The Art of Textile Design:Samples,Patterns,and Innovation
In the realm of textile design, innovation is not just about creating new patterns or materials but also embracing the art of sampling and patterning to create unique pieces that stand out. From classic designs to modern trends, designers must have a keen eye for detail, a deep understanding of fabrics, and a willingness to experiment with different techniques to bring their visions to life. Whether it's using a sample to guide a pattern or incorporating a pattern into a sample, every element counts in creating a truly innovative textile design. As technology continues to advance, so too must designers adapt their methods to stay ahead of the curve, embracing digital tools and software to enhance their creative process. By combining these elements, textile designers can push the boundaries of what's possible, bringing new beauty to an already vast world of fabrics and textures.
Introduction: Textile design is a dynamic field that encompasses the art of creating functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable fabrics. It's a blend of creativity, technology, and craftsmanship that has captivated designers and consumers alike for centuries. Today, textile designers are pushing boundaries in terms of innovation by exploring new materials, techniques, and patterns that not only meet the demands of the fashion industry but also cater to the changing needs of the global population. In this article, we will delve into the world of textile design samples, explore various design patterns, and showcase some innovative cases to highlight the ever-evolving nature of textile design.

Textile Design Samples: Designers use sample fabrics to visualize their ideas before committing to full production runs. These samples serve as a crucial step in the design process, allowing creators to test their concepts, make adjustments, and ensure that their designs meet specific requirements. Here's an overview of how textile samples are created and used:
-
Fabric Preparation: Before designing any sample, the designer must select the appropriate fabric, yarn, and fibers. This selection is based on factors such as colorfastness, texture, weight, and durability. The chosen fabric is then cut into small pieces or woven into a pattern to create a foundation upon which the final design can be built.
-
Pattern Making: Once the fabric is prepared, the designer creates a pattern using various tools such as scissors, rotary cutters, rulers, templates, and software programs. Patterns can be simple or complex depending on the desired outcome and the level of detail required.
-
Cutting and Weaving: The pattern is then transferred onto the fabric using various cutting techniques such as straight cuts, jagged stitches, or intricate handwork. Afterward, the fabric pieces are woven together using a loom or other weaving machinery, resulting in a finished sample.
-
Adjustments and Testing: During the design process, it's essential to make necessary adjustments and conduct tests to ensure that the final product meets the specified requirements. This may involve altering patterns, adding or removing layers, or adjusting the overall fit and drape of the garment.
-
Quality Control: Finally, the sample is subjected to thorough quality control checks to ensure its accuracy and consistency. This includes measuring dimensions, checking colorfastness, evaluating fabric strength, and assessing overall wearability and functionality.
Innovative Textile Design Patterns: Textile design patterns play a vital role in defining the look and feel of a fabric. Here are some innovative patterns that have been developed over the years:
-
Embroidery Patterns: Embroidery is a traditional technique that adds depth and texture to a fabric. However, modern designs incorporate embroidery patterns into geometric shapes, abstract forms, or even digital illustrations, making them more versatile and adaptable to contemporary styles.
-
Digital Printing Patterns: With advancements in technology, digital printing has become increasingly popular in textile design. Designers can now create intricate and detailed patterns using computer software that can simulate various effects such as screen-printing, heat transfer, silk screening, or laser cutting. These patterns can be printed onto various substrates such as cotton, linen, and even leather.
-
Mixed Media Patterns: A combination of different techniques such as embroidery, knitting, and crocheting can create unique patterns that offer a multidimensional look. For example, a knitted sweater could incorporate embroidered details around the neckline or cuffs, while the back could feature a more subdued pattern made up of simple stitches.
-
Sustainable Patterns: As awareness about sustainability grows, designers are experimenting with patterns that are both eco-friendly and stylish. These patterns may incorporate organic materials like bamboo, hemp, and recycled polyester, or they may use minimal water or electricity during production.
Innovative Textile Design Case Study: One of the most innovative textile design cases we have seen recently is a collection launched by British luxury brand Burberry. This collection features a range of high-quality, luxuriously soft, and breathable fabrics designed with sustainability in mind. One standout piece in the collection is a tweed coat made from recycled wool. The coat features intricate embroidery patterns inspired by traditional Japanese motifs and incorporates sustainable materials sourced from Burberry's own factories. The design not only embodies Burberry's commitment to sustainability but also offers a sophisticated and timeless look that appeals to a discerning clientele.
Conclusion: Textile design is constantly evolving and adapting to meet the needs of the industry and society at large. Through sample fabrics, innovative patterns, and case studies like that of Burberry, we can witness the remarkable strides being made in this dynamic field. As we continue to push boundaries in terms of style, function, and sustainability, we can expect to see more exciting textile design innovations in the future.
