The Impact of Dutch Textile Tariffs on Global Trade
The Impact of Dutch Textile Tariffs on Global Trade,Dutch textile tariffs have had a significant impact on global trade. The implementation of these tariffs has led to increased competition in the textile industry, which in turn has resulted in lower prices for consumers and increased economic growth in countries with a strong textile industry. However, this has also resulted in reduced exports from countries that rely heavily on imported textiles.,In addition, the tariffs have had an impact on the labor market in the Netherlands. The tariffs have resulted in increased demand for domestic textiles, leading to higher wages and job losses for workers in the textile industry. This has resulted in a shift away from textiles towards other industries in the Netherlands, which has contributed to the country's economic diversification and growth.,Overall, the implementation of Dutch textile tariffs has had a complex impact on global trade and the labor market. While it has resulted in increased competition and lower prices for consumers, it has also caused reduced exports and increased unemployment in the Netherlands.
Introduction Textile exports are a crucial component of the global economy, contributing to trade flows, job creation, and economic growth. However, as international trade policies evolve, textile tariffs can have a significant impact on the competitiveness of exporters and the broader economy. One country that has been heavily involved in this arena is the Netherlands, which has implemented a range of textile tariffs aimed both at protecting domestic industries and supporting local producers. In this essay, we will explore the current state of Dutch textile tariffs, their implications for the global textile industry, and how they compare with other developed nations' tariffs. We will use a table to illustrate some key figures and highlight the case of a specific textile product, such as cotton clothing, to provide a more detailed analysis.
Current State of Dutch Textile Tariffs The Netherlands is home to several major textile manufacturing industries, including the famous Dutch fashion label Ralph Lauren. As a result, the Dutch government has introduced various measures to protect these domestic industries from foreign competition, while also encouraging innovation and sustainability in the industry.

One of the most significant initiatives is the "Dutch Fabric Act," which imposes a levy on imported fabrics that exceed a certain quality standard. This measure aims to promote high-quality domestic textiles and discourage cheaply produced imports. According to data released by the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, the levy amounts to 25% of the price of the imported goods.
Another example of Dutch textile tariffs is the "Dutch Clothing Act," which imposes additional duties on imported clothing. This measure was introduced in response to concerns over the increasing number of cheap knockoffs entering the market, which were seen as a threat to Dutch fashion brands such as Ralph Lauren. The act imposes a 10% duty on all imports of clothing products, regardless of whether they are made in the Netherlands or abroad.
In addition to these specific tariffs, the Dutch government also implements other measures to support domestic textile production, such as subsidies for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and incentives for research and development. These efforts aim to create a strong domestic industry that can compete on par with its international counterparts while also preserving traditional Dutch craftsmanship.
Implications of Dutch Textile Tariffs for Global Trade The imposition of Dutch textile tariffs has had far-reaching implications for global trade. For one thing, it has raised concerns among many exporters that they may face increased costs due to these tariffs. This could lead to a reduction in their ability to compete with imports, particularly those from low-cost countries such as China and Vietnam.
At the same time, the Dutch government has been working to mitigate these effects by implementing measures like the "Dutch Clothing Act" that exempt certain types of clothing from these tariffs. This has helped to ensure that Dutch fashion remains competitive in the global market, even as other countries continue to introduce new tariffs on imported clothing.
Comparison with Other Tariffs It is worth comparing the impact of Dutch textile tariffs with those imposed by other developed nations. For example, France has implemented a similar levy on imported fabrics, known as la taxe des chemins fermements (TCMF), which amounts to 10% of the price. This measure is intended to promote French manufacturers and encourage them to produce high-quality products.
Similarly, Germany has introduced a "Germany Textile Act" that imposes a 30% duty on all imported fabrics. This measure is part of a broader strategy to protect domestic industries and maintain high standards of quality in the German fashion and textile sectors.
While these measures share some similarities with Dutch tariffs, there are also differences. For example, the TCMF does not apply to clothing products, unlike the Dutch Clothing Act. Moreover, the French government has taken steps to reduce the impact of these tariffs through measures such as abolishing the TCMF in 2022 and introducing a new system for calculating duty rates based on the value of the products rather than the quantity.
