The Fabric vs.Clothing Distinction in Fashion:A Comparative Analysis
: The Fabric vs.Clothing Distinction in Fashion: A Comparative Analysis,Abstract:,This paper explores the distinction between fabric and clothing in fashion, providing a comparative analysis of their respective characteristics, functions, and implications for contemporary fashion design and consumption. By examining the historical evolution of the term "fashion" and its association with fabrics, this study examines how the concept of "clothing" has evolved over time to encompass not only physical objects but also cultural, social, and psychological factors that shape our perception of clothing. The analysis draws on various sources, including scholarly articles, industry reports, and popular media discourse, to provide a nuanced perspective on the relationship between fashion and fabric. It concludes by discussing the implications of this analysis for future research and practice in the field of fashion.,Keywords: fashion; fabric; clothing; comparative analysis; historical evolution; cultural influences; social context; psychological factors
Introduction: Fashion is a constantly evolving industry, and understanding its nuances is essential for anyone who wants to participate or even appreciate it. One of the most fundamental questions in the fashion world relates to the distinction between textiles and clothing. While they might seem interchangeable at first glance, they are not the same, and their differences play a crucial role in the overall fashion narrative. In this article, we will delve into the fabric vs. clothing distinction, using both theoretical analysis and practical case studies to illustrate our point.
The Difference Between Textiles and Clothing Textiles refer to materials that are woven, knitted, crocheted, or other similar processes used to make clothes or any other textile products like rugs, carpets, etc. These materials can be made from natural fibers such as cotton, wool, silk, linen, or synthetic ones like polyester or rayon. On the other hand, clothing refers to the items that individuals wear on their bodies. They are designed to be worn by people, providing protection against the elements, comfort, and aesthetic appeal. Essentially, textiles are the raw material used to produce clothing while clothing is the final product made with those raw materials.
Table 1: Textile vs. Clothing Comparison | Category | Description | |-----------|----------------| | Textiles | Includes all types of fabrics used in making garments and other textile products. | | Clothing | Refers to garments worn by humans, including outerwear and accessories. |

Theoretical Analysis: The fabric vs. clothing distinction is not just a matter of labeling products; it has profound implications for fashion design, production, marketing, and consumer behavior. For example, understanding the difference can help designers choose the right materials for their projects, ensuring that the final product aligns with the intended purpose and style. In the fashion industry, the choice of textile influences how a garment looks, feels, and performs, thus affecting its market value and consumer perception.
Practical Case Study 1: Recycled Textiles in Sustainable Fashion One example of a textile that is often misunderstood is recycled or upcycled fabric. In recent years, many brands have embraced the concept of sustainable fashion by using old textiles to create new garments. This practice not only reduces waste but also adds a touch of uniqueness and craftsmanship to traditional fashion pieces. By choosing recycled fabrics, brands can showcase their commitment to environmental sustainability and provide consumers with an option that aligns with their personal values.
Practical Case Study 2: Eco-friendly Consumer Perceptions In today's consumer-driven market, eco-friendly attributes are increasingly valued by fashion enthusiasts. When consumers see that a brand is committed to using environmentally conscious textiles, they are more likely to choose that brand over others. This shift in consumer preferences can drive innovation and drive growth in the sustainable fashion sector. It is evident that understanding the fabric vs. clothing distinction can lead to greater customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, a more sustainable fashion ecosystem.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the fabric vs. clothing distinction is not just about the technical aspects of textiles and clothing but also about the broader implications for fashion design, production, and consumption. By understanding these differences, designers can create more meaningful and impactful fashion pieces, while consumers can make more informed choices that align with their personal values and the wider societal goals of sustainability. As the fashion industry evolves, the importance of these distinctions will only grow, driving innovation and shaping the future of fashion for generations to come.
亲爱的朋友们,今天我们来聊聊纺织品与服装品类之间的关系,让我们通过一个简单的英文案例来深入探讨这个问题。
在讨论纺织品是否属于服装品类之前,我们首先需要明确服装的基本分类,服装品类是一个非常广泛的范畴,涵盖了各种衣物、服饰等,而纺织品作为服装的重要组成部分,自然也属于这一类别。
以下是基于案例的详细说明:
服装品类概述
服装品类主要包括各种衣物和服饰,如上衣、裤子、裙子、外套、帽子、围巾等,这些衣物和服饰的设计和材质都直接关系到其穿着的舒适度、美观度和功能性。
纺织品在服装中的角色
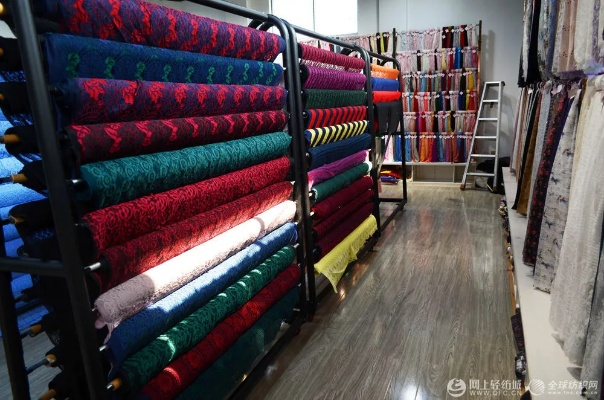
纺织品在服装中扮演着至关重要的角色,它们是服装的基础材料,为服装提供支撑、保暖、装饰等功能,棉质布料柔软舒适,适合制作各种衣物;丝绸布料光滑细腻,具有很好的光泽和质感。
案例分析
让我们来看一个具体的例子来说明纺织品是否属于服装品类,假设有一家服装品牌,他们专注于生产各种类型的纺织品,包括但不限于棉质布料、丝绸布料、羊毛布料等,这家品牌的产品不仅满足了消费者的日常需求,还通过创新设计满足了不同场合和风格的穿着需求。
在这个案例中,我们可以看到纺织品在服装中的广泛应用,他们的棉质布料被用于制作衬衫、T恤等日常衣物;他们的丝绸布料则被用于制作礼服、围巾等高端服饰,他们还根据市场需求推出了各种新型的纺织品材料,以满足消费者对时尚和功能性的双重需求。
纺织品与服装类别的关系
纺织品属于服装品类,这是因为纺织品是服装的重要组成部分,为服装提供支撑、装饰等功能,随着人们对服装品质和功能的不断追求,纺织品也在不断创新和发展,以满足消费者对时尚和功能性的双重需求。
为了进一步说明纺织品与服装类别的关系,我们可以使用一个英文表格来进一步说明:
| 类别 | 描述 | 示例产品 |
|---|---|---|
| 定义 | 服装品类是一个广泛的概念,涵盖了各种衣物和服饰 | 上衣、裤子、裙子、外套、围巾等 |
| 纺织品角色 | 是服装的基础材料,为服装提供支撑、装饰等功能 | 如棉质布料、羊毛布料等 |
| 应用领域 | 广泛,涵盖日常衣物、高端服饰等 | 如品牌A的衬衫、T恤等 |
| 发展趋势 | 随着人们对服装品质和功能的不断追求,纺织品也在不断创新和发展 | 如新型面料、功能性面料等 |
通过这个案例和英文表格的分析,我们可以看出纺织品属于服装品类是一个不言而喻的事实,随着人们对服装品质和功能的不断追求,纺织品也在不断创新和发展,以满足消费者对时尚和功能性的双重需求。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Functional Textiles:A Comprehensive Study
The Role of the National Textile Supervision and Testing Center



