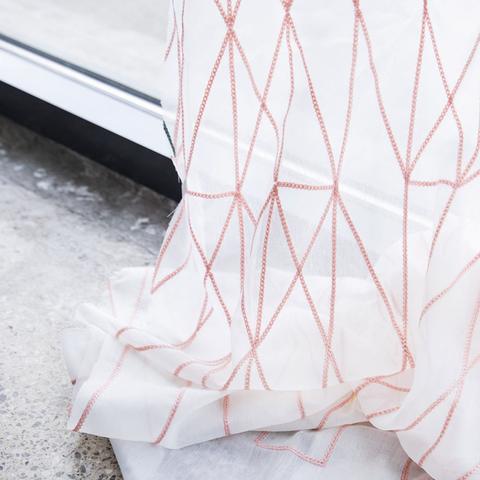
The Textiles Technique of Matrix Patterning
This study focuses on the textile technology of matrix patterning, an innovative method that involves creating a patterned surface on a textile material using a matrix. The primary goal is to create a visually appealing design by utilizing a matrix as both the pattern and the support for printing or dyeing the textile. The technique involves several key steps, including designing the pattern, selecting the appropriate matrix, preparing the textile substrate, and applying the matrix to achieve the desired pattern.,One significant advantage of matrix patterning is its versatility in generating complex and multi-colored designs. This technique can be used for various applications, such as apparel, home decor, and even industrial materials. It provides designers with the flexibility to create intricate patterns and designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and durable.,In conclusion, matrix patterning is a fascinating textile technology that offers endless possibilities for creating visually striking designs on textiles. Its versatility and ease of application make it an essential tool for those seeking innovative and high-quality products.
Introduction: In the realm of textile design and production, matrix patterning stands out as a versatile and innovative technique used to achieve a variety of visual effects. Originating from the concept of using two-dimensional grid patterns on fabrics to create a three-dimensional effect, this method has become a staple in modern fashion, home décor, and industrial applications. In this article, we will delve into the principles of matrix patterning, its application examples, and how it can transform the way we perceive textiles.
Principles and Techniques: Matrix patterning involves the use of geometrical shapes, often square or rectangular, arranged in an array on a substrate material like cotton or polyester. This process is typically done by cutting these shapes from a continuous length of fabric and then placing them onto the surface. The fabric's fibers are aligned with the lines of the pattern, resulting in a distinct pattern that appears as if the fabric is being cut along these lines.
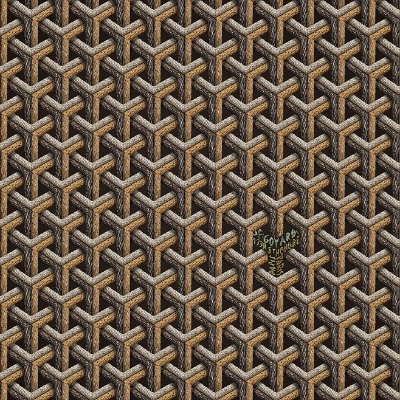

The process of matrix patterning can be further enhanced through various techniques such as stenciling, embossing, and digitization. Stenciling involves manually tracing designs onto the fabric and applying them with a stencil. Embossing involves using a die to press down the fabric onto a pattern, creating a raised texture. Digitization allows for the use of software to design and apply patterns digitally on fabrics, offering more precise control and flexibility.
Application Examples: The matrix patterning technique is not limited to just fashion garments or home decor. Here are some examples of how this technique has been applied in different sectors:
Fashion Design:
- Streetwear: Many streetwear brands use matrix patterning to create unique and eye-catching garments. For instance, Nike's Air Max shoes feature a grid pattern printed on the upper part of the shoe, creating a playful yet stylish look.
- Leather Jackets: Leather jackets often feature a matrix pattern printed on the exterior to give them a rugged and sophisticated look.
Home Decor:
- Throw Blankets: Home decor enthusiasts have begun incorporating matrix patterns into their throw blankets, adding a touch of elegance without breaking the bank.
- Wall Art: Matrix patterned canvases and wallpapers have become popular in contemporary homes, offering a bold contrast against plain walls.
- Tablecloths: Tablecloths featuring intricate matrix patterns add a modern flair to dining experiences.
Industrial Applications:
- Textile Printing: Matrix patterning is widely used in textile printing, where it enhances the durability and appearance of printed fabrics.
- Sportswear: Sports apparel manufacturers utilize matrix patterning in their designs to provide better support and breathability.
Transformation of Perception: Matrix patterning isn't just about aesthetics; it also plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality of fabrics. For example, the grid pattern on a shirt can help distribute pressure evenly across the shoulders, making it comfortable to wear. Additionally, certain patterns may serve practical purposes such as preventing pilling or improving the durability of the fabric.
Conclusion: The textiles technique of matrix patterning offers a wide range of possibilities for designers looking to bring their vision to life. From the runway to the home, from the fashion industry to industrial applications, this technique continues to inspire and captivate audiences around the world. As technology continues to advance, so too does our ability to manipulate fabrics and create unique designs. Let's keep exploring the limitless potential of matrix patterning and its many facets of textile design.
纺织品变格排列方法概述
在纺织品行业中,变格排列方法是一种重要的工艺技术,它涉及到对纺织品材料、颜色、纹理等要素的优化组合和排列组合,以下是关于纺织品变格排列方法的简要介绍。
纺织品变格排列方法的基本步骤
- 材料选择与评估:需要选择适合变格排列的纺织品材料,这需要考虑材料的质地、颜色、纹理等因素。
- 设计布局:根据市场需求和设计理念,设计出合理的纺织品排列布局,这包括颜色搭配、图案组合、层次感等要素。
- 切割与整理:根据设计布局,对纺织品进行切割和整理,使其达到最佳排列效果。
- 质量控制:在排列过程中,严格控制质量标准,确保每一步骤都符合要求。
案例分析

以纺织品变格排列为例,我们可以采用英文表格进行详细说明。
纺织品变格排列案例
| 序号 | 纺织品材料 | 材料特性 | 设计布局 | 切割与整理步骤 | 质量控制标准 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 案例一 | 纯棉面料 | 柔软、透气、舒适 | 颜色搭配鲜艳,图案简洁大方 | 切割成不同尺寸的条状或块状 | 严格按照质量标准进行切割和整理 |
| 案例二 | 丝绸面料 | 光滑、细腻、高贵 | 色彩丰富,纹理独特 | 设计成波浪形或条纹状排列 | 在排列过程中注重纹理的层次感和光泽度 |
| 案例三 | 混纺面料 | 综合性能优良,颜色丰富 | 根据市场需求设计布局,注重色彩搭配和层次感 | 采用不同的切割方式,如块状与条状结合,注重整体美观效果 | 在排列过程中严格控制颜色搭配和纹理一致性 |
纺织品变格排列方法的具体方法
- 材料选择与评估的方法:根据市场需求和设计理念,选择适合变格排列的纺织品材料,这需要考虑材料的质地、颜色、纹理等因素,可以通过观察样品、测试样品等方式进行评估。
- 设计布局的方法:在设计布局时,需要考虑色彩搭配、图案组合、层次感等因素,可以通过色彩搭配、图案组合等方式来营造出不同的视觉效果,还需要考虑纺织品的尺寸、形状等因素,以确保排列后的纺织品符合要求。
- 切割与整理的具体步骤:在切割与整理过程中,需要严格按照设计布局的要求进行操作,这包括切割成不同尺寸的条状或块状,整理成整齐划一的形式等,还需要注意切割和整理的质量标准,确保每一步骤都符合要求。
纺织品变格排列是一种重要的工艺技术,它涉及到对纺织品材料、颜色、纹理等要素的优化组合和排列组合,在变格排列过程中,需要选择适合的材料和设计布局,并严格按照质量控制标准进行操作,还需要注意细节和技巧,以确保排列后的纺织品符合要求,通过不断学习和实践,可以不断提高纺织品变格排列的技术水平。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Multifaceted Landscape of Textile Finishing
The Dynamics of Sustainable Fashion:An Exploration into Lichuang Textile