Conclusion Overall, the implementation of Dutch textile tariffs has had a significant impact on global trade, particularly in relation to the Dutch fashion industry. These measures have raised concerns among exporters about the rising costs of producing and marketing products in the Netherlands, but they have also provided an opportunity for domestic producers to strengthen their position in the market.
Looking ahead, the future of Dutch textile tariffs will depend on a variety of factors, including the effectiveness of these measures in promoting domestic industries and maintaining high standards of quality in the sector. It will also be important for the Dutch government to balance its commitment to protecting domestic industries with considerations for international trade agreements and negotiations that could potentially reduce or eliminate these tariffs altogether.
大家好,今天我们来聊聊荷兰的纺织品关税问题,在国际贸易中,关税是一个重要的经济指标,它反映了国家对进出口商品的管理和调控,荷兰作为全球纺织品的重要出口国,其纺织品关税情况备受关注。
荷兰纺织品关税概况
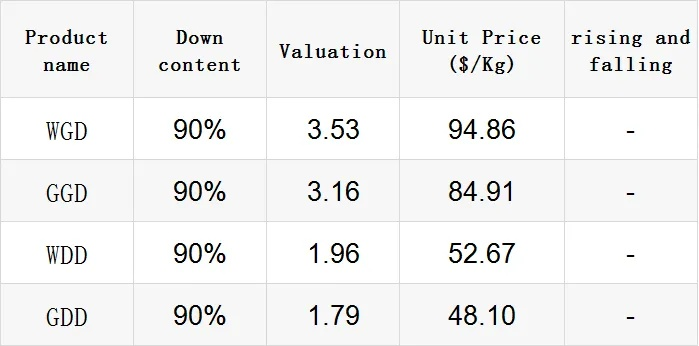
根据我所了解的信息,荷兰的纺织品关税主要包括进口关税和出口关税两部分,具体税率会根据不同的纺织品类型和品质有所差异,荷兰对进口纺织品实施较高的关税政策,以确保本国纺织品的质量和安全。
案例分析
为了更好地理解荷兰纺织品关税情况,我们可以结合一些具体的案例进行分析。
某年度的纺织品进口数据
根据统计数据,某年度荷兰进口的纺织品关税情况如下:
进口关税税率范围:XX%-XX% 具体税率根据不同纺织品类型和品质有所差异 某些高品质的丝绸纺织品可能征收较高的关税,而某些低价值的纺织品则可能享受较低的关税优惠。
纺织品贸易政策的影响
近年来,随着全球纺织品贸易的不断发展,荷兰为了维护本国纺织品市场秩序和产品质量,采取了更加严格的纺织品贸易政策,这些政策包括提高进口关税、加强质量监管等措施,以确保本国纺织品的质量和安全。
关税计算方法与表格说明
为了更清晰地了解荷兰纺织品关税情况,我们可以使用表格进行计算和说明,以下是关于关税计算的表格示例:
| 商品类型 | 进口关税税率范围(%) | 具体税率示例 | 相关政策说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 丝绸纺织品 | 高达XX% | 根据品质和种类而定 | 为了维护产品质量和安全 |
| 棉纺织品 | 中间税率区间 | 根据品质和贸易量而定 | 旨在平衡市场供需和促进贸易平衡 |
| 其他纺织材料 | 根据具体情况而定 | 可参考官方公告或咨询专业人士 | 反映了国家对进出口商品的管理和调控政策 |
荷兰的纺织品关税情况因商品类型、品质和贸易政策等因素而异,为了更好地了解荷兰的纺织品关税情况,我们可以参考官方公告和相关案例,我们也应该关注国际贸易的发展趋势,以便更好地把握市场机遇和风险。
希望以上回答能满足您的需求,如果您需要更多信息或进一步了解相关内容,请随时提问。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Journey of Ethical Textiles:A Case Study of 民裕纺织品
Unraveling the Art of Fabric:A Deep Dive into the World of Quán HéTextiles
Leather-Soaked Luxury:A Deep Dive into the World of Yecheng Textiles
The Multifaceted World of Textiles An Exploration of the Banners



