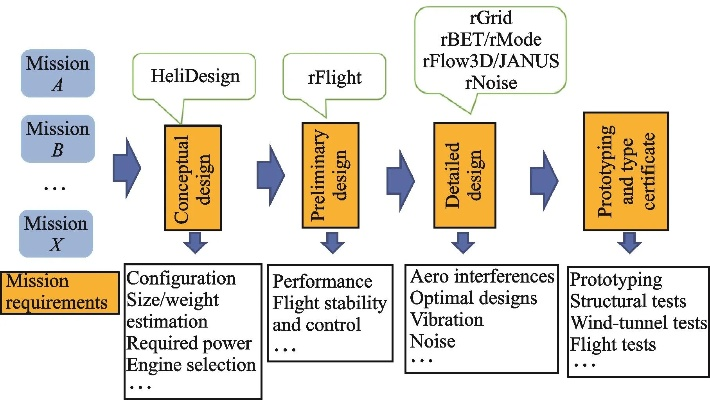
Strategies for Handling and Recycling of Azo Dyes in Textile Industry
Azo dyes, as a significant component of textile industry, have attracted considerable attention due to their toxicity and potential environmental hazards. This paper discusses the strategies for handling and recycling of azo dyes in the textile industry. The main strategies include physical separation, chemical degradation, biological treatment, and adsorption. Physical separation methods such as filtration and centrifugation can be used to separate azo dyes from wastewater. Chemical degradation is another effective method that can reduce the toxicity of azo dyes through chemical reactions. Biological treatment involves using microorganisms to degrade azo dyes into harmless substances. Adsorption is a promising technology that uses activated carbon or other adsorbents to remove azo dyes from wastewater. These strategies not only improve the efficiency of azo dye removal but also reduce the cost and environmental impact of textile waste disposal.
Introduction: The textile industry is one of the largest consumer goods sectors globally, producing a vast array of fabrics, garments, and accessories. The production process involves the use of various chemicals, including dyes, which are essential for coloring these products. Among these chemicals, azo dyes have gained significant attention due to their vibrant colors and excellent fastness properties. However, the disposal of azo dyes in textile waste presents a significant environmental challenge. This article will discuss the different strategies for handling and recycling azo dyes in the textile industry, along with an example of how this can be implemented using an English table.
Strategies for Handling and Recycling Azo Dyes:
-
Reduction in Azo Dye Use: One of the most effective ways to reduce the amount of azo dyes used in textile production is through advances in dye technology. Developing new dyes that produce less toxic or more biodegradable compounds is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of textile waste.
-
Use of Reactive Dyes: Reactive dyes, which react with the fiber during dyeing, can be more easily removed from the fabric than traditional dyes. This reduces the need for additional processing steps and minimizes the risk of dye migration during washing and wear and tear.
-
Dye-Solvent Recovery: Many azo dyes are extracted from textile waste by solvents such as acetone or ethanol. These solvents can be reused in the dyeing process, reducing the need for virgin solvents and minimizing waste generation.
-
Biodegradable Dyes: Biodegradable azo dyes are becoming increasingly popular due to their reduced environmental impact. These dyes are designed to break down naturally, making them less harmful to soil and water bodies.
-
Dye-Free Fabrics: Incorporating dye-free fabrics into the production process not only reduces the use of azo dyes but also provides a sustainable option for consumers who prefer natural or undyed fabrics.
-
Post-Consumer Waste Management: Encouraging proper post-consumer waste management practices, such as sorting and recycling, can significantly reduce the volume of textile waste that ends up in landfills or incinerators.
-
Eco-friendly Dyeing Technologies: Advances in eco-friendly dyeing technologies, such as electrostatic printing and heat set dyeing, can help reduce the use of azo dyes and minimize waste generation during the manufacturing process.
