A Comprehensive Guide to Textile Testing and the Risks Related to It
This comprehensive guide to textile testing provides an in-depth understanding of the various types of tests that are conducted in the industry. The guide covers topics such as tensile strength, elongation, abrasion resistance, and water absorption, among others. It also explores potential risks associated with these tests, including safety hazards and environmental concerns. Additionally, the guide offers practical advice on how to conduct these tests safely and effectively, ensuring that they provide accurate results and prevent any undue harm to the materials under testing. Overall, this guide is essential for anyone working in the textile industry, providing valuable insights into the science behind textile testing and the importance of following proper procedures to ensure the safety and quality of products.
Introduction: Textile products, including clothing, textiles, and materials for home furnishing, have a significant role in our daily lives. However, their production and use often come with potential health risks due to exposure to chemicals, fibers, and dyes used in the manufacturing process. As consumers become more aware of these risks, it is crucial to understand how to identify and manage them through proper testing. In this article, we will explore the different types of textile testing and the associated safety risks, as well as practical examples from real-world scenarios.
Types of Textile Testing:
-
Chemical Residue Testing: This test measures the amount of harmful chemicals present in textiles, such as heavy metals like mercury and lead, pesticides, solvents, and fragrances. The goal is to ensure that textiles do not contain harmful substances that could pose health threats to humans or animals.

-
Fiber Content Testing: This involves identifying the type and concentration of natural fibers (like cotton and wool) and synthetic fibers (like polyester and nylon) present in textiles. The purpose is to assess whether the product is made from sustainable or eco-friendly materials.
-
Dyes and Pigment Testing: This evaluates the quality of dyes used in textiles, focusing on the colorfastness (the ability of the dyes to resist washing and wear), hue, chroma, and other properties. This information ensures that the colors produced are consistent and safe for human use.
-
Microbiological Testing: This tests for bacteria, fungi, and viruses that may be present in textiles. The goal is to guarantee that the textiles are free from contamination that could cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, or infections.
-
Environmental Impact Testing: This evaluates the impact of textile products on the environment, including water usage, energy consumption, and waste generation during the manufacturing process. The aim is to promote eco-friendly practices and minimize environmental damage.
Safety Risks: While many of the above tests help protect consumer health and the environment, they can also pose safety risks if improperly performed or if certain materials are used inappropriately. Here are some common safety issues related to textile testing:
-
Chemicals: Exposure to harmful chemicals through textiles can cause skin irritation or respiratory problems, especially for those sensitive to certain chemicals. For example, high levels of formaldehyde found in some latex gloves can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
-
Fibers: Improper disposal of synthetic fibers containing microplastics can contaminate soil and water sources, posing a threat to marine ecosystems and wildlife. Additionally, certain types of synthetic fibers, like nylon, can release toxic gases when burned, posing a fire hazard.
-
Dyes and Pigments: Colorfastness testing can sometimes result in false positives or negatives, leading to products that fail to meet standards but are labeled as safe. Similarly, some dyes and pigments may contain toxic additives that can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
-
Microbiological Contamination: Proper testing is essential to ensure that textiles are free from harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites, but failure to follow proper cleaning procedures can result in cross-contamination between products or even contamination of finished goods.
-
Environmental Impact: While testing helps promote eco-friendly practices, incorrect disposal of textiles can lead to pollution and harm wildlife habitats. For example, improperly treated textile waste can contaminate waterways, leading to fish kills or harming aquatic organisms.
Case Studies: One example is the case of a popular children's clothing company that was found guilty of selling faulty products that contained dangerous chemicals. The company had failed to adequately test their fabrics for chemical residues, leading to hundreds of complaints from parents who reported their children experiencing skin allergies or respiratory issues. This led to increased regulatory scrutiny and resulted in fines and penalties for the company, highlighting the importance of proper textile testing and the need for responsible manufacturers to prioritize the safety of consumers and the environment.
