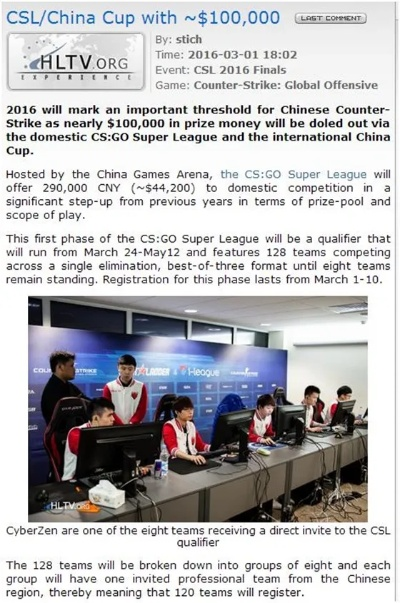
Understanding and Managing Textile Moisture Content
Introduction: Textiles are essential components of our daily lives, from everyday clothing to high-end fashion. They provide warmth, comfort, and style. However, moisture can cause significant problems for textiles, leading to damage, reduced performance, and even safety hazards. This is why it's crucial to understand how to detect and manage the moisture content in textiles effectively. In this guide, we will explore the various methods and techniques used to measure textile moisture content and provide practical examples to help you make informed decisions about your garments.
Methods for Measuring Textile Moisture Content:
-
Hygrometers: Hygrometers are instruments that measure the relative humidity in a given environment. They work by measuring the amount of water vapor present in the air, which is directly related to the moisture content of the textile. Hygrometers can be manual or electronic, with manual models often being more accurate but less convenient.
-
Gravimetric Methods: These methods involve weighing the textile before and after exposure to a known moisture source to determine the change in weight. The difference in weight is then converted into a percentage of moisture content. Gravimetric methods are relatively simple to use but may not provide precise results if the textile is exposed to multiple sources of moisture at once.
-
Capillary Action Tests: This method involves placing a small piece of textile on a surface and observing how much water it absorbs over time. It provides an indication of the textile's ability to hold moisture and its surface properties. Capillary action tests are useful for determining the level of absorbency of a textile but may not be suitable for measuring total moisture content.
-
Water Vapor Permeability Tests: These tests measure the rate at which water vapor can pass through a textile material. The higher the permeability, the better the textile's ability to regulate moisture levels. Water vapor permeability tests are typically performed using a gravimetric method and involve exposing the textile to a controlled environment with varying levels of humidity.
-
Drying Rate Tests: These tests measure how quickly a textile dries after exposure to a known moisture source. By comparing the drying rates of different textiles under similar conditions, manufacturers can assess their fabric's moisture absorption and drying capabilities. Drying rate tests are useful for evaluating the performance of new fabrics or for selecting materials for specific applications.
Practical Example: Let's say you have a client who wants to produce high-quality sportswear made from a blend of polyester and spandex. To ensure the garments meet the required moisture management standards, they need to test the moisture content of the fabrics before production. Here's how they could approach this task:
- Choose a suitable hygrometer and calibrate it according to manufacturer guidelines.
- Place a small sample of each fabric on a flat surface and measure its weight before and after exposure to a controlled environment with a known humidity level (e.g., 60% relative humidity).
- Calculate the percentage of moisture content by subtracting the initial weight from the final weight and multiplying by 100.
- Analyze the results and select the fabric with the lowest moisture content for further testing or production.
- Conduct additional tests such as capillary action tests and dry-to-wet ratio measurements to evaluate the overall moisture management capabilities of the fabrics.
Conclusion: Understanding and managing textile moisture content is crucial for ensuring the quality, performance, and longevity of garments. By employing a range of methods and techniques, manufacturers can accurately measure the moisture content of their fabrics and choose materials accordingly. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently evaluate the moisture content of your textiles and make informed decisions about your garments. Remember, proper moisture management is just as important as other aspects of textile production, so don't hesitate to seek professional guidance when needed.
随着纺织行业的快速发展,纺织品的质量和性能越来越受到关注,湿度含量检测作为纺织品质量控制的重要环节,对于保障纺织品的质量和消费者的使用体验至关重要,本文将围绕纺织品湿度含量检测展开讨论,并提供相关的英文案例说明。
纺织品湿度含量检测的重要性
纺织品湿度含量检测是确保纺织品在生产、储存和使用过程中符合特定标准的重要手段,通过湿度含量检测,可以及时发现纺织品中存在的湿度问题,避免因湿度过高或过低导致的质量问题,从而保障纺织品的质量和消费者的使用体验。
检测方法及流程
检测方法:

(1)湿度传感器法:利用湿度传感器检测纺织品表面的湿度含量。 (2)实验室检测法:通过实验室仪器进行纺织品湿度的测定。
检测流程:
(1)样品准备:选择待检测的纺织品样品。 (2)样品预处理:对样品进行清洗、干燥等处理。 (3)使用湿度传感器进行测量。 (4)数据分析:通过数据分析软件对测量结果进行处理和分析。 (5)报告生成:根据检测结果生成相应的报告。
案例分析
以某纺织企业为例,介绍纺织品湿度含量检测的具体操作流程和案例分析。
-
案例背景:该纺织企业生产多种类型的纺织品,其中涉及棉布、丝绸等,为了确保产品质量和消费者使用体验,对其生产的纺织品进行了湿度含量检测。
-
检测过程:
(1)样品选择:选择该企业生产的棉布样品进行检测。 (2)样品预处理:对样品进行清洗、干燥等处理,确保测量准确性。 (3)使用湿度传感器进行测量:在实验室环境下,使用湿度传感器对样品进行湿度含量检测。 (4)数据分析:通过数据分析软件对测量结果进行处理和分析,发现棉布样品存在一定程度的湿度问题。 (5)解决方案:根据检测结果,企业采取相应的措施,如加强仓储管理、控制环境湿度等,以确保纺织品的质量和消费者的使用体验。
注意事项
在进行纺织品湿度含量检测时,需要注意以下几点:
- 选择合适的检测方法,根据样品的特点选择合适的检测方法。
- 确保样品处理和测量过程的准确性,避免因误差导致检测结果不准确。
- 注意环境因素对测量结果的影响,确保测量结果的可靠性。
- 根据检测结果采取相应的措施,确保纺织品的质量和消费者的使用体验。
纺织品湿度含量检测是保障纺织品质量的重要手段,对于保障消费者使用体验和产品质量具有重要意义,在实际操作中,需要注意选择合适的检测方法、确保样品处理和测量过程的准确性、注意环境因素对测量结果的影响等,还需要不断更新和完善检测技术,提高检测的准确性和可靠性。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Exploring the World of Weijer Textiles:A Journey into Quality and Innovation
The Ugandan Textile Market A Global Perspective and Regional Insights
An Overview of Textile Product Testing
A Comprehensive Overview of Textile Industry Knowledge Notes
The Innovation and Growth of Qingdao Shenglong Textiles
Navigating the New Trends in Xinxiang Textile Fabric Wholesale Market