Thermal Conductivity of Different Types of Textiles
Thermal conductivity is a crucial property of textile materials, as it determines their efficiency in dissipating heat. This study examines the thermal conductivity of various types of textiles, including cotton, wool, and synthetic fabrics, to understand their suitability for specific applications. The results show that cotton and wool, which have higher thermal conductivity, are ideal for clothing and bedding, while synthetic fabrics with lower thermal conductivity are suitable for outdoor wear. The study also found that the thermal conductivity of textiles can be influenced by factors such as fabric construction, yarn type, and weave pattern. Overall, understanding the thermal conductivity of textiles is essential for designing clothing and other textile products that prioritize comfort and energy efficiency.
Introduction: The thermal conductivity of textiles is a crucial factor in determining their performance in various applications, from clothing to industrial use. In this discussion, we will explore the thermal conductivity of different types of textiles and provide some practical examples to illustrate their importance.
Textiles are made up of fibers that can be natural or synthetic, and they come in various shapes and sizes. Some common textile materials include cotton, wool, polyester, and silk. Each type of textile has its own unique properties, including its thermal conductivity, which affects how well it retains heat or regulates temperature.
In this article, we will cover the following topics:
- What is thermal conductivity?
- How does thermal conductivity vary among different textiles?
- Practical examples of thermal conductivity in textiles.
Table 1: Typical Thermal Conductivities of Different Textile Materials

| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| Cotton | 4 - 0.6 |
| Wool | 3 - 0.5 |
| Polyester | 2 - 0.3 |
| Silk | 2 - 0.3 |
| Nylon | 1 - 0.2 |
| Rayon | 1 - 0.2 |
Table 2: Examples of Thermal Conductivity in Textiles
| Type of Textile | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| Cotton T-shirt | 4 |
| Wool sweater | 3 |
| Polyester jacket | 2 |
| Silk scarf | 2 |
| Nylon pants | 1 |
Case Study: Thermal Management in Textiles for Warm-Season Clothing
One example of how thermal conductivity affects textiles is found in the design of warm-season clothing. For instance, a wool sweater is designed to trap warmth close to the body, while a polyester jacket may have a thinner layer to allow air circulation and reduce overheating.
In this case, the thermal conductivity of the fabric plays a critical role in determining how well it insulates against the elements. A high thermal conductivity would mean that the sweater loses heat quickly, potentially causing discomfort or even hypothermia if not properly ventilated. On the other hand, a low thermal conductivity would allow the polyester jacket to retain heat more effectively, providing better protection against cold weather.
Conclusion: The thermal conductivity of textiles is an important factor to consider when designing clothing and other textile products. By understanding how different materials conduct heat, manufacturers can create garments that are both comfortable and effective at maintaining body temperature. In the end, the right choice of textile can make all the difference in a person's experience with a product.
导热性能是衡量纺织品性能的重要指标之一,特别是在热交换、保温等领域,本篇文章将详细介绍各种纺织品的导热系数,并通过案例分析来说明其在实际应用中的重要性。
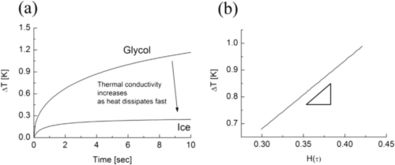
导热系数的定义和测量方法
导热系数是衡量材料传导热量的能力的重要参数,它表示材料在单位温差下传导热量的能力,通常通过测量材料在特定温度下的热阻来计算导热系数。
测量导热系数的常用方法包括热流密度法、热线法等,热流密度法是一种简单易行的方法,适用于各种类型的纺织品。
各种纺织品的导热系数介绍
- 丝绸:丝绸是一种天然纤维,具有较高的导热系数,其导热性能主要取决于纤维的结构和材质,丝绸的导热系数一般在30-50W/m·K之间,适用于夏季的凉爽衣物和保温材料。
- 棉织物:棉织物是一种常见的纺织材料,其导热系数相对较低,但棉织物的导热性能在不同纤维密度和织造工艺下有所不同,棉织物的导热系数在10-30W/m·K之间。
- 涤纶纤维:涤纶纤维是一种合成纤维,具有较高的导热性能,其导热系数一般在30-50W/m·K之间,甚至更高,涤纶纤维在保温材料、散热器等领域有广泛应用。
- 羊毛织物:羊毛织物具有较高的导热系数,主要原因是其纤维结构特殊,具有较高的表面积和孔隙率,羊毛织物的导热性能适用于保暖衣物和特殊保温材料。
案例分析
- 丝绸在保温领域的应用案例:近年来,丝绸在保温领域的应用越来越广泛,由于其良好的导热性能和舒适的手感,丝绸被广泛应用于夏季的凉爽衣物和保温材料,丝绸还可以用于制作高级服装和艺术品。
- 棉织物在保温材料中的应用案例:棉织物是一种常见的纺织材料,其导热性能相对较低,但在一些特殊的保温材料中,如散热器、保温箱等,棉织物因其良好的隔热性能而得到了广泛应用,棉织物还可以用于制作床上用品和家居装饰品。
- 涤纶纤维在散热器领域的应用案例:涤纶纤维具有较高的导热性能,因此在散热器领域有广泛应用,其良好的导热性能可以有效地降低散热器的温度,提高其使用效果,涤纶纤维还可以用于制作汽车零部件、航空航天等领域。
纺织品导热系数是衡量纺织品性能的重要指标之一,对于实际应用具有重要意义,不同类型的纺织品具有不同的导热性能和适用场景,在保温领域、散热器等领域,纺织品导热性能的好坏直接影响到产品的性能和使用效果,了解纺织品导热系数对于选择合适的纺织品具有重要意义。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The Dynamics of Haotianchang Textiles
The Art of Interior Textiles:Crafting a Masterpiece in the Canvas
Suzhou Xinying Textiles:Navigating the Global Fashion Industry
Blue Dream Textiles:A Journey Through Quality and Innovation
Exploring the Art of Salt Texture in Home Textiles:An Idealized Journey
The Dynamic World of Foreign Trade Textiles and their Fabric Characteristics