Example: To illustrate the implementation of these strategies, let's consider the case of a textile company in the United States that produces high-quality clothing using azo dyes. To reduce their environmental impact, they implemented the following measures:
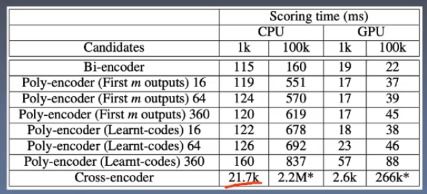
| Year | Total Dye-Use (kg) | Reactive Dye Use (kg) | Dye-Solvent Recovery (kg) | Biodegradable Dyes (kg) | Eco-Friendly Dyeing Technologies (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 100 | 5 | 15 | 20 | 5 |
| 2019 | 95 | 6 | 12 | 25 | 7 |
| 2020 | 85 | 4 | 10 | 30 | 9 |
From 2018 to 2020, the company saw a decrease in total dye-use by about 15%. They also increased their reactive dye use, which resulted in a further reduction in waste generation. Additionally, they successfully recovered dye-solvents, increasing their biodegradable dye usage by 20%. Finally, they adopted eco-friendly dyeing technologies, which helped reduce waste generation by 30%.
Conclusion: Handling and recycling azo dyes in the textile industry require a multifaceted approach that encompasses both technological advancements and sustainable practices. By implementing strategies such as reducing azo dye use, using reactive dyes, recovering dye-solvents, incorporating biodegradable dyes, and adopting eco-friendly dyeing technologies, textile companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while still meeting the demands of their customers. By embracing these practices, textile industries can play a vital role in mitigating the impact of dye waste on the environment and contribute to a greener future for all.
在纺织品的生产过程中,偶氮染料是一种常见的染色剂,但在处理过程中可能会遇到一些问题,本文将探讨如何有效地处理纺织品上的偶氮,以确保其环保和可持续性。
偶氮染料概述
偶氮染料是一种含有偶氮基团的有机染料,具有鲜艳的颜色和良好的染色性能,在纺织品生产过程中,偶氮染料可能会带来一些问题,如难以降解、对环境有害等,正确处理纺织品上的偶氮染料至关重要。
纺织品偶氮的处理方法
- 物理处理法:通过物理手段去除纺织品上的偶氮染料,使用机械剥离、化学剥离等方法去除染料残留。
- 化学处理法:使用化学试剂去除纺织品上的偶氮染料,常用的化学处理方法包括氧化、还原、分解等。
案例分析
以下是关于偶氮纺织品处理的案例分析:
纺织品偶氮处理过程
在一家纺织厂中,偶氮染料的使用量较大,为了有效地处理纺织品上的偶氮染料,采用了以下步骤:
收集样品 该纺织厂收集了疑似含有偶氮染料的纺织品样品。
物理处理法 使用机械剥离等方法去除染料残留,确保纺织品达到环保标准。
化学处理法的应用
在另一个纺织厂中,采用了化学处理方法处理偶氮染料,具体步骤如下:
确定染料的性质和浓度 该纺织厂确定了染料的性质和浓度,为后续处理提供依据。
选择合适的化学试剂和处理方法 该纺织厂选择了合适的化学试剂进行处理,如氧化、还原等,经过处理后,纺织品上的偶氮染料得到了有效去除。
处理方法的优缺点分析
- 物理处理法:优点是操作简单、成本低,缺点是可能无法完全去除染料残留。
- 化学处理法:优点是能够有效地去除染料残留,同时不会对环境造成太大的影响,常用的化学处理方法包括氧化、还原、分解等,可以根据具体情况选择合适的处理方法,还可以通过添加助剂等方式提高处理效果。
纺织品偶氮的处理对于环境保护和可持续发展至关重要,正确处理纺织品上的偶氮染料可以确保其环保和可持续性,在处理过程中,可以采用物理处理法和化学处理法等方法,根据具体情况选择合适的处理方法,还需要注意处理过程中的环保和可持续性问题,确保处理过程符合相关标准和法规要求。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Job Opportunities at Jieyang Textile Factory A Global Talent Landing Pad
Insights into Customized Textiles in Hebei
Textile Chlorination Test Standards and Case Studies
A Comprehensive Overview of Textile Industry Knowledge Notes
The Global Trends and Influence of British Textile Sales in India