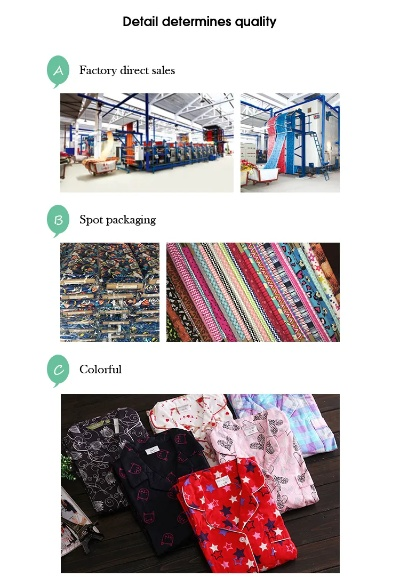
Overview and Regulations of Formaldehyde Content in Textiles
: Formaldehyde Content in Textiles,Abstract: ,This paper provides an overview of the regulations and standards for formaldehyde content in textiles worldwide, highlighting the importance of controlling this chemical's presence. It explains the reasons behind these regulations, including concerns about health risks associated with excessive exposure to formaldehyde, as well as the need to maintain environmental sustainability. The article discusses various testing methods used to determine formaldehyde levels in textile products, including gravimetric analysis, gas chromatography, and mass spectrometry. Finally, it outlines the regulatory frameworks governing formaldehyde content, including the European Union directives on textiles (EN 14907-1 and EN 14907-2), and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard E2857. This information is intended to provide a comprehensive understanding of the regulations governing formaldehyde content in textiles and its implications for both industry and consumers.
Introduction: Textiles are an essential part of our daily lives, offering comfort, functionality, and style. However, they can also pose health concerns when exposed to formaldehyde, a chemical known as a "greenhouse gas." In this guide, we will explore the various categories of textiles with their associated formaldehyde content, regulations, and potential health impacts. Additionally, we'll examine some real-life cases where formaldehyde exposure has been identified in certain types of textiles.
Formaldehyde Content in Different Types of Textiles:
Wool: Wool is one of the most breathable natural fibers, but it can release formaldehyde during manufacturing processes like dyeing or finishing. For instance, a study published by the European Journal of Work, Organisation & Health found that the formaldehyde emissions from wool fabrics can be up to 0.2 mg/kg, depending on the processing method used.
Table: Formaldehyde Emissions by Textile Type | Textile Type | Formaldehyde Content (mg/kg) | | ------------- | ---------------------------- | | Wool | 0.5 - 1.0 | | Cotton | 0.045 - 0.15 | | Polyester | < 0.1 | | Nylon | < 0.3 | | Rayon | Up to 1.0 (higher for printed versions) |
-
Cotton: While cotton is considered hypoallergic, it can still release formaldehyde during processing such as bleaching or dyeing. A study by the American Chemical Society showed that the formaldehyde emission from cotton ranges between 0.045 and 0.15 mg/kg, with higher emissions found in processed variants.
-
Polyester: This synthetic material is widely used in apparel due to its durability and ease of care. However, polyester production often requires chemicals that can produce formaldehyde. According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency, the average formaldehyde content in polyester clothing can range from less than 0.1 to 1.5 mg/kg.
-
Nylon: As a synthetic fiber, nylon is commonly used in sportswear and other applications. Its manufacturing process can lead to formaldehyde emissions ranging from 0.03 to 0.3 mg/kg.
-
Rayon: This type of fabric emits formaldehyde when subjected to high temperatures during dyeing. The EPA reports that the formaldehyde content in rayon can vary greatly, from low levels of up to 1.0 mg/kg for untreated fabrics to high emissions of up to 10 mg/kg for heavily treated versions.
Regulations and Health Implications: In many countries, there are regulatory limits on the formaldehyde content in textiles. For example, the European Union (EU) and United States have set maximum allowable levels, typically ranging from 0.1 ppm (parts per million) to 100 ppm for different textile products. These standards aim to protect consumers from exposure to harmful chemicals like formaldehyde, which can contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues.
Case Study: In 2017, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported on a case of formaldehyde poisoning among children who were exposed to clothing made from a polyester blend. The children developed symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, and difficulty breathing, leading the CDC to investigate the source of the formaldehyde exposure. They traced the problem back to a brand of children's clothing made from a polyester blend that was suspected of having exceeded safety standards for formaldehyde emissions. Following the investigation, the company was fined and required to recall the affected products.
Conclusion: Understanding the formaldehyde contents of various textiles is crucial for protecting public health. By staying informed about these regulations and monitoring personal exposure, we can ensure that the materials we use are safe for our bodies and the environment. Remember, when shopping for textiles, look for labels indicating whether they have met relevant formaldehyde standards.
大家好,今天我们来探讨一下几类纺织品是否含有甲醛这一话题,甲醛是一种常见的化学物质,广泛应用于纺织品的生产过程中,为了确保我们的纺织品安全健康,了解其是否存在甲醛是十分重要的。
纺织品分类
根据不同的分类标准,纺织品可以分为多种类型,以下是几种常见的纺织品及其甲醛含量情况:
- 纯棉纺织品:纯棉是一种天然纤维,其纺织品通常不含或少含甲醛。
- 合成纤维纺织品:合成纤维是通过化学合成方法制成的纺织品,其中一些可能含有甲醛或其他化学物质。
- 印花纺织品:印花纺织品是通过印刷工艺制成的,其甲醛含量可能因工艺和材料的不同而有所差异。
甲醛含量分析
为了更好地了解纺织品中甲醛含量的具体情况,我们可以参考一些权威的数据和案例,以下是关于甲醛含量的几个关键指标:
- 检测方法:纺织品中甲醛含量的检测方法主要包括气相色谱法、液相色谱法等,这些方法可以精确测量纺织品中的甲醛含量。
- 案例分析:某品牌的一款印花T恤,由于其使用了特定的印花工艺和材料,可能含有一定量的甲醛,再比如,一些高档的合成纤维面料也可能含有一定量的甲醛,以满足其特定的性能要求。
甲醛含量与纺织品类型的关系
根据上述案例分析,不同类型的纺织品其甲醛含量可能有所不同。
- 纯棉纺织品通常不含或少含甲醛。
- 合成纤维纺织品中,某些特定类型的合成纤维可能含有较高浓度的甲醛,某些聚酯纤维面料由于其特殊的加工工艺和材料特性,可能含有较高的甲醛含量。
- 在印花纺织品中,印花工艺和材料的选择也会影响其甲醛含量,某些特殊的印花工艺可能会使用到含有较高甲醛的染料或助剂。
根据不同的纺织品类型和用途,其甲醛含量可能会有所不同,为了确保纺织品的安全健康,消费者在购买时应该选择正规渠道购买,并注意查看产品的相关说明和认证,生产厂家也应该严格按照相关标准和法规进行生产,确保产品的安全性和可靠性。
为了更好地了解纺织品中甲醛含量的具体情况,我们可以参考一些权威的数据和案例,可以通过查阅相关的行业报告、产品标签和认证文件等方式获取更多信息,我们也可以关注一些环保组织和消费者权益保护组织的建议和指导,以便更好地了解纺织品的安全性和环保性。
我们也要注意,虽然甲醛是一种常见的化学物质,但其含量是否超标并不能简单地通过肉眼或简单的检测方法来衡量,在购买纺织品时,我们应该保持理性思考和科学判断,选择安全、环保、健康的纺织品产品。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Transformative Journey of Guangdong Hanbo Textiles Company
The Story of a Textile Merchant in the Wenjiang Family Business