Another example is the story of a woman who developed cancer from exposure to synthetic fibers while working in a garment factory. The woman worked in an area where she handled a variety of synthetic textiles and exposed herself to high levels of chemicals, including formaldehyde and other toxic substances. Despite regular testing by the factory, the woman continued to work in potentially harmful conditions. This incident highlights the importance of proper training and awareness programs for workers exposed to hazardous substances and underscores the need for stringent regulations and enforcement to prevent similar tragedies.
Conclusion: Textile testing plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and sustainability of our daily products. By understanding the different types of testing and their associated safety risks, consumers can make informed decisions about what products they choose to purchase. Manufacturers, too, must adhere to strict standards and regulations to minimize the risk of exposure to harmful substances and maintain public trust in their products. With ongoing improvements in testing techniques and regulations, we can expect to see further advancements in protecting both human health and the environment.
纺织品检测的重要性
在纺织品行业中,安全风险检测至关重要,这不仅关乎消费者的健康与安全,也关系到企业的声誉和可持续发展,本文将围绕纺织品检测安全风险展开讨论,并辅以英文案例说明。
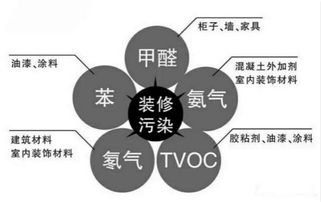
纺织品检测的安全风险
化学成分风险:纺织品中可能含有各种化学物质,如染料、助剂等,这些化学成分可能对人体健康产生潜在影响,因此需要进行严格的检测。
英文案例说明:近年来,纺织品中某些化学物质可能引发过敏反应或健康问题,导致消费者投诉增多,纺织品检测机构必须严格遵守相关法规,确保纺织品中化学成分的安全性。
-
微生物风险:纺织品在使用过程中可能会接触到各种微生物,如细菌、病毒等,这些微生物可能对人类健康构成威胁,因此纺织品检测中必须关注微生物风险。
-
安全性能风险:纺织品在生产、加工、使用等环节中可能存在安全隐患,某些纤维可能存在燃烧不充分、静电等问题,这些安全隐患可能导致火灾或安全事故,纺织品检测必须关注安全性能。
纺织品检测的安全措施
-
建立严格的质量控制体系:企业应建立完善的质量控制体系,确保纺织品检测的准确性和可靠性,这包括制定严格的标准、规范和检测流程,确保检测过程符合相关法规和标准。
-
采用先进的检测技术:企业应采用先进的检测技术,如色谱分析、免疫分析、微生物培养等,提高纺织品检测的准确性和可靠性,企业还应定期对检测设备进行校准和维修,确保检测结果的准确性。
-
加强与相关机构的合作:企业应加强与相关机构的合作,共同开展纺织品检测工作,这包括与行业协会、检测机构等合作,共同制定纺织品检测标准和方法,提高纺织品检测的公正性和权威性。
英文案例说明
以某知名纺织品品牌为例,该品牌在纺织品检测中采取了以下措施:
-
化学成分检测:该品牌严格按照相关法规和标准进行化学成分检测,确保纺织品中化学成分的安全性,该品牌还采用了先进的色谱分析技术,提高了检测的准确性和可靠性。
-
微生物风险控制:该品牌在纺织品生产、加工过程中严格控制微生物风险,采用了严格的清洁和消毒措施,确保纺织品在使用过程中不会接触到有害微生物,该品牌还与相关机构合作,共同开展纺织品微生物污染情况的监测工作。
纺织品检测是保障纺织品安全与健康的重要手段,在纺织品检测中,企业应建立严格的质量控制体系,采用先进的检测技术,加强与相关机构的合作,企业还应关注安全性能风险,确保纺织品在使用过程中不会存在安全隐患,通过这些措施的实施,可以有效降低纺织品检测的安全风险,保障消费者的健康与安全。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Exploring the World of Textiles:A Glossary of Different Fabric Materials