The Basic Structure of Textiles:An Insight into the Fundamentals
The Basic Structure of Textiles: An Insight into the Fundamentals,Textiles are a fundamental aspect of our lives and have evolved over time to become an integral part of human civilization. The basic structure of textiles is made up of three main components: fiber, weft, and warp. Fibers are the building blocks of textiles and come in various forms such as cotton, wool, silk, and synthetic materials. Weft refers to the continuous thread that runs along the length of the textile, creating its intricate patterns and designs. Warp, on the other hand, is the vertical thread that creates the foundation for the weft threads. Together, these three components form the structure of a textile and contribute to its unique characteristics and properties. In addition to their structural importance, textiles also play a crucial role in promoting cultural exchange and preserving traditions. As technology continues to advance, new materials and techniques are being developed to create textiles with even greater durability, sustainability, and functionality.
In the realm of textiles, a fundamental understanding of their structure is crucial for designers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. This article delves into the key parameters that underpin the fabrication of these textiles, providing an overview of the materials used, the processes involved, and the resulting characteristics. We will also delve into the importance of these parameters in shaping the end product's performance and functionality.
The basic structure of textiles can be broken down into several key components: fibers, yarns, and weaves. These are all essential building blocks of any textile product.

-
Fibers: The primary material used in textiles is the fibrous element, which gives them their shape and texture. Fibers can be natural or synthetic, with varying properties such as strength, flexibility, and resilience. Common examples include cotton, wool, silk, polyester, and nylon. Each fiber has its unique set of characteristics that determine how it behaves when subjected to different conditions, from temperature to moisture content.
Example: Cotton, a staple fiber derived from the seeds of various species of cotton plants, is soft to the touch and breathable. It offers a range of colors and patterns, making it versatile for use in a wide variety of textile applications.
-
Yarns: Yarn is a bundle of fibers held together by twist or by using a binder such as starch or cellulose. Yarns serve as the backbone of textile products, determining the strength and durability of the final item. They are categorized based on their thickness (e.g., thick, medium, thin) and their level of twist (e.g., single, double, triple).
Example: A simple but effective yarn example would be a cotton-polyester blended yarn used in a t-shirt shirting. The cotton provides comfort and breathability, while the polyester adds durability and resistance against wear and tear.
-
Weaves: Finally, the weave refers to the way the fibers are interlaced to create a pattern. There are many types of weaves, including plain weave, satin weave, rib weaves, and others. Each type imparts different levels of strength, stretchiness, and texture to the finished product.
Example: In terms of weaves, consider a classic cotton sateen weave. This weave is characterized by a soft, lightweight feel and a smooth finish due to the open spaces between the threads. It is perfect for summer dresses and other casual wear, where lightness and breathability are priorities.
Beyond just the basic structure, there are numerous other parameters to consider when working with textiles. For instance, the environmental impact of the materials used, the energy required for production, and consumer preferences all play a role in shaping the industry's future.
In conclusion, textiles are multifaceted materials that embody the essence of craftsmanship and innovation. By understanding their basic structure, one can appreciate their beauty and functionality, and even begin to explore more advanced techniques and applications. Whether you're designing new garments, creating functional textiles, or simply admiring the artistry of existing pieces, the principles behind textile structure hold great promise for both artistic expression and practical application.
纺织品基本结构参数概述
纺织品是日常生活中不可或缺的组成部分,其基本结构参数对于保证产品的质量和性能至关重要,本文将详细介绍纺织品的基本结构参数及其在实际应用中的重要性。
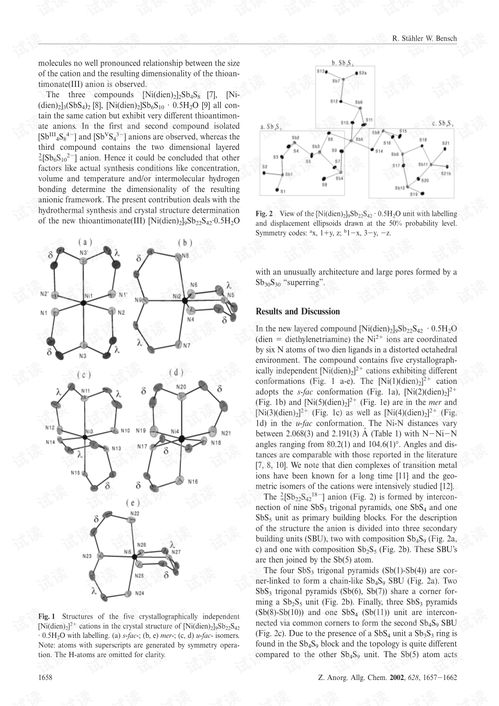
纺织品基本结构参数的表格说明
以下是关于纺织品基本结构参数的表格说明:
| 参数名称 | 英文术语 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 纤维类型 | Fiber Type | 如棉、涤纶等,用于描述纺织材料的种类 |
| 密度 | Density | 每单位体积内纤维的数量,影响织物的厚度和强度 |
| 织造方式 | Weaving Method | 如平纹、斜纹等,用于描述织物的纹理和结构 |
| 纱线直径 | yarn diameter | 纱线细度的衡量标准,影响织物的纹理和手感 |
| 织物厚度 | Fabric Thickness | 通过单位面积内的纱线数量来衡量,影响织物的柔软度和舒适度 |
| 织物宽度 | Fabric Width | 织物横截面尺寸,影响产品的尺寸和形状 |
| 抗皱性 | Wrinkle Resistance | 纺织材料抵抗褶皱的能力,影响产品的使用寿命和外观质量 |
| 吸湿性 | Moisture Absorption | 纺织材料吸收水分的能力,影响产品的透气性和舒适度 |
纺织品案例说明
以纺织品为例,说明其基本结构参数在实际应用中的重要性,以下是一个具体的纺织品案例:
纯棉面料
纯棉面料是一种常见的纺织品,其基本结构参数包括纤维类型(纯棉)、密度(适中)、织造方式(平纹)等,纯棉面料具有吸湿性好、透气性强、柔软舒适等特点,适合制作各种衣物和家居用品,在具体应用中,可以根据产品需求选择合适的纤维类型和织造方式,以达到最佳的产品性能和外观质量。
涤纶高密网布面料
涤纶高密网布面料是一种高性能纺织品,其基本结构参数包括纤维类型(涤纶)、高密度(高强度和高透气性)等,涤纶高密网布面料具有高强度、高耐磨性、高吸水性等特点,适用于制作各种工业用品和运动器材,在具体应用中,可以根据产品需求选择合适的纤维类型和织造方式,以及合适的厚度和宽度,以达到最佳的产品性能和外观质量。
纺织品的基本结构参数对于保证产品的质量和性能至关重要,在纺织品的生产过程中,需要综合考虑纤维类型、密度、织造方式、纱线直径、织物厚度、织物宽度等多个因素,以达到最佳的产品性能和外观质量,在实际应用中,还需要根据产品需求选择合适的结构参数,以达到最佳的使用效果和经济效益。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Top Picks for Shanghai Home Textile Essentials
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Fabrics for Your Next Project
Exploring the Art of Craftsmanship at Shaoxing Xiezhi Textiles
Exploring the Rich Tapestry of Textiles from Nantong Mei Nián Hua
Essential Guidelines for Verifying Furniture amp;Textile Items During Import
The Pinnacle of Fashion at Nantong A Closer Look at Nanton Power-Up Textiles



