defining the Dimensions of Textile Thickness
Textile thickness is a critical factor in determining the quality and performance of textile products. It refers to the distance between the fibers or yarns in a textile material, measured in micrometers or millimeters. The thickness of a textile can affect its strength, durability, and appearance. For example, thicker fabrics are more resistant to creasing, while thinner ones may be more prone to pilling or wrinkling. Additionally, the thickness of a textile can impact its weight, which can affect comfort and functionality. Therefore, it is important for manufacturers to carefully define the dimensions of textile thickness to ensure that their products meet the desired specifications and meet the needs of their intended users.
Introduction: Textile thickness is a critical factor that affects the quality, durability, and performance of various textile products. It refers to the distance between two parallel planes in a fabric, measured perpendicularly to the length of the fabric. In this discussion, we will explore the different types of textile thicknesses and their applications in various industries.
Types of Textile Thickness:

-
Coarse Thickness (CTH): This type of thickness is characterized by a large distance between the fibers. It is commonly found in rugs, carpets, and other outdoor fabrics that require resistance to wear and tear. For example, a coarse thickness of 3 mm may be suitable for a rug that is exposed to heavy foot traffic.
-
Medium Thickness (MT): This type of thickness has a moderate distance between the fibers. It is commonly used in apparel, curtains, and upholstery fabrics. A medium thickness of 1 mm may be suitable for a shirt that requires breathability and comfort.
-
Fine Thickness (FT): This type of thickness is characterized by a small distance between the fibers. It is commonly used in sportswear, swimwear, and other garments that require flexibility and moisture management. For example, a fine thickness of 0.5 mm may be suitable for a swimsuit that needs to be lightweight and quick-drying.
-
Ultrafine Thickness (UFT): This type of thickness is extremely thin, with a very small distance between the fibers. It is commonly used in microfiber materials, such as face masks and surgical gowns. A ultrafine thickness of 0.1 mm may be suitable for these products due to their ability to trap and filter particles effectively.
Applications of Textile Thickness: Textile thickness plays a crucial role in determining the performance and usability of various textile products. Here are some examples of how textile thickness can be applied in different industries:
-
Fashion Industry: Textile thickness is an important factor in determining the style and fit of clothing. For example, a thicker fabric may provide more support and coverage, while a thinner fabric may be more comfortable and breathable.
-
Home Decoration: Textile thickness can affect the appearance and functionality of home decor items. For example, a thicker rug may provide better protection against dirt and stains, while a thinner one may be easier to clean and maintain.
-
Sportswear: Textile thickness is essential for sportswear to provide adequate support and protection during physical activities. For example, a thicker fabric may provide better cushioning and shock absorption, while a thinner one may be more flexible and comfortable.
-
Medical Equipment: Textile thickness is crucial for medical equipment to ensure safety and effectiveness. For example, a thinner material may be more resistant to bacterial growth, while a thicker one may provide better protection against infection.
Conclusion: Textile thickness is a critical factor that affects the quality, durability, and performance of various textile products. By understanding the different types of textile thicknesses and their applications, we can make informed decisions about the materials we use in our daily lives and work. Whether it's choosing the right fabric for a piece of clothing or selecting the appropriate thickness for a home decor item, textile thickness plays a vital role in ensuring that our products meet our needs and expectations.
大家好,今天我们将一起探讨纺织品厚度这一重要指标及其在纺织行业中的应用,在讲解过程中,我们将结合图表和案例,帮助大家更好地理解纺织品厚度的定义及其在实际应用中的重要性。
纺织品厚度定义图例讲解
基础概念
纺织品厚度通常用单位毫米(mm)或微米(μm)来表示,图例中通常会显示不同厚度级别的标识,例如超薄、轻薄、中等厚度和厚型等,这些标识可以帮助消费者了解不同纺织品的厚度特性。
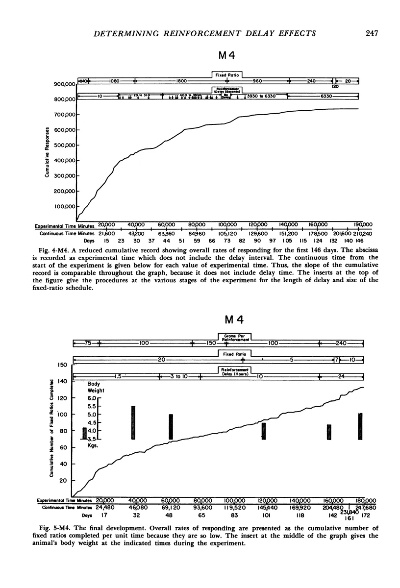
图例展示
(1)毫米级图例示例:
图1:纺织品厚度图例示例
+ 超薄:表示厚度极薄,适合追求轻便、舒适感的场合。
+ 轻薄:表示厚度适中,适合日常穿着或轻便场合。
+ 中等厚度:表示具有一定厚度,适合特定用途或特定款式。
+ 厚型:表示厚度较大,适合需要承受一定重量或特殊性能的场合。(2)微米级图例示例:
图2:纺织品厚度微米级图例示例
在微米级别,厚度通常以微米为单位进行测量,例如XX微米,这种级别的厚度测量对于精确控制纺织品的性能和品质至关重要。
案例分析
(1)案例一:纺织品轻薄度的应用场景
假设某品牌的新款轻薄型针织衫,其厚度仅为XX微米,非常适合追求时尚和舒适感的年轻消费者,这款针织衫不仅轻便,而且具有良好的透气性和保暖性,非常适合春夏季节穿着。
(2)案例二:纺织品厚度的特殊用途
在某些特殊场合,如航空航天领域,纺织品需要承受高强度和耐久性要求,在这些场合下,厚型纺织品被广泛应用于制造高性能的防护服和宇航服,这些厚型纺织品不仅具有出色的防护性能,而且能够承受极端环境下的压力和温度变化。
图例补充说明
在纺织品厚度图例中,除了基本的标识外,还可以添加一些补充说明来帮助消费者更好地理解不同厚度的特性,可以添加以下补充说明内容:
- 材料类型说明:不同材料的厚度特性不同,例如棉、涤纶等材料的厚度特性会有所差异,在图例中可以明确标注材料类型。
- 工艺流程说明:对于特殊工艺流程的纺织品,可以在图例中说明其厚度控制过程和工艺特点,某些纺织品的制造过程中需要进行特殊的涂层处理或织造工艺等。
- 应用领域说明:对于不同应用领域的纺织品,可以在图例中说明其适用场景和特点,某些纺织品适用于高档服装、运动装备等领域。
通过本次讲解,我们希望大家能够更好地理解纺织品厚度这一重要指标及其在实际应用中的重要性,在实际应用中,我们需要注意选择合适的厚度级别和材料类型,以确保纺织品具有良好的性能和品质,我们还需要注意纺织品的特殊工艺流程和特殊用途要求,以确保其符合特定场合的需求。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Understanding the World of Textile Ingredients and Components
A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up a Textile Company
The Unique Sites of the Special Needlework Textiles Wholesale Market in Suzhou