随着人们对生活品质的追求不断提高,纺织品面料作为家居装饰、服装搭配等方面的重要元素,其设计的重要性日益凸显,本篇将围绕纺织品面料设计样品图展开讨论,结合实际案例分析,旨在为读者提供纺织品面料设计方面的参考。
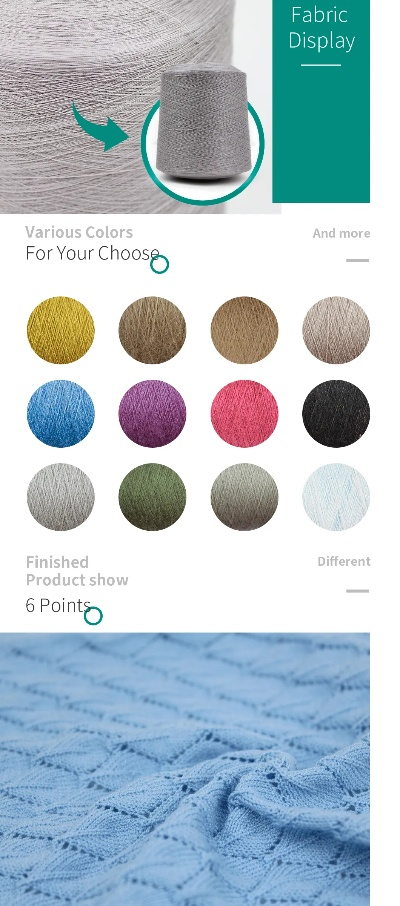
纺织品面料设计样品图展示
以下是纺织品面料设计样品图的详细展示:
【样品图一:简约时尚风格】
- 面料材质:采用高质量的天然纤维面料,如棉、麻等,具有舒适透气、柔软亲肤的特点。
- 设计元素:简约时尚的设计风格,色彩搭配柔和自然,图案以几何图案为主,展现出现代时尚的气息。
- 细节展示:面料表面光滑细腻,质地均匀,手感舒适。
【样品图二:复古风格】
- 面料材质:采用复古风格的织物,如丝绸、缎子等,具有优雅高贵的气质。
- 设计元素:采用传统图案和花纹,结合现代元素进行创新设计,展现出浓郁的复古风情。
- 细节展示:面料纹理清晰,手感柔软细腻,色彩搭配典雅大方。
纺织品面料设计案例分析
在实际纺织品面料设计中,我们可以看到许多成功的案例,以下是一些具体的案例分析:
【案例一:舒适家居装饰】
某品牌在纺织品面料设计方面注重舒适性和实用性,其设计样品图采用了天然纤维面料,色彩搭配柔和自然,图案以几何图案为主,展现出现代家居的舒适氛围,该品牌还注重细节处理,如面料表面光滑细腻、质地均匀等,为消费者提供了优质的家居装饰体验。
【案例二:时尚服装搭配】
某品牌在纺织品面料设计方面注重时尚感和个性化,其设计样品图采用了多种不同材质的面料,如丝绸、缎子等,展现出优雅高贵的气质,该品牌还结合现代元素进行创新设计,为消费者提供了丰富的服装搭配选择,通过不断尝试和改进,该品牌成功打造出了一系列时尚服装,深受消费者喜爱。
纺织品面料设计要点分析
在纺织品面料设计中,需要注意以下几个方面:
- 材料选择:选择高质量的材料是纺织品面料设计的关键,应注重材料的环保性、舒适性和耐用性等方面。
- 设计风格:根据不同的设计需求和目标客户群体,选择适合的设计风格,简约时尚、复古风格、民族风等都是常见的设计风格。
- 图案设计:图案是纺织品面料设计的核心元素之一,应注重图案的创新性和实用性,同时也要考虑图案与面料材质的匹配度。
- 细节处理:细节处理也是纺织品面料设计的重要环节,应注重面料表面的光滑细腻、质地均匀等细节处理,为消费者提供优质的穿着体验。
纺织品面料设计是纺织品制造过程中的重要环节之一,在纺织品面料设计中,应注重材料选择、设计风格、图案设计和细节处理等方面,通过不断尝试和改进,可以打造出更多优质、时尚、个性化的纺织品面料产品,满足消费者的不同需求,也可以借鉴成功案例和案例分析中的经验教训,为纺织品面料设计提供更多的参考和启示。
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Luxurious Threads:The Evolution of Luo Lai Home Textiles
The Unique Appeal of the Three Dragon Needle Textile Wholesale Market
The Story of the佛山市禅城区颖兴纺织品批